Petrophysical Techniques; Geology/Geophysics 449
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Questions on Petrophysical Log Interpretation will not appear in the following exam. Log questions are published under a separate section.
Go to: Midterm II | Well Log Interpretation
Geology (GLGY 449-UCAL) Midterm I
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 449-UCAL) Midterm I.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | 35% |
B | 29% |
C | 2.9% |
D | 34% |
E | 3.0% |
porosity = (2.80 - 2.25) / (2.80 - 1.20) = 0.34 = 0.34%
Question 2 |
A | Dissolution of grains at the grain to grain contact boundaries. |
B | Fractures of cements and minerals. |
C | Dissolution of early diagenetic cements. |
D | Break up of mineral compounds causing in situ porosity. |
Question 3 |
A | ...a response close to the calibrated zero position. |
B | ...no response at all (at zero level). |
C | ...a very low negative response. |
D | ...a very high positive response. |
Question 4 |
A | Organic activity |
B | Dissolution of early diagenetic cements |
C | Dissolution of cemented materials due to high temperature and pressure |
D | Disintegration of minerals |
E | Fracture development |
Question 5 |
A | Porous formations filled with oil or gas. |
B | High vibrations caused by drilling tools. |
C | Porous formations filled with water. |
D | Fractures formed due to drilling itself (non-natural fractures). |
Question 6 |
A | 15o to 25o Celsius per kilometer of depth. |
B | 20o to 30o Celsius per kilometer of depth. |
C | 15o to 50o Celsius per kilometer of depth. |
D | 30o to 50o Celsius per meter of depth. |
E | 30o to 50o Celsius per kilometer of depth. |
F | 20o to 30o Celsius per meter of depth. |
Question 7 |
A | sudden increase in density |
B | high natural radiation levels |
C | gradual increase in density |
D | gas effect |
Question 8 |
A | clean coal |
B | clean clay |
C | clean shale |
D | clean sandstones |
E | clean limestones |
Question 9 |
A | Fast mudcake buildup with very shallow mud filtrate. |
B | Fast mudcake buildup with very deep mud filtrate. |
C | Slow mudcake buildup with very shallow mud filtrate. |
D | Slow mudcake buildup with very deep mud filtrate. |
E | It all depends on the type of mud used for the drilling process. |
Question 10 |
A | In the electronics bay. |
B | In the bottom hole assembly |
C | In the logging equipment casing. |
D | Inside the equipment pads. |
E | Outside of the borehole; in the data collection truck. |
Question 11 |
A | Gamma ray logs |
B | Spectral gamma ray logs |
C | Spontaneous potential logs |
D | Neutron logs |
E | Density logs |
F | Caliper logs |
Question 12 |
A | ~ 65 o C |
B | ~ 45 o C |
C | ~ 43 o C |
D | ~ 55 o C |
E | ~ 49 o C |
Question 13 |
A | ...the neutron radiation omitted by the formation nuclei. |
B | ...the radiation omitted by elastic collisions between the neutron and the formation nuclei. |
C | ...the radiation that was not absorbed by the formation. |
D | ...the radiation omitted by inelastic collisions between the neutron and the formation nuclei. |
Question 14 |
(START) Dirty/used mud return to...
I. Distiller
II. Mud storage and settling tubs
III. Annulus spit out
IV. Desander
V. Shale shaker
VI. Mud pumps
A | I --> V --> VI --> II --> IV --> III |
B | V --> IV --> I --> II --> VI --> III |
C | III --> V --> I --> II --> VI --> V |
D | II --> V --> I --> III --> VI --> V |
E | I --> III --> VI --> IV --> V --> II |
F | I --> V --> IV --> II --> VI --> III |
Question 15 |
A | Identification of non-radioactive clays and dolostones. |
B | Primary depth control. |
C | Calculate the volume of shale to sand ratio. |
D | Analysis of grain volumes and grain characteristics of formation. |
E | Calculate the bulk porosity of formation. |
Question 16 |
Depth of Investigation: 15 -25 cm
Resolution: 50 cm
-Very high readings when shales or coals detected
A | Gamma Ray or Special Gamma Ray long |
B | Spontaneous Potential log |
C | Neutron log |
D | Density log |
E | Caliper log |
Question 17 |
A | Gamma ray bouncing effect |
B | Radioactive capture |
C | Compton scattering |
D | Natural gamma rays |
E | Pair production |
Question 18 |
A | A high log value of density indicates a very good reservoirs. |
B | The density can be used to calculate porosity of formations. |
C | It can help determine the type of drill bit to use to cut into the formations. |
D | It provides an overview of the lithological formations (for example, quartz from calcite). |
E | The density logs can be used to resolve extremely thin formations and transitional zones. |
Question 19 |
A | Spontaneous potential tools |
