Notice
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations(if available) with additional information.My personal advice: Since the exams are written, if you score less than 90% on the following MC questions, seriously reconsider your study strategies for this class.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please provide a description of the question because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm II | Final
Geology (GLGY 381-UCAL) Midterm Exam I
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 381-UCAL) Midterm Exam I.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | sedimentation |
B | erosion |
C | paleosols |
D | pedogenesis |
Question 2 |
A | C |
B | D |
C | E |
D | B |
E | A |
Question 3 |
A | Sediment load |
B | Gravity |
C | Flow velocity |
D | Potential energy |
E | Flow separation |
Question 4 |

A | Chemical |
B | Physical |
C | Hydration/dehydration |
D | Simple solution |
Question 5 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 6 |
A | Grain flow |
B | Turbidity current |
C | Liquified flow |
D | Debris flow |
Question 7 |
A | physical weathering |
B | biological weathering |
C | chemical weathering |
D | artificial weathering |
Question 8 |
A | The rock is composed of highly angular clasts. |
B | The rock is composed of just one clast type. |
C | The rock is composed of just two or three clast types. |
D | The rock is dominated by matrix and has very few clasts. |
Question 9 |
A | Burrows and borings are created by two distinct type of creatures that in burrows the sediments are removed mechanically and in borings the sediments are dissolved chemically. |
B | Burrows are trace fossils and borings are body fossils. |
C | Borings are trace fossils and burrows are body fossils. |
D | Borings are created by pushing the grains to walls of the structure and boring are created by mechanically/chemically cutting the grains. |
E | I have no freaking clue what the hell you asking about. |
F | Burrows are created by pushing the grains to walls of the structure and borings are created by mechanically/chemically cutting the grains. |
Question 10 |
A | Within oxbow lakes |
B | Under low- to medium-density turbidity currents |
C | Under current ripples |
D | Under high-density turbidity currents |
E | Within river deltas |
Question 11 |
A | Resting |
B | Dewlling |
C | Escape |
D | Grazing |
E | Crawling |
F | Feeding |
Question 12 |
h(D) = 55 m
g = 9.81 m/s2
u = 33 m/s
A | 1.42 |
B | 0.06116 |
C | 2.37 |
D | 1.95 |
E | 0.6116 |
Question 13 |
A | Shelf (sublittoral zone) |
B | Sandy shore (littoral zone) |
C | Above the normal sea level |
D | Abyssal zone |
E | Bathyal zone |
Question 14 |
-high viscosity
-poorly sorted grains
-often larger clasts are separated by fine grained materials
-low Reynolds number and considered as a laminar flow
-low velocity (40-50 km/h)
A | Liquified flow |
B | Grain flow |
C | Turbidity flow |
D | Debris flow |
Question 15 |

