Basic concepts: basic biological themes, hierarchy of organisms, diversity and domains, genetics and evolution, adaptations, fossil record and early life, geology, reproduction, genome and speciation.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm II | Midterm III | Final Exam
Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm I
Congratulations - you have completed Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm I.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | phylogenetic |
B | ecological |
C | morphological |
D | biological |
Question 2 |
A | It is the process in which DNAs react with other biochemicals to produce life. |
B | It is the process in which one species splits into two or more species. |
C | It is a process in which the new species are created with completely independent (100% different) characteristics from that of the original species. |
D | It is the process in which two interbreeding individuals produce a zygote. |
Question 3 |
A | Mutations |
B | Gene flow |
C | Introduction of new species |
D | Genetic drift |
Question 4 |
A | It is a proposed explanation for a set of observations. |
B | It is a statement of facts supported by a large body of evidence. |
C | It is an idea which is still not been proven with a body of evidence. |
D | It is a conceptual model developed by a scientist before a research project is undertaken. |
Question 5 |
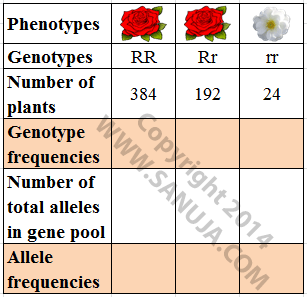
According to the following table, what are the genotype frequencies for all three possible outcomes?
Table 1: Gene pool of the original rose plants.Red is dominant and White is recessive.
A | RR = 0.60 , Rr = 0.32 , rr = 0.08 |
B | RR = 0.62 , Rr = 0.30 , rr = 0.04 |
C | RR = 0.62 , Rr = 0.30 , rr = 0.08 |
D | RR = 0.64 , Rr = 0.30 , rr = 0.08 |
E | RR = 0.64 , Rr = 0.32 , rr = 0.04 |
F | RR = 0.60 , Rr = 0.36 , rr = 0.04 |
Note that you divide possible number of genotypes by the total number of plants for the each frequency.
Question 6 |
A | Theory and hypothesis are two terms that can be used interchangeably (same or very similar meaning). |
B | Theory is used to describe fundamental principles of science while a hypothesis is used to describe first-order observable properties. |
C | Theory is similar to hypothesis but it covers a broader scope of the subject than a hypothesis. |
D | Theory is similar to hypothesis but it covers a specific area of the subject than a hypothesis. |
E | Theory can not be disproved with new evidence but hypothesis can be because hypothesis is a "working theory". |
Question 7 |
A | DNA |
B | Nucleotide |
C | Bacteria |
D | Organelle |
E | Cell |
F | Nucleus |
Question 8 |
A | The total collection of genes in a population at any one time. |
B | The total collection of genes in a species at any one time. |
C | The total collection of genes in a family at any one time. |
D | The total collection of genes in a kingdom at any one time. |
Question 9 |
A | Reproductively isolated speciation |
B | Habitat speciation |
C | Geographic speciation |
D | Polyploidy speciation |
Question 10 |
A | I. prokaryotes II. 4.3 billion |
B | I. eukaryotes II. 4.3 billion |
C | I. eukaryotes II. 3.5 billion |
D | I. prokaryotes II. 3.5 billion |
Question 11 |
A | No, because there is no useful evidence for the history without living or non-living (abiotic) organisms within the rock strata. |
B | Yes, because we can use radiometric dating of the sediments. |
C | No, because we use fossils record for age determination. |
D | Yes, because we can extrapolate the history from the type of sediments. |
Question 12 |
A | It is the process which an organism enhances the probability of survival through acquired characteristics. |
B | It is the process in which organisms evolve. |
C | It is the process in which the new genes are produced in order to survive in a changing environment. |
D | It is an inherited characteristic that enhances an organism's ability to survive and reproduce in a particular environment. |
Question 13 |
A | Bacteria and Eukarya |
B | Plants and Animals |
C | Plants and Eukarya |
D | Bacteria and Archaea |
E | Bacteria and fungi |
Question 14 |
A | Nuclear energy from the remaining elements within the gas cloud from the original nebula. |
B | Nuclear energy released from binding of monomers. |
C | Thermal energy from hydrothermal vents. |
D | Frictional energy generated by plate tectonics in the deep sea. |
E | Thermal energy from the sun. |
Question 15 |
A | ...the outer layer. |
B | ...the crust. |
C | ...the mantle. |
D | ...the outer core. |
Question 16 |
A | It is the process in which RNA copy the DNA sequences and reproduce them by binding to proteins. |
B | It the process in which natural selection either modify, delete or replicate alleles from genes. |
C | It is the process in which alleles are randomly selected for fertilization. |
D | It a process in which alleles from one population is transferred to another as a result of movement of individuals or gametes. |
Question 17 |
A | It is the process in which genetic mutation occur and lead to new forms of life. |
B | It is the process in which the current organism differentiate from its' ancestors. |
