Go to: Midterm II | Final
Since it is a 400-level class, I assume that you have the prior background in first (and second) year Geology classes. Note that I have separated all Protistans related questions into a separate exam database (second quiz).
Geology (GLGY 491-UCAL) Midterm I General
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 491-UCAL) Midterm I General.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
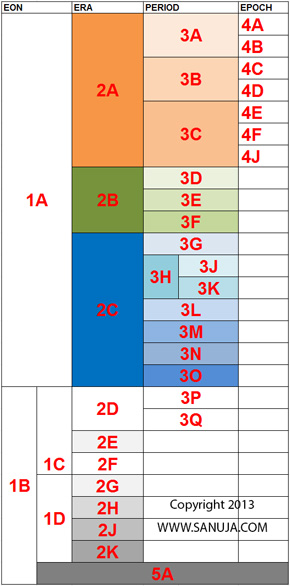
What is 3L on the following diagram?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.
A | Jurassic |
B | Devonian |
C | Pennsylvanian |
D | Ordovician |
Question 2 |
A | living environments |
B | genetic structures |
C | growth stages. |
D | genetic variation |
Question 3 |
A | Phylum Helmichordata |
B | Phylum Brachiopoda |
C | Phylum Porifera |
D | Phylum Cnidaria |
Question 4 |
A | Animalia |
B | Hexagonaria |
C | Cristata |
D | Cnidaria |
Question 5 |
This particular Period is known for high volumes of coal formations. It is first appears on Geological records around 358.9 Ma. What is the Period and it's location on the following diagram?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | Carboniferous; 3H |
B | Carboniferous; 3B |
C | Jurassic; 3E |
D | Jurassic; 3D |
Question 6 |
A | Ordovician-Devonian |
B | Cretaceous to Neogene |
C | Cambrian to Mississippian |
D | Ordovician to Permian |
Question 7 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 8 |
- the frustule is composed of organic silica
- radial symmetry
- found in sediment samples throughout Jurassic to Holocene
- is a microfossil
This sample most like be a...
A | tasmanitid. |
B | diatom. |
C | slilicoflagellate. |
D | not enough data to distinguish. |
E | coccolithophorid. |
Question 9 |
A | Carboniferous - Permian |
B | Permian - Triassic |
C | Devonian - Carboniferous |
D | Cretaceous - Paleogene |
E | Devonian - Silurian |
Question 10 |
A | The last appearance of an organism/group. |
B | The first appearance of an organism/group. |
C | Sudden fluctuation in morphological features of an organism/group. |
D | Abundance of specific organisms in a given time window. |
Question 11 |
A | Carboniferous |
B | Neogene |
C | Neoproterozoic |
D | Paleozoic |
Question 12 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 13 |
A | index fossils |
B | identity fossil |
C | trace fossils |
D | characteristic fossil |
E | most abundant fossils |
Question 14 |
A | young. |
B | mature. |
C | under development. |
D | old. |
Question 15 |
A | The trace fossils left by the organism during certain growth periods. |
B | Abundance in organic matter in some parts of the stratigraphic windows. |
C | Fossils of the organism were found without the exoskeleton. Hint: Impossible due to soft body dissolution. |
D | The lack of exoskeletons in some parts of the stratigraphic windows. |
Question 16 |
A | 2500 Ma |
B | 4560 Ma |
C | 4030 Ma |
D | 541 Ma |
Question 17 |
A | Pentremites |
B | Lingula |
C | Archaeocyathid |
D | Inoceramus |
Question 18 |
A | four |
B | five |
C | two |
D | three |
Question 19 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 20 |
A | Early middle Cambrian |
B | Early Lower Permian |
C | Middle Ordovician |
D | Lower Silurian |
Question 21 |