A | grain size in mm |
B | grain size in um |
C | flow velocity in cm/s |
D | depth in m |
E | flow velocity in m/s |
Question 16 |
A | Low pH solutions in high temperature solutions |
B | Acids |
C | High pH solutions |
D | Base |
E | Base solutions in high temperature environment |
Question 17 |
A | At the base of the sourced region (very bottom) |
B | Below hemipelagic mud |
C | Below massive/rapid deposition |
D | Within the upper flow regime |
E | None of the answers are correct |
Question 18 |
A | original horizontality |
B | lowerposition |
C | superposition |
D | parsimony |
E | Uniformitarianism |
Question 19 |
A | Differential pressure-temperature gradient that increases with depth. |
B | Extreme temperatures and pressures between different sediment successions. |
C | Differential lateral compaction within bed forms resulting high pressures between bed contacts. |
D | High pressures excreted on sediments from both through uplift and loading processes. |
E | Extreme pressure concentrated at the contacts between grains within sediments. |
Question 20 |
A | Matrix is formed when the clasts are deposited under high temperatures while cement is formed when clasts are deposited under low temperatures. |
B | Matrix is the substance that binds clasts together while cement is a fined grained material that deposits within crystals. |
C | Matrix is deposited at the same time as clasts while cement forms after the deposition of sediment as precipitate. |
D | Both terms describes a material that binds clasts but the term "matrix" is used when the rock is mostly composed of clasts while cement is used when majority of the rock is composed of fined grained materials. |
Question 21 |
A | Paleotracology Hint: LOL What the hell? |
B | Ichnology |
C | Paleogeology |
D | Genology |
Question 22 |
A | surface of the fluid. |
B | highest velocity point of the velocity profile. |
C | (around) middle of the velocity profile. |
D | bed surface of the velocity profile. |
Question 23 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 24 |
A | spatial acceleration |
B | inertial acceleration |
C | gravitational acceleration |
D | upwards acceleration |
E | temporal acceleration |
Question 25 |
A | rough bed velocity model |
B | laminar velocity model |
C | smooth current velocity model |
D | turbulent velocity model |
Question 26 |
A | low viscous forces in the folow |
B | turbulent flow |
C | gravity driven flow |
D | laminar flow |
Question 27 |
A | High volume sediment loads |
B | Gravity: hard sediments sinking into soft underlying sediments |
C | Significant density contrast |
D | Pressure: soft water-bearing sediments escaping through overlying sediments |
Question 28 |
A | quartz |
B | biotite |
C | amphibole |
D | olivine |
Question 29 |
A | False |
B | Yep |
Question 30 |
A | detrital |
B | sedimentary |
C | native |
D | authigenic |
E | metamorphic |
Question 31 |
A | Sedimentary rocks are unconsolidated materials that forms at the Earth's surface while sediments are formed as a result of burial and lithification of these sediment materials. |
B | Even though they have the similar names, they are unrelated each other because sedimentary rock is a geologic structure and sediment is a type of geologic material. |
C | Even though they have the similar names, they are unrelated each other because sediment is a geologic structure and sedimentary rock is a type of geologic material. |
D | Sediments are unconsolidated materials that forms at the Earth's surface while sedimentary rocks are formed as a result of burial and lithification of these sediment materials. |
Question 32 |
A | type of fluid |
B | amplitude of the wave |
C | period of the wave |
D | viscosity of the fluid |
Question 33 |
A | Within channels |
B | Lee side of ripples |
C | Between dunes |
D | At the mouth of rivers |
E | Stoss side of ripples |
Question 34 |
A | Above the normal sea level |
B | Abyssal zone |
C | Sandy shore (littoral zone) |
D | Shelf (sublittoral zone) |
E | Bathyal zone |
Question 35 |
A | Velocity increases as the depth increases. |
B | The highest velocity is at the bed. |
C | At the bed, there is no slip conditions due to lower velocity. |
D | It is difficult to determine the velocity hence we heavily relies on speed of flowing rivers for analysis. |
Question 36 |
A | True |
B | False |
Antidunes can be formed as a result of beds deposition in phase to the surface water wave.
Question 37 |
A | Study of the mode of preservation. |
B | Classification of the trace fossils. |
C | Study of behavior. |
D | Description of the identifiable parts. |
Question 38 |
A | Organic activities such as roots and biodegradation causing increase in the mineral volume. |
B | Freeze-thaw cycle result in change in volume. |
C | Increase of stress as a result of pressure increase. |
D | Hydration of minerals result in increase in volume. |
E | Release of stress as a result of pressure decrease. |
F | Organic activities such as roots and biodegradation causing decrease in the mineral volume. |
Question 39 |
A | It transforms igneous rocks into sedimentary rocks |
B | It transforms sedimentary rocks into metamorphic rocks |
C | It transforms sediments into metamorphic rocks |
D | It occurs under temperatures above 500 degree Celsius |
E | It change the chemical and physical characteristics of sediments after the deposition |
Question 40 |
A | Change in flow regime |
B | Gradient change |
C | Hydraulic jump |
D | Critical flow |
E | Change in normality |
Question 41 |
A | How flow rate, density of the fluid and pathway of flow dictates type of flows. |
B | Flow of a fluid through a tapered tube results in an increase in velocity. |
C | Depositional sequences in very high energy environments. |
D | Settling velocity of particles in a fluid. |
Question 42 |
A | The relationship between an object's mass m, its acceleration a, and the applied force F is F = ma. Acceleration and force are vectors (as indicated by their symbols being displayed in slant bold font); in this law the direction of the force vector is the same as the direction of the acceleration vector. |
B | For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. |
C | Gravitational force is proportional to the mass and acceleration due to gravity. |
D | Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. |
Question 43 |
A | sub-normal stress |
B | normal stress |
C | super-normal stress |
D | shear stress |
E | tangential stress |
Question 44 |
A | False because pedogenesis is the process of creating soil. |
B | False because pedogenesis is the process of creating rivers. |
C | True |
D | False because pedogenesis is the process of erosion by both physical and chemical weathering. |
Question 45 |
A | Bioturbation is between 30% and 60% of the sediment affected and bedding is distinct |
B | Sediment is totally reworked by bioturbation |
C | Bioturbation is over 90% of sediment bioturbated, and bedding
is barely detectable |
D | Bioturbation affects less than 30% of the sediment sample and the bedding is distinct |
E | A sample with few discrete traces of bioturbation |
F | Bioturbation is between 60% to 90% of the sediment bioturbated and bedding indistinct |
Question 46 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 47 |
A | saltation |
B | rolling |
C | suspension traction |
D | sliding |
E | paleoflow |
Question 48 |
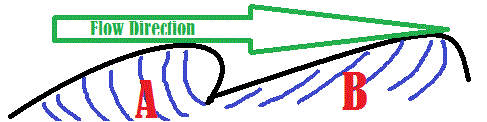
A | Left side has the scour region and right side is the stoss side. |
B | Left side has the scour region and right side is the lee side. |
C | Left side is the stoss side and right side is the lee side. |
D | All statements are incorrect. |
E | Left side is the lee side and right side is the stoss side. |
Question 49 |
A | Turbidity currents |
B | Glacial breakups |
C | Debris flows |
D | Rock falls |
E | Slumps |
Question 50 |
Description
-high velocity
-larger Reynold's number
-inertial forces dominates over the viscous forces