B | Neutron tools |
C | Caliper tools |
D | Gamma ray tools |
E | Density tools |
Question 20 |
A | Gamma ray logs |
B | Neutron logs |
C | Spontaneous potential logs |
D | Caliper logs |
E | Density logs Hint: Nope, that's an indicator of porosity. |
Question 21 |
A | 60 - 70 cm |
B | 10 - 15 cm |
C | 5 -10 cm |
D | 20 - 30 cm |
E | 40 - 50 cm |
Question 22 |
A | The mid invasion is enhanced by the fast build up of mudcake. |
B | The invaded zone is larger in low porosity and permeability formations because slower flow result in slow build up of mudcake. |
C | The invaded zone is larger in high porosity and permeability formations because faster flow result in slow build up of mudcake. |
D | Larger invaded zones provides the best resolutions of LWD logs because it allow the waves/signals to be penetrated deep into the formation. |
Question 23 |
A | High radioactive formations hence with more constructive interference. |
B | Very low density where fewer gamma rays are absorbed hence increasing the propagation distance. |
C | Formations that naturally produce very high rates of gamma rays hence allowing the artificial gamma rays to be amplified. |
D | Low radioactive formations hence less destructive interference. |
E | Very high density allowing gamma rays to bounce off from atom to atom deep into the formation. |
Question 24 |
A | It is that of the drilling mud. |
B | It is dependent on what type of logging tool is used. |
C | It is that of the formation. |
D | It is that of the surface. |
Question 25 |
A | 25 - 35 cm |
B | 40 - 50 cm |
C | 15 - 20 cm |
D | 0 - 10 cm |
E | 10 - 40 cm |
Question 26 |
A | Higher formation fluid content allowing gamma rays to penetrate the formation. |
B | Lower formation density resulting fewer gamma rays being absorbed. |
C | Higher formation density resulting more gamma rays being absorbed. |
D | Higher formation porosity allowing more gamma rays to penetrate the formation. |
E | Higher radioactivity within the formation allowing gamma rays to interact with minerals within the formation. |
Question 27 |
A | 40 - 50 cm |
B | 25 - 30 cm |
C | 30 - 35 cm |
D | 0 - 10 cm |
E | 15 - 20 cm |
Question 28 |
A | Use high pressured drilling mud. |
B | Use larger boreholes and wider cutting tools. |
C | Use fracking to fracture the formations to increase permeability. |
D | Use horizontal drilling. |
Question 29 |
A | Subsurface formation waters as trace substance. |
B | In radioactive natural deposits of uranium as a by product. |
C | In stable minerals such as phosphates. |
D | Within clay minerals such as illite and smectite. |
Question 30 |
A | To allow cutting to be transported to the surface. |
B | To balance the lithostatic pressure of the formation to prevent borehole collapses. |
C | To increase the speed of the drilling by applying pressure to the drill bit. |
D | To prevent mud filtrate from reaching inner parts of the formation of interest. |
E | To balance the hydrostatic pressure of the formation to prevent borehole collapses. |
Question 31 |
A | Gamma rays do not react with any chemical components in the natural world. |
B | Gamma rays are more penetrative than the others. |
C | Gamma rays are not naturally produced in the subsurface hence removes the uncertainty factor. |
D | Gamma rays produce a much higher energy difference that can be easily measurable by logging tools. |
E | Gamma rays travel faster than other rays. |
Question 32 |
A | Hydrostatic pressure of the formation. |
B | Lithostatic and hydrostatic pressure of the formation. |
C | Lithostatic pressure of the formation. |
D | Thin mud film between the casing and the formation. |
E | Mudcake itself surrounding the borehole. |
Question 33 |
A | Clean coal |
B | Black shale |
C | Clean sand |
D | Carbonates |
E | Mudstone |
F | Organic content poor shale |
Question 34 |
A | As neutron density. |
B | As fluid density. |
C | As matrix density. |
D | As a difference between bulk and fluid density. |
E | As bulk density. |
Question 35 |
A | Improved cost efficiency (low cost). |
B | Improved drill bits. |
C | Improved logistics due to smaller equipment. |
D | Improved logging tools. |
E | Improved speeds of drilling. |
Question 36 |
A | Highly radioactive formation; |
B | Highly non-radio active formation; |
C | Shale; |
D | Coal; |
E | Very thin formation; |
Question 37 |
A | About 2 years |
B | About 15 minutes |
C | About 4 hours |
D | About 10 hours |
E | About a day |
Question 38 |
A | 60 - 70 cm |
B | 5 - 10 cm |
C | 10 - 15 cm |
D | 40 - 50 cm |
E | 20 - 30 cm |
Question 39 |
