Mobile users: This page is best viewed in desktop format.
To be honest, this is one of those “grey” areas in science. The classifications (naming) of rocks are usually based on empirical observations. Rarely a Geologist would name a rock based on chemical analysis. The qualitative observations of minerals in a sample is commonly used in place of chemical analysis. Therefore, we can categorically argue naming conventions are based on the chemical properties of the rock. Depending on the scheme, the rock name may be sightly varies. This is why I recommend recording the modal proportions of minerals when naming a rock (or should include a plotted diagram). This will avoid confusion in different classification schemes.
Identification of Igneous Rocks
| Grain Size | Usual Color | Other | Composition | Rock Type |
| fine | dark | glassy appearance | lava glass | Obsidian |
| light | many small bubbles | lava froth from sticky lava | Pumice | |
| dark | many large bubbles | lava froth from fluid lava | Scoria | |
| fine or mixed |
light | contains quartz | high-silica lava | Felsite |
| medium | between felsite and basalt | medium-silica lava | Andesite | |
| dark | has no quartz | low-silica lava | Basalt | |
| mixed | any color | large grains in fine-grained matrix | large grains of feldspar, quartz, pyroxene or olivine | Porphyry |
| coarse | light | wide range of color and grain size | feldspar and quartz with minor mica, amphibole or pyroxene | Granite |
| light | like granite but without quartz | feldspar with minor mica, amphibole or pyroxene | Syenite | |
| light to medium | little or no alkali feldspar | plagioclase and quartz with dark minerals | Tonalite | |
| medium to dark | little or no quartz | low-calcium plagioclase and dark minerals | Diorite | |
| medium to dark | no quartz; may have olivine | high-calcium plagioclase and dark minerals | Gabbro | |
| dark | dense; always has olivine | olivine with amphibole and/or pyroxene | Peridotite | |