A | It could be either A or B because the description is is insufficient. |
B | A |
C | Neither |
D | B |
Question 51 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 52 |
A | High energy environment with a one single direction of water flow. |
B | Deltaic environment with high sediment influx. |
C | Deep subsurface environments under high pressures and temperatures. |
D | Glacial environment where clasts are dragged across a flat surface. |
Question 53 |
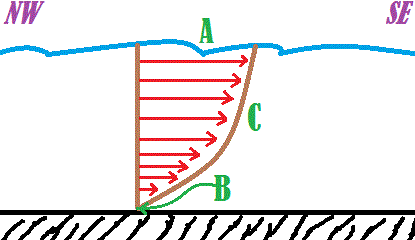
A | False |
B | True |
Question 54 |
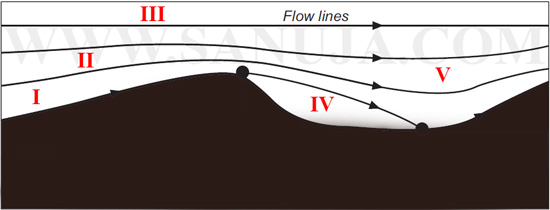
A | Position I in the stoss side of the ripple |
B | Position V between two ripples |
C | Position III where the flow rate is consistent and smooth |
D | Position IV in the lee side of the ripple |
E | Position II just above the ripple |
Question 55 |
A | Precipitation of inorganic compounds out of water due to evaporation |
B | Magmas rich in calcium carbonates |
C | Calcium carbonate produced as a by product of chemical weathering |
D | Transported rock fragments |
E | Hard organic parts from invertebrates |
Question 56 |
A | Semi- relief structures are preserved within a single type of sediment while full-relief structures are preserved at an interface between two strata. |
B | Full relief structures are preserved as 2D structures while semi-relief structures are preserved as 3D structures. Both are preserved within a single type of sediment. |
C | Full relief structures are preserved within a single type of sediment while semi-relief structures are preserved at an interface between two strata. |
D | Full relief structures are partially preserved within a single type of sediment while semi-relief structures are fully preserved at an interface between two strata. |
Question 57 |
A | False-it should be other way around. |
B | True |
Question 58 |
A | ~ 10 degrees |
B | ~ 30 degrees |
C | ~ 100 degrees |
D | ~ 90 degrees |
E | ~ 50 degrees |
Question 59 |
A | 90% |
B | 50% |
C | 5% |
D | 98% |
E | 75% |
Question 60 |