C | It is a process in which a new forms of traits are developed into a phenotype (as opposed to just genotypes). |
D | It is the process in which certain inherited traits are survived and reproduced than the other traits. |
E | It is the process in which the dominant hunters eliminates another group of organisms. |
Question 18 |
A | The individual organisms are unable to produce a fertilized cell. |
B | The species live in different habitat within the same area and would not meet each other. |
C | The mating behavior of one species is completely different from the other. |
D | The new offspring have a weak immune system. |
Question 19 |
A | Similarity in characteristics caused by one dominant allele is known as analogy, while similarity in characteristics caused by two recessive alleles known as homology. |
B | Similarity in characteristics caused by convergent evolution is known as homology, while similarity in characteristics caused by is sharing a common ancestor known as analogy. |
C | Similarity in characteristics caused by one dominant allele is known as homology, while similarity in characteristics caused by two recessive alleles known as analogy. |
D | Similarity in characteristics caused by convergent evolution is known as analogy, while similarity in characteristics caused by is sharing a common ancestor known as homology. |
Question 20 |
A | Eukaryotic cells are usually unicelluar and thought to be responsible for early life on Earth while Prokaryotics cells evolved later in the biological evolution. |
B | Prokaryotics cells are the most common type of cells in the living world that made up of plants, animals and fungi. The Prokaryotics cells are only found in bacterias. |
C | Eukaryotic cells are specialized cells while Prokaryotics cells can be specialized into any type of cell. |
D | Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. |
Question 21 |
A | Diablo |
B | Gondwanaland |
C | Laurasia |
D | Pangaea |
Question 22 |
A | Gene division and recombination |
B | Evolution |
C | Sexual reproduction |
D | Natural selection |
E | Speciation |
Question 23 |
A | An ecosystem study. |
B | Organisms study. |
C | A population study. |
D | A community study. |
Question 24 |

A | stromatolites |
B | bacteria |
C | fungi |
D | eukaryotic cells |
Question 25 |
A | The main statement in this question itself is the evidence that we all evolved from Africa. |
B | Your great great (great....) grand parents must be nonhuman primates. |
C | These relationships between human and nonhuman primates demonstrate unity among all living organisms. |
D | nonhuman primates must have exchanged DNA with humans millions of years ago. |
Question 26 |
A | I. Biology II. evolution |
B | I. Ecology II. natural selection |
C | I. Ecology II. genetic drift |
D | I. Biology II. natural selection |
E | I. Biology II. genetic drift |
Question 27 |
A | The variation in depth of view in eyesight among humans. |
B | The eye colour of humans. |
C | The amount of semen/sperms that will be ejected during an ejaculation by humans. |
D | The number of brains humans could have. |
Question 28 |
A | carbon dioxide |
B | ammonia |
C | nitrogen |
D | oxygen |
E | hydrogen |
F | water |
Question 29 |
On 26 December 2004, undersea megathrust earthquake West of Sumatra, Indonesia resulted in a Tsunami. The waves wiped out a population of cattle (cows) on the Eastern part of Sri Lanka. However, out of 2000 cattle, about 150 were able to escape death. Since the 2004 Tsunami, the cattle population has rebounded back to almost its original level. What is the major impact on the gene pool of the new generation of cattle after the Tsunami in this particular region?
A | The population is most likely underwent extremely fast evolution. |
B | The new population most likely will not survive for a long period without a gene flow between themselves and another unrelated population. |
C | The population most likely benefited from this catastrophic event because with reduce number of individuals, there is less competition for mating. |
D | The new population most likely experiencing large scale genetic mutations due to limited partners for mating. |
E | The population is most likely experiencing bottleneck effect, where there is a drastic reduction in genetic variations. |
Question 30 |
A | Postzygotic barriers |
B | Prezygotic barriers |
C | Neither because natural selection do not act at this level of life. |
D | Either because it is all depend on the type of organisms and their living environment. |
Question 31 |
A | experimental process. |
B | inductive reasoning. |
C | scientific process. |
D | deductive reasoning. |
E | first-order reasoning or first order analysis. |
Question 32 |
A | The better taste and large size of famed berries verses smaller wild berries. |
B | Large variation in types of dogs (breeds) due to selective breeding. |
C | Human females choosing specific traits such as eye colour and height of donors when selecting sperm from a sperm bank. |
D | Dramatic reduction in salmon population due to excessive overfishing. |
E | Genetically modified food such as bananas that converted wild inedible fruits to consumables. |
Question 33 |
According to the following table, what is the total number of alleles in the gene pool?