| dark | dense | mostly pyroxene with olivine and amphibole | Pyroxenite | |
| green | dense | at least 90% olivine | Dunite | |
| very coarse | any color | usually in small intrusive bodies | typically granitic | Pegmatite |
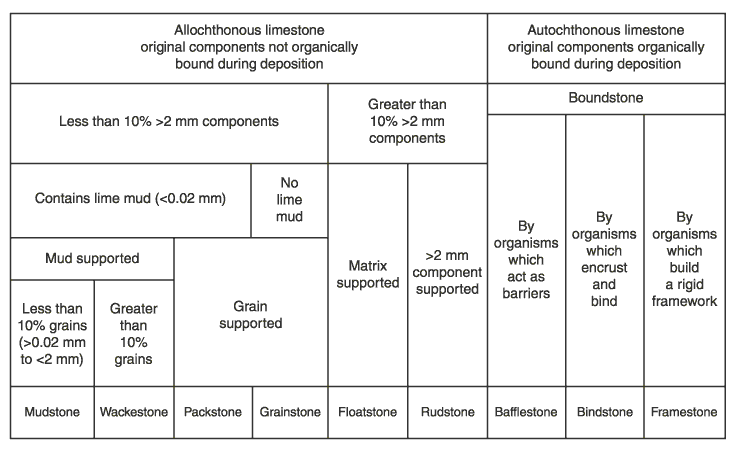
Identification of Sedimentary Rocks
| Hardness | Grain Size | Composition | Other | Rock Type |
| hard | coarse | clean quartz | white to brown | Sandstone |
| coarse | quartz and feldspar | usually very coarse | Arkose | |
| fine | very fine sand; no clay | feels gritty on teeth | Siltstone | |
| fine | chalcedony | no fizzing with acid | Chert | |
| hard or soft |
mixed | mixed sediment with rock grains and clay | gray or dark and “dirty” | Wacke/ Graywacke |
| mixed | mixed rocks and sediment | round rocks in finer sediment matrix | Conglomerate | |
| mixed | mixed rocks and sediment | sharp pieces in finer sediment matrix | Breccia | |
| soft | fine | clay minerals | splits in layers | Shale |
| fine | carbon | black; burns with tarry smoke | Coal | |
| fine | calcite | fizzes with acid | Limestone | |
| coarse or fine | dolomite | no fizzing with acid unless powdered | Dolomite rock | |
| coarse | fossil shells | mostly pieces | Coquina | |
| very soft | coarse | halite | salt taste | Rock Salt |
| coarse | gypsum | white, tan or pink | Rock Gypsum |
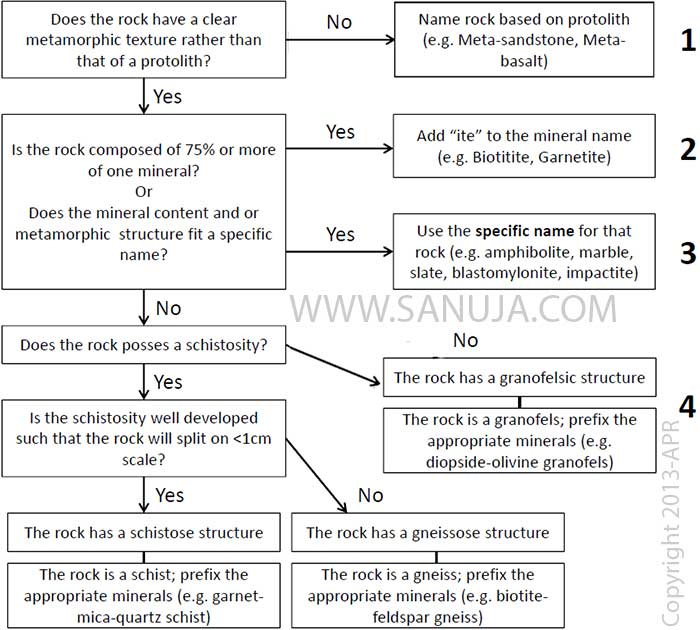
Identification of Metamorphic Rocks
| Foliation | Grain Size | Usual Color | Other | Rock Type |
| foliated | fine | light | very soft; greasy feel | Soapstone |
| fine | dark | soft; strong cleavage | Slate | |
| fine | dark | shiny; crinkly foliation | Phyllite | |
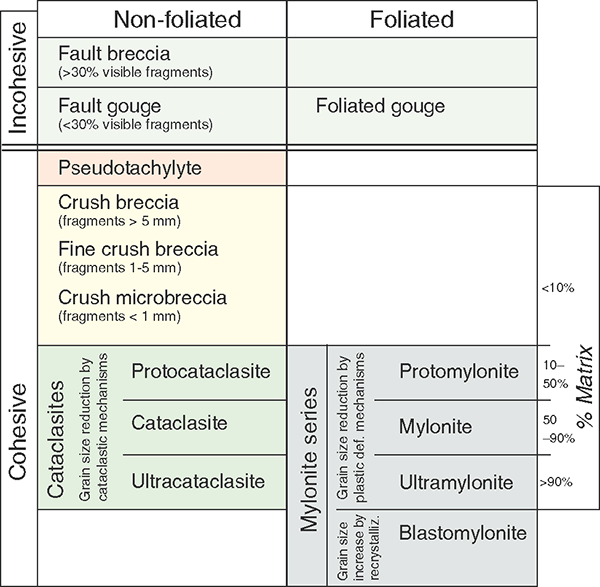
| coarse | mixed dark and light | crushed and stretched fabric; deformed large crystals | Mylonite | |
| coarse | mixed dark and light | wrinkled foliation; often has large crystals | Schist | |
| coarse | mixed | banded | Gneiss | |