A | E |
B | F |
C | No such thing on the diagram above. |
D | C |
E | D |
Question 61 |
A | increasing , increasing |
B | decreasing , decreasing |
C | None of the answers are correct because it is not the acidity that is important, it is the pH. |
D | increasing , decreasing |
E | decreasing , increasing |
Question 62 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 63 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 64 |
A | 98% lithics
1 % feldspar
1% quartz |
B | 50% lithics
40 % feldspar
10% quartz |
C | 60% quartz
1 % lithics
90% feldspar |
D | 98% quartz
1 % lithics
1% feldspar |
Question 65 |

A | A |
B | Neither due to incorrect representation of the initial flow direction. |
C | B |
D | Neither due to incorrect representation of the internal flow direction. |
Question 66 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 67 |
A | Long contacts |
B | Sutured contacts |
C | Point contacts |
D | Subrounded contacts |
E | Concavo-convex contacts |
Question 68 |

A | NW to SE |
B | S to N |
C | N to S |
D | SE to NW |
E | NE to SE |
Question 69 |
A | A. bed load B. suspended load |
B | A. inertial forces driven load B. gravity driven load |
C | A. gravity driven load B. inertial forces driven load |
D | A. suspended load B. bed load |
Question 70 |
A | Turbidity current |
B | Debris flow |
C | Sheet wash |
D | Rock fall |
E | Slump |
Question 71 |

A | A |
B | C |
C | B |
Question 72 |
A | Low energy and low sedimentation environments. |
B | Low energy and high sedimentation environments. |
C | High energy and high sedimentation environments. |
D | High energy and low sedimentation environments. |
Question 73 |
A | Fluctuating velocity currents. |
B | Medium velocity currents. |
C | High velocity currents. |
D | Low velocity currents. |
Question 74 |
A | A. felsic minerals B. mafic minerals |
B | A. mafic minerals B. felsic minerals |
C | A. oceanic crust B. continental crust |
D | A. mafic and felsic minerals B. silica rich minerals |
E | A. iron rich minerals B. oxygen rich minerals |
Question 75 |

A | The stream lines(red lines) converging at the yellow arrow cause the velocity to increase significantly(at that point). |
B | The pressure right above the yellow arrow is much lower than the pressure near the black rocks/sediments. |
C | The pressure from above is much higher causing the grains to push hard against the bed. |
D | The lift at the yellow arrow is caused by the high pressure at the top caused by converging streamlines. |
E | The stream lines(red lines) converging at the yellow arrow cause the velocity to decrease significantly(at that point). |
Question 76 |
A | In the middle of the profile, the velocity is close to zero. |
B | Deeper in the fluid lower the velocity. |
C | Uniformly moving fluids will have an equal instantaneous velocities regardless of depth. |
D | Deeper in the fluid higher the velocity. |
E | At the top of a moving current, the velocity is close to zero. |
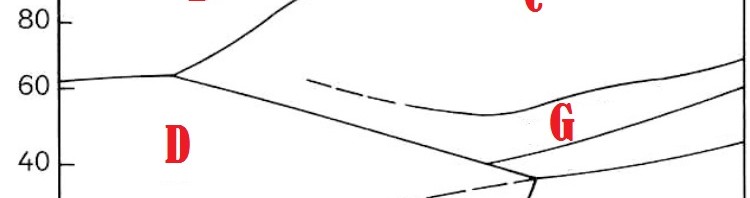
Question 77 |