Table 1: Gene pool of the original rose plants.Red is dominant and White is recessive.

A | 660 |
B | 500 |
C | 600 |
D | 570 |
E | 1200 |
Question 34 |
A | Genetic drift |
B | Disruptive selection |
C | Higher relative fitness |
D | Founder effect |
E | Adaptive radiation |
Question 35 |
A | Nails |
B | Hypothalamus |
C | Spinal cord |
D | Appendix |
Question 36 |
A | ...no natural selection. |
B | ...very small population. |
C | ...no mutations. |
D | ...no gene flow between populations. |
E | ...random mating. |
Question 37 |
A | mRNAs |
B | RNAs |
C | homeotic genes |
D | DNAs |
Question 38 |
According to the following table, what are the two possible number of total alleles for Rr in this gene pool?
Table 1: Gene pool of the original rose plants.Red is dominant and White is recessive.

A | 61 (R) + 131 (r) |
B | 131 (R) + 61(r) |
C | 192 (R) + 192 (r) |
D | 61 (R) + 323 (r) |
E | 323 (R) + 61 (r) |
Question 39 |
A | ...eukaryotic cells with mostly microscopic unicellular organisms. |
B | ...prokaryotic cells with mostly macroscopic muticellular organisms. |
C | ...eukaryotic cells with mostly macroscopic unicellular organisms. |
D | ...prokaryotic cells with mostly macroscopic unicellular organisms. |
E | ...prokaryotic cells with mostly microscopic unicellular organisms. |
F | ...eukaryotic cells with mostly macroscopic multicellular organisms. |
Question 40 |
A | Intra- and inter-sexual selection |
B | Heterozygote advantage |
C | Genetic drift |
D | Continental drift |
Question 41 |
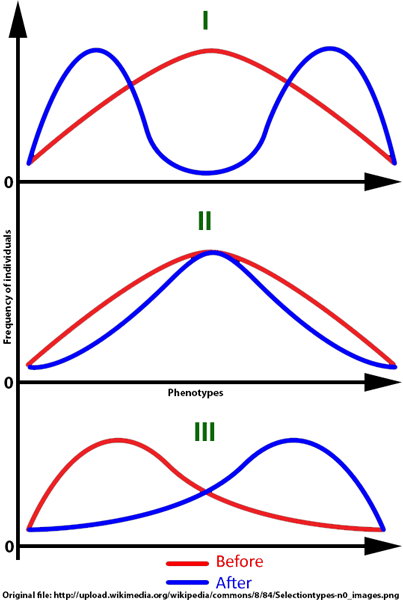
Modified from: http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/8/84/Selectiontypes-n0_images.png
A | I. Disruptive selection II. Directional selection III. Stabilizing selection |
B | I. Disruptive selection II. Stabilizing selection III. Directional selection |
C | I. Stabilizing selection II. Directional selection III. Disruptive selection |
D | I. Directional selection II. Stabilizing selection III. Disruptive selection |
E | I. Stabilizing selection II. Disruptive selection III. Directional selection |
F | I. Directional selection II. Disruptive selection III. Stabilizing selection |
Question 42 |
According to the following table, what is the total number of plants in this gene pool?
Table 1: Gene pool of the original rose plants.Red is dominant and White is recessive.

A | 500 |
B | 600 |
C | 216 |
D | 576 |
E | 408 |
Question 43 |
A | All the living organisms and their interaction among each other. |
B | A specific area of study used to derive a hypothesis or a theory. |
C | A specific group of species, such as humans, living under a specific area and their interactions among living organisms. |
D | All the organisms in a specific area along with nonliving factors with which they interact. |
E | An isolated system of organisms in which a specific population lives. |
Question 44 |
According to the following table, what are the allele frequencies in this gene pool (last row in the table, but remember, there are only two frequencies)?
Table 1: Gene pool of the original rose plants.Red is dominant and White is recessive.