A | Genetic studies |
B | Morphological studies |
C | Behavioral studies (trace fossils) |
D | Chemical compositional studies |
Question 22 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 23 |
A | Miocence |
B | Holocene Hint: This is the Epoch and NOT the era. |
C | Cenozoic |
D | Quaternary Hint: This is the period and NOT the era. |
Question 24 |
A | Mesozoic |
B | Paleozoic |
C | Cenozoic |
D | Precambrian |
E | Carboniferous |
Question 25 |
A | Populations that naturally breed together and provide viable offspring. |
B | Grouping of kingdoms which have the height precedence in taxonomy. |
C | Diagnosable cluster within which there is a pattern of ancestry. |
D | Set of organisms with similar physical characteristics. |
Question 26 |
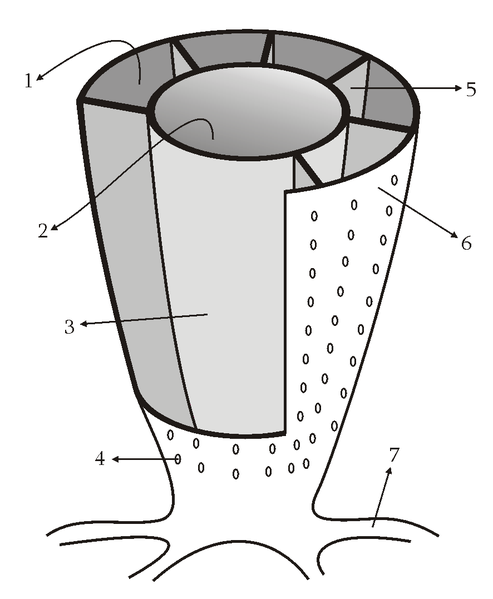
A | feet |
B | central cavity |
C | holdfast |
D | basal ring |
Question 27 |
A | Sycon |
B | Leucon |
C | Rhagon |
D | Hyperdemia |
E | Ascon |
Question 28 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 29 |
A | Impregnation |
B | Canonization |
C | Recrystallization |
D | Moldic fossilization |
Question 30 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 31 |
On the following diagram, around what time 5A ended?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | 66.0 Ma |
B | 252.17 Ma |
C | 4030 Ma |
D | 4560 Ma |
Question 32 |
Choose the odd one out based on the process of fossilization. (Choose the best option!)
InsectsDiatoms
Bivalves
Coccolithophorids
Sponges
Gastropods
A | Insects |
B | Gastropods |
C | Diatoms |
D | Bivalves |
Question 33 |
A | coprolites (poops). |
B | insects. |
C | mammals. |
D | dinosaurs. |
Question 34 |
A | Spherical |
B | Circular |
C | Radial |
D | Pentameral |
Question 35 |
A | Genetic |
B | Stratigraphic |
C | Chemical |
D | Morphological |
Question 36 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 37 |
A | taxonomy. |
B | biostratigraphy. |
C | evolutionary biology. |
D | taxa. |
Question 38 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 39 |
A | Radial symmetry |
B | Bilateral symmetry |
C | Biradial symmetry |
D | Spherical symmetry |
Question 40 |
A | I. Permian II. Devonian |
B | I. Permian II. Neogene |
Question 41 |
A | two |
B | one |
C | three |
D | infinite |
Question 42 |
A | biocherms. |
B | ecologic. |
C | reefs. |
D | platonic. |
Question 43 |
A | I. non-symmetrical II. symmetrical |
B | I. anisometric II. isometric |
C | I. isometric II. anisometric |
D | I. symmetrical II. non-symmetrical |
Question 44 |
A | trilobite. |
B | humans. |
C | bivalves. |
D | echinoids. |
Question 45 |
A | SpongeBob SquarePants can NOT be classified into Phylum Proifera. |
B | They are planktonic organisms. |
C | They have well specialized organs. |
D | They lived attached to the substratum with the aid of root-like structures. |
Question 46 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 47 |
A | classes |
B | phyla |
C | genera |
D | families |
E | orders |
Question 48 |
A | euryproct |
B | platyproct |
C | amblyproct |
D | stenoproct |
Question 49 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 50 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 51 |
A | 541 Ma |
B | 252.17 Ma |
C | 0.011710 Ma |
D | 66.0 Ma |
Question 52 |