A | D |
B | G |
C | C |
D | F |
E | E |
Question 78 |
A | Minerals that primarily formed from organic materials. |
B | Minerals that formed as a result of magmatic processes that occurs under water. |
C | Minerals that replaces (take others' place) other minerals during sedimentation. |
D | Minerals that are formed as a result of erosion due to chemical weathering. |
E | Minerals with very high densities resulting deposition at the bottom of a flow. |
Question 79 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 80 |
A | fighting |
B | dwelling |
C | crawling |
D | feeding |
E | extractions(pooping) |
Question 81 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | I. higher II. laminar |
C | I. lower II. turbulent |
D | I. lower II. laminar |
E | I. zero II. turbulent |
Question 82 |
A | A type of trace fossils created by echinoids. |
B | A type of depositional environment that provides the best suitable conditions for organisms to thrive. |
C | A a body of rock with specified mineralogical characteristics. |
D | A sub set of beds and laminations that is defined by certain depositional structures. |
E | An assemblage of trace fossils that provides an indication of the palaeoenvironment. |
Question 83 |
A | Bioerosion is the reworking of soils and sediments by animals or plants. Bioturbation is caused by mechanically or chemically cutting/removing the grains by organisms. |
B | Bioturbation is the reworking of soils and sediments by animals or plants. Bioerosion is caused by mechanically or chemically cutting/removing the grains by organisms. |
C | They are the same except Bioturbation is the British English word for Bioerosion(US-English) |
D | Bioturbation is caused by plants. Bioerosion is caused by animal activities. |
Question 84 |

A | F |
B | B |
C | C |
D | A |
E | G |
F | D |
Question 85 |
A | A. critical B. supercritical C. subcritical |
B | A. subercritical B. critical C. supcritical |
C | A. supercritical B. subcritical C. critical |
D | A. supercritical B. critical C. subcritical |
E | A. critical B. subcritical C. supercritical |
supercritical = Fr > 1 and the velocity of the stream is greater than the velocity of the surface wave.
subcritical = Fr < 1 and the velocity of the stream is lower than the velocity of the surface wave.
Question 86 |
A | At the bed, there is no slip conditions due to higher velocity. |
B | Velocity decreases as the depth increases. |
C | The highest velocity is at the bed. |
D | The lowest velocity is at the bed. |
E | Velocity increases as the depth increases. |
Question 87 |

A | C |
B | A |
C | B |
Question 88 |
A | mudstone |
B | dolostone |
C | gypsum |
D | limestone |
E | sandstone |
Question 89 |

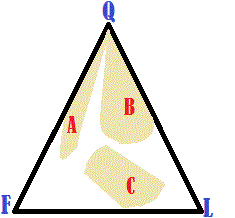
A | A. Continental block B. Recycled origin C. Magmatic arc |
B | A. Magmatic arc B. Continental block C. Recycled origin |
C | A. Quartz B. Feldspar C. Lilith fragments |
D | A. Continental block B. Magmatic arc C. Recycled origin |
E | A. Quartz B. Lilith fragments C. Feldspar |
F | A. Recycled origin B. Continental block C. Magmatic arc |
Question 90 |
A | Muscovite mica |
B | Pyroxene |
C | Kaolinite |
D | Calcium Feldspars |
E | Olivine |
Question 91 |
A | Trough cross-lamination |
B | Turbulent sweeps |
C | Starved ripples |
D | Climbing ripples |
E | Planar cross-lamination |
Question 92 |
A | Deep sea ocean beds with rich organic matter |
B | Dry climates with year-round permafrost |
C | Humid climates |
D | Dry climates with long periods of droughts |
E | Temperate climate with long cold winters and short warm summers |
Question 93 |
A | a type of physical weathering caused by biogenic processes which result in breakdown of rocks/sediments. |
B | a type of physical weathering caused by water or hydrous fluids penetrate rocks/sediments and expand as a result of freezing; leads to cracks and physical breakdown of materials. |
C | a type of erosion caused by temperature and pressure change caused by exhumation of rocks/sediments. |
D | a type of chemical weathering caused by dissociation of water into H+ and OH- ions as a result of acidifying agent. |
E | a type of chemical weathering caused by oxidation of chemical compounds within rocks. |
Question 94 |