| coarse | mixed | distorted “melted” layers | Migmatite | |
| coarse | dark | mostly hornblende | Amphibolite | |
| non foliated | fine | dark | soft; massive structure | Argillite |
| fine | greenish | soft; shiny, mottled surface | Serpentinite | |
| fine or coarse | dark | dull and opaque colors, found near intrusions | Hornfels | |
| coarse | red and green | dense; garnet and pyroxene | Eclogite | |
| coarse | light | soft; calcite or dolomite by the acid test | Marble | |
| coarse | light | quartz (no fizzing with acid) | Quartzite |
Few tricks…
Igneous rocks
- If grains can not be observed with little or no magnification aid, then
- It must be aphanitic AND based on colour
-dark = mafic
-medium = intermediate
-light = felsic
-volcanic glass
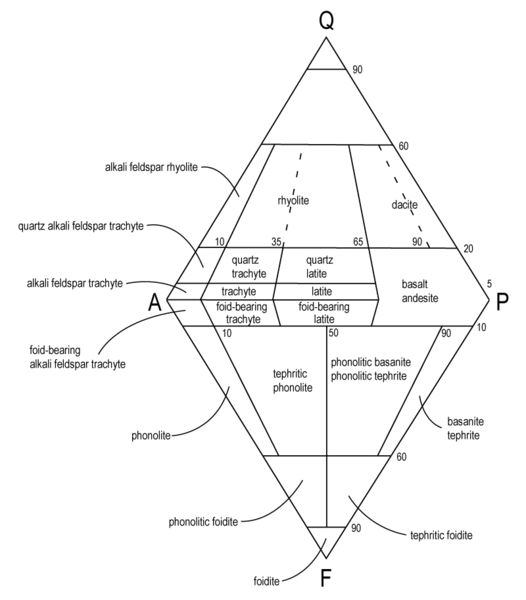
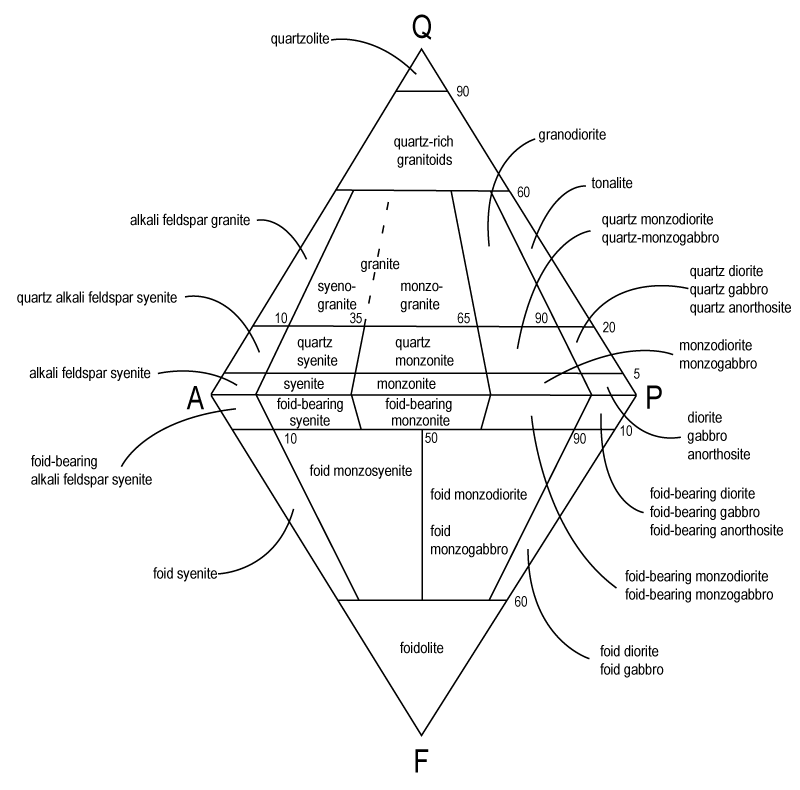
…use QAPF Aphenetic diagram
- If grains can be observed with little or no magnification aid, then
- It must be phaneritic AND based on colour
record the crystal shapes, sizes and mineral inclusions
…use QAPF Phaneritic diagram
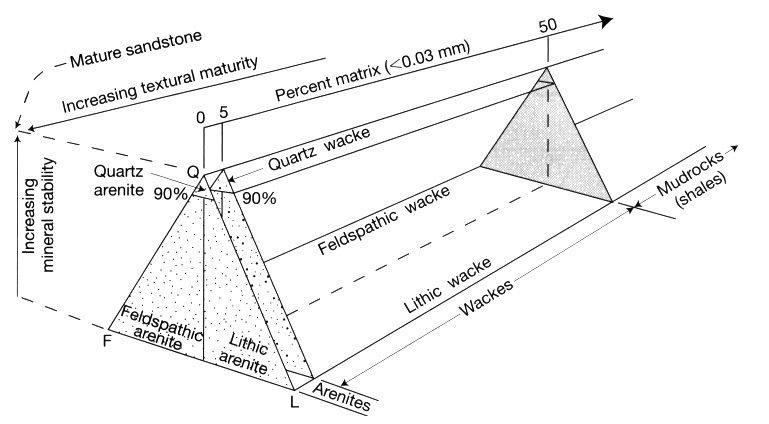
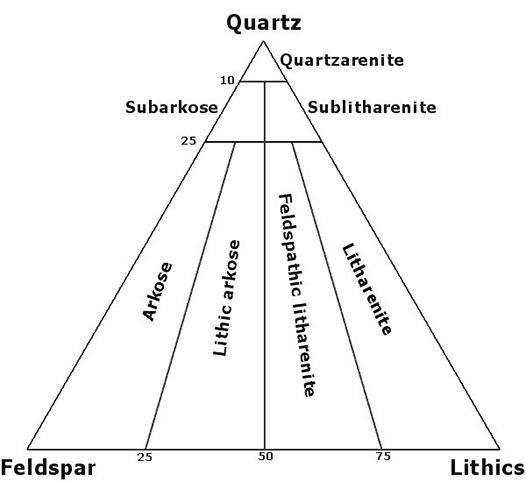
Sedimentary rocks
- Based on the modal proportions of quartz-feldspars-lithics (Q-F-L diagram);
1. quartzarenite
2. graywacke
3. arkose
4. lithic arenite
Indicates metamorphism
- If it has a shale protolith AND it is foliated (regional), then
- Must be Barrovian sequence
Chloorite (low grade)
-Biotite
-Garnet
-Staurolite
-Sillimanite
-Sillimanite and K-feldspar (high grade)
- If it has a shale protolith AND it is not foliated (regional), then
- Must be Buchan sequence
-Spotted phyllite (low grade)
-Cordierite-andalusite hornfels
-K-feldspar hornfels
-Sillimanite (high grade)
- If it has a basalt protolith AND it is foliated, then
- What are the mineralogical characteristics?
Classification Charts
References
BGS Rock Classification Scheme
Structural Geology by Haakon Fossen