A | 1 |
B | 7 |
C | 5 |
D | 2 |
Question 53 |
A | Molting |
B | Modification |
C | Accretion |
D | Addition |
Question 54 |
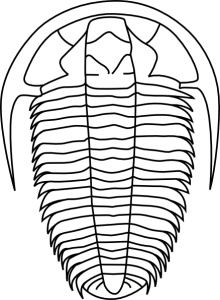
A | Brachiopod |
B | Trilobite |
C | Cruziana |
D | Ammonite |
Question 55 |
A | 6000 years |
B | 22,000 years |
C | 8,000 years |
D | 11,700 years |
E | 50,000 years |
Question 56 |
A | Holocene |
B | Ediacaran |
C | Cretaceous |
D | Eoarchean |
Question 57 |
A | Superclass |
B | Kingdom |
C | Phylum |
D | Order |
Question 58 |
A | Class Germaphobia |
B | Class Calcarea |
C | Class Hexactinellida |
D | Class Demospongea |
Question 59 |
A | opaline silica |
B | test |
C | cells |
D | frustule |
Question 60 |

A | Pentameral |
B | Not enough information is given. |
C | Radial |
D | Bilateral |
Question 61 |
A | Morphological Trajectory |
B | Ontogeneric Trajectory |
C | Nongenetic Trajectory |
D | Genetic Trajectory |
Question 62 |
A | Choanocytes |
B | Sclerocytes |
C | Pinacocytes |
D | Archaeocytes |
Question 63 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 64 |
A | Acme Zones |
B | Assemblage Zones |
C | Morphological Zones |
D | Interval Zones |
Question 65 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 66 |
There are only two sub-Periods (subdivisions) on this diagram. They are represented by 3J and 3K. What are they?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | 3J - Silurian 3K - Devonian |
B | 3J - Devonian 3K - Silurian |
C | 3J - Mississippian 3K - Pennsylvanian |
D | 3J - Pennsylvanian 3K - Mississippian |
Question 67 |
A | Archean |
B | Permian |
C | Silurian |
D | Devonian |
Question 68 |
A | Genus and Species |
B | Class and Species |
C | Order and Family |
D | Phylum and Family |
Question 69 |
A | Archaeocytes |
B | Amblyprocts |
C | Porocytes |
D | Scierocytes |
Question 70 |
A | PTD |
B | Acme Zone |
C | Evolutionary Occurrence |
D | LAD |
Question 71 |
A | archaeocytes |
B | choanocytes |
C | pinacocytes |
D | sclerocytes |
Question 72 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 73 |
On the following diagram, what is highlighted in 3C?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | Quaternary |
B | Paleogene |
C | Permian |
D | Cretaceous |
Question 74 |
A | Impregnation |
B | Congealment |
C | Impressions |
D | Carbonization |
Question 75 |
A | Triassic |
B | Mississippian |
C | Jurassic |
D | Devonian |
Question 76 |
A | 0.0117 millions of years ago |
B | 13 millions of years ago |
C | 66 millions of years ago |
D | 541 millions of years ago |
Question 77 |
-underwent rapid burial
-internal structures were often preserved
-most fossils from Ediacaran period were fossilized through this process.
A | Impressions |
B | Permineralization |
C | Permineralization |
D | Carbonization |
Question 78 |
A | Modern Linnaean hierarchy |
B | Improved Linnaean hierarchy |
C | Original Linnaean hierarchy |
Question 79 |
A | Discontinuous genetic variability is less frequent than continuous genetic variability. |
B | Discontinuous genetic variability is more frequent than continuous genetic variability. |
C | Continuous genetic variability occurs in species with large morphological differences between sexes. |
D | Echinoids great are examples discontinuous genetic variability. |
Question 80 |
A | differentiation between growth stages. |
B | ecological conditions. |
C | sudden changes in genetic variation. |
D | sexual dimorphism. |
Question 81 |
What are the Eons represented by 1A and 1B respectively on the following diagram?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | Cenozoic and Paleozoic |
B | Phanerozoic and Precambrian |
C | Cenozoic and Mesozoic |
D | Proterozoic and Archean |
Question 82 |
A | Fossilization in Amber |
B | Moldic fossilization |
C | Congealment |
D | Impregnation |
Question 83 |
On the following diagram, what is highlighted in 2D?
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this without using any AIDS.