A | 1. is an antidune 2. is an antidune |
B | 1. is a dune 2. is an antidune |
C | 1. is a dune 2. is a dune |
D | 1. is an antidune 2. is a dune |
Question 95 |
A | ore deposits |
B | clastic deposits |
C | carbonates |
D | chemical deposits |
E | evaporites |
Question 96 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 97 |
A | Burial(shrinking) and exfoliation(swelling). |
B | Hydration(swelling) and dehydration(shrinking) |
C | Freezing(swelling) and thawing(shrinking). |
D | Freezing(shrinking) and thawing(swelling). |
E | Hydration(shrinking) and dehydration(swelling) |
Question 98 |
A | None of the answers posted here are correct. |
B | Warm and tropical wet environments |
C | Shallow marine environments |
D | Deep marine environments |
E | River bed environments |
Question 99 |
A | clastic sediments |
B | precipitates |
C | evaporates |
D | organic deposits |
E | carbonates |
Question 100 |
A | Dunes forms in turbulent waters and ripples forms in calm waters. |
B | Dunes are distinctly larger than ripples. |
C | Dunes have interbedded cross laminations and ripples do not. |
D | Dunes form in marine environments and ripples form in non-marine river type environments. |
Question 101 |
A | Geostatic pressure |
B | Pressure dissolution |
C | Pore waters |
D | Salt Diapirs |
Question 102 |

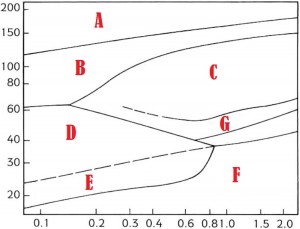
A | G |
B | F |
C | D |
D | A |
E | C |
F | B |
G | E |
Question 103 |
A | erosion |
B | chemical weathering |
C | physical weathering |
D | denudation |
Question 104 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 105 |
A | A. mafic rocks B. felsic rocks |
B | A. carbonates B. silicates |
C | A. felsic rocks B. mafic rocks |
D | A. silicates B. carbonates |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 |
| 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 |
| 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 |
| 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Melissa Giovanni during Fall 2012.
FAQ | Report an Error
Some of the Lab Midterm sample images | Click here
Concepts and Additional Questions for Fall 2012 Midterm I
Important!
↑ Some of these are already in the exam type questions in the quiz(above) ↑
Answers to these will NOT be posted. These are based on lecture notes!
-velocity profile; what is idealized modal’s limitations; where is the viscous sublayer and what is it
-bed formation; shape of the bed, x-beds, directional flows
-bed load vs suspended load
-Stoke’s law and the settling velocity
-flow separation concepts; eddy; stoss/lee with respect to x-beds in dunes and anti-dunes; water surface in or out of phase of bed formation
-unidirectional flow vs ocillating flow; be able to draw and describe the differences between them; wave base “feel my bottom”.
-type of sediment gravity flows; debris flow; grain flow; liquefied flow (remember that debris flow and liquefied flow are similar in operation, but different in terms of size of rocks/grains involved.
Dr. Spila’s stuff
-4 steps involving accurately identifying fossils; preservation, description, behaviour, classification(we don’t have to know how to name them)
-What is ichnology
-difference between biotrubation and bioerrosion; which is the most common type; what is the formula for degree of bioturbation
-what are borings and what are borrows
-6 major common categories of behaviours and their reliefs; crawling(semi), resting(semi), feeding(full), gazing(semi), dewlling(full), escape(full).
-meniscae and few other definitions
-preservation differences between full and semi-relief