A | R = 0.37 and r = 0.63 |
B | R = 0.20 and r = 0.80 |
C | R = 0.80 and r = 0.20 |
D | R = 0.04 and r = 0.96 |
E | R = 0.96 and r = 0.04 |
F | R = 0.63 and r = 0.37 |
Question 45 |
A | The natural selection may have created new alleles that are resistant to pesticides. |
B | The evolutionary mechanisms may have introduced a new alleles to the population that resist pesticide. |
C | The environment in which the pest population live may have acted as a barrier to the pesticides' effectiveness. |
D | Some individuals in a particular pest population may have the pesticide resistant alleles. |
Question 46 |
A | ...very large populations. |
B | ...small populations. |
C | ....asxually reproducing populations. |
D | ...sexually reproducing populations. |
E | ...genetically isolated populations. |
F | ...geographically isolated populations. |
Question 47 |
A | It favors only the characteristics that benefit the specific population. |
B | It can produce new genotypes that favors the entire global population of a species. |
C | It can change the characteristics of a population in one of very few changes to the genetic code in a very short period of time. |
D | It favors characteristics in a population that fit the current local environment. |
Question 48 |
A | A group of organisms living in the same community. |
B | A population in which whose members are genetically related to each other. |
C | A group of populations whose members have the potential to interbreed. |
D | A group of organisms whose members have the potential to reproduce either by sexual or asexual reproduction. |
Question 49 |
A | 23 x 2 = 46 combinations |
B | 23 combinations |
C | 223 = 8.39 x 106 combinations |
D | 232 = 529 combinations |
E | 23/2 = 11.5 combinations |
Question 50 |
I. Polymerization of monomers
II. Replication of RNA molecules and passing of biological information from one cell to another.
III. Abiotic synthesis of important molecules from simpler chemicals in the atmosphere.
IV. Enclosure within a lipid membrane ("protocells"), which maintained a distinct internal environment.
A | III (first to occur) , I , II , IV (last to occur) |
B | III (first to occur) , I , IV , II (last to occur) |
C | I (first to occur) , III , IV , II (last to occur) |
D | I (first to occur) , IV , III , II (last to occur) |
E | I (first to occur) , III , II , IV (last to occur) |
F | III (first to occur) , IV , I , II (last to occur) |
Question 51 |
A | organ |
B | individual |
C | community |
D | DNA |
E | population |
Question 52 |
A | Metamorphic rocks |
B | Igneous rocks |
C | Punk rocks |
D | Sedimentary rocks |
E | Clastic rocks |
Question 53 |
A | Because he assumed that inheritance traits can only be passed down to the offspring by the male population (fathers). |
B | Because he assumed that inheritance traits also includes acquired characteristics. |
C | Because he refused genetic variation within the same species. |
D | Because he refused that the environment also pays a vital role in evolution of desired traits. |
Question 54 |
A | 4.6 bya |
B | 1.5 bya |
C | 2.1 bya |
D | 3.5 bya |
Question 55 |
A | ...the origins of life plus how new species adapt and evolve. |
B | ...how new species adapt and evolve. |
C | ...the origins of life. |
D | ...genetic variation caused by mass extinctions and repopulation cycles. |
Question 56 |
A | The observation he made that all species will only produce offspring than the environment can support. |
B | Domesticated species like dogs in which humans have used artificial selection to produce animals with desirable traits. |
C | The observation he made that members of a population often vary in their inherited traits. |
D | Ideas and concepts taken out of the book: Principles of Geology by Charles Leyell. |
Question 57 |
A | Oak leaf and oak root. |
B | Human thumb and chimpanzee arm. |
C | Bat wing and insect wing. |
D | Oak leaf and maple leaf. |
E | Human limb and whale flipper. |
Question 58 |
A | p2 |
B | pq |
C | 2p |
D | 2q |
E | 2pq |
Question 59 |
A | 90% or more |
B | 30% or more |
C | 10% or more |
D | 100% |
E | 50% or more |
Question 60 |
A | adaptation |
B | bottleneck effect |
C | genetic drift |
D | evolution |
E | genetic shift |
Question 61 |
A | evolutionary adaptations |
B | advanced civilization |
C | sudden specialization of DNA |
D | sexual reproduction |
Question 62 |
A | I. potential to interbreed in nature II. fossils only. |
B | I. potential to interbreed in nature II. asexually and sexually reproducing organisms. |
C | I. physical characteristics/traits II. asexually and sexually reproducing organisms. |
D | I. DNA/chemical characteristics/traits II. asexually and sexually reproducing organisms. |
E | I. physical characteristics/traits II. fossils only. |
Question 63 |
A | ...by interbreeding. |
B | ...through sudden changes in gene frequencies. |
C | ...by sexual reproduction at first and later by both sexual and asexual reproduction. |
D | ...by accumulating small changes over a a long period of time. |
Question 64 |
A | molecule, tissue, cell, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem |
B | cell, molecule, organ system, organ, tissue, population, organism, ecosystem, community |
C | ecosystem, population, organ system, cell, community, molecule, organ, organism, tissue |
D | cell, molecule, organ system, organ, population, tissue, organism, ecosystem, community |
E | molecule, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism, population, community, ecosystem |
Question 65 |
A | All the humans living in the City of Calgary. |
B | All the dogs and cats living in the City of Calgary. |
C | All the birds living in the entire world. |
D | All the insects living in the City of Calgary. |
E | All the insects living in the entire world. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. K. Ruckstuhl during Fall 2014.
FAQ | Report an Error
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.