A | Ordovician |
B | Cretaceous |
C | Ediacaran |
D | Neoproterozoic |
E | Devonian |
Question 84 |
A | Accretion |
B | Molting |
C | Modification |
D | Addition |
Question 85 |
A | Suborder |
B | Subfamily |
C | Subtribe |
D | Tribe |
E | Subspecies |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 |
| End |
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.
Geology (GLGY 491-UCAL) Midterm I Protistans
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 491-UCAL) Midterm I Protistans.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
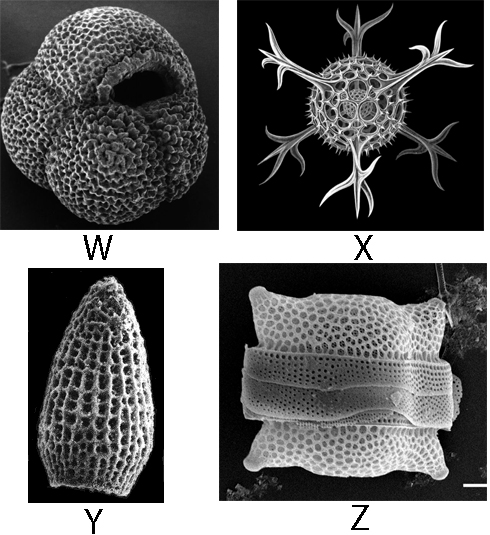
A | W |
B | Y |
C | Z |
D | X |
Question 2 |
A | Jurassic to Holocene (recent) |
B | Paleozoic to Holocene (recent) |
C | Cambrian to Miocene |
D | Cretaceous to Holocene (recent) |
Question 3 |
A | Diatoms |
B | Archaeocyatha |
C | Coccolithophorids |
D | Profiera |
Question 4 |
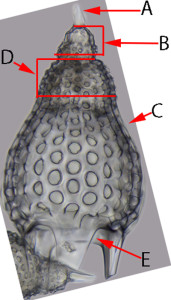
A | Aperture |
B | Cephalon |
C | Basal ring |
D | Sagittal ring |
Question 5 |

A | Cephalon |
B | Aperture |
C | Abdomen |
D | Thorax |
Question 6 |
Find the odd one out.
SilicoflagellatesDiatoms
Radiolarians
Coccolithophorids
Sponges
Foraminifera
A | Silicoflagellates |
B | Sponges |
C | Radiolarian |
D | Coccolithophorids |
Question 7 |
A | Lower Jurassic |
B | Upper Silurian |
C | Middle Cambrian |
D | Upper Devonian |
Question 8 |
A | True |
B | False because the availability of other micro-organisms for food supply that dictates the distribution. |
C | False because it is the temperature of the upper water column. |
D | False because it is the abundance of oxygen and light. |
Question 9 |
A | microsphere |
B | cortical shell |
C | medullar shell |
D | basal ring |
Question 10 |
A | Upper Cambrian |
B | Lower Cretaceous |
C | Middle Jurassic |
D | Upper Devonian |
Question 11 |
Find the odd one out.
SilicoflagellatesDiatoms
Radiolarians
Coccolithophorids
Tasmanitids
A | Radiolarians |
B | Coccolithophorids |
C | Diatoms |
D | Silicoflagellates |
E | Tasmanitids |
Question 12 |
A | Tasmanitids |
B | Diatoms |
C | Nassellaria |
D | Silicoflagellates |
Question 13 |
A | True |
B | False |
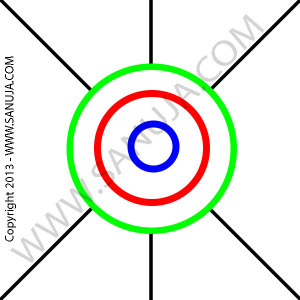
Question 14 |

A | Black lines indicating the spines. |
B | Middle part in red. |
C | Outer most part in green. |
D | Central part in blue. |
Question 15 |
A | Foraminifera |
B | None; all of them have plant-like metabolism |
C | Diatoms |
D | Silicoflagellates |
Question 16 |
A | Epicingulum |
B | Epitheca |
C | Hypotheca |
D | Epiproferia |
Question 17 |

A | Aperture |
B | Thorax |
C | Abdomen |
D | Cephalon |
Question 18 |
A | Carbon |
B | Silicon |
C | Nitrogen |
D | Oxygen |
Question 19 |

A | W |
B | X |
C | Y |
D | Z |
Question 20 |
A | Anything above 40% |
B | Anything above 5% |
C | Anything above 1% |
D | Anything above 10% |
Question 21 |
A | Tasmanitids |
B | Radiolarians |
C | Silicoflagellates |
D | Diatoms |
Question 22 |
A | Albaillaria |
B | Sponges |
C | Spumellaria |
D | Foraminifera |
Question 23 |
A | Jurassic to Cretaceous |
B | Cambrian to Holocene (recent) |
C | Ediacaran to Cretaceous |
D | Jurassic to