A | Lower porosity loss in clay sequence compared to sandstone and shale due to clay being very dry in nature. |
B | Rapid loss of porosity within the sandstone sequence due to sandstone having higher permeability. |
C | No porosity loss within shale sequence due to shale being already compacted by the time of burial. |
D | Increased rate of friction between clay particles due to overburden pressure. |
E | Lower rate of porosity loss within the shale sequence due to tightly packed ionic bonds in shale. |
Question 40 |
A | ~ 5% |
B | ~ 45% |
C | ~ 15% |
D | ~ 20% |
E | ~ 35% |
Question 41 |
A | As basic solutions. |
B | Within water molecules. |
C | As a part of hydrous minerals. |
D | In the chemical structures of clay. |
E | As saline solutions. |
Question 42 |
A | Oil-based mud because oils do not react with evaporates and the mud can be formulated to not to react with subsurface formations. |
B | Water-based mud because it the most effective way to reduce the environmental impact. |
C | All-oil based mud because it is the cheapest and can overcome the environmental cleanup costs. |
D | Synthetic-based mud because the mud can be engineered to be inactive with the evaporate formations and reduce the environmental impact. |
Question 43 |
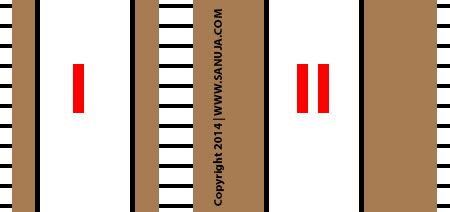
A | The Well-I most likely surrounded by a lithology that is very porous and permeable than Well-II; hence faster mudcake build up have lead to smaller invaded zone. |
B | The Well-I most likley surrounded by a lithology that poor in porosity and permeability than Well-II; hence faster mudcake build up have lead to smaller invaded zone. |
C | The Well-II most likley surrounded by a lithology that poor in porosity and permeability than Well-II; hence the faster mud flow resulted in a large invaded zone. |
D | The Well-II most likely surrounded by a lithology that is very porous and permeable than Well-I; hence the faster mud flow resulted in a large invaded zone. |
Question 44 |
A | The Cl- ion diffuse because it is much smaller in size than Na+. |
B | The Na+ ion diffuse because Cl- attracts more water molecules. |
C | The Cl- ion diffuse because it has a stronger charge (attraction) than Na+. |
D | The Na+ ion diffuse because it is much smaller in size than Cl-. |
E | The Cl- ion diffuse because Na+ attracts more water molecules. |
F | The Na+ ion diffuse because it has a stronger charge (attraction) than Cl-. |
Question 45 |
A | ...the depth of investigation is much higher than expected hence increasing the vertical minimum bed resolution. |
B | ...the contrast between the nearby formations and the resolved formation is higher. |
C | ...the radioactivity of the formations are much higher. |
D | ...the distance between formations are lower. |
E | ...the porosity and permeability of formations are higher. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Rudi Meyer during Fall 2014.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you are a company or an organization willing to donate copies of well logs, please contact me. I really appreciate your contributions.
| Type of tool |
DOI | Resolution | Used for… | Processes | Notes |
| Caliper | NA | NA | -Borehole size and shape |
Spring loaded arms |
2 arm = diameter 4 arm = shape, orientation |
| Gamma Ray |
10 – 15 cm | ~40 cm | -Lithology(vol. Shale/Sand often due to high K), geosteering, facies, depth control |
-Photoelectric effect (dom) -Compton scattering -Pair production -Scintillation counter + photomultiplier |
High (right kick): -Shale line -Organic content -K-Feldspars Low (left kick): -Clean sand -Carbonates -Clean coals |
| Spectral Gamma Ray |
-Radioactive anomalies -Clay types -Volume of shale(clay) |
-Same as GR, but much better/larger scintillator | |||
| Density & Photoelectric Factor |
< 10 cm | 11 – 40 cm | -Porosity, general lithology, min ids | ||
| Neutron | 15 – 25 cm | ~50 cm | -Fluid, porosity, density, cross-over gas effect -Meassures porosity; used for calulating density |
Hydrogen | High (left kick): -Shales and coals Low (right kick): -Gas breaing fm./rocks Use Dphi & Nphi chart *Decreased with increased permeability |
| Spontaneous Potential |
Depends | Depends | -Permeability(even small), lithology, facies, shale volume(not so much) |
Natural potential differences between fms. caused by: -Diffusion -Mambrane or shale potential |
Important: -Salinity of drilling fluid to fm. -Conductive drilling fluid -Constrasting permeability in adj. beds -Surface electrode(earth) No absolute scale(relatove +/-) Positive kick (relative): -Clean sand or sand stone, shaly sand Negative kick (relative): -Shale *Decreased with increased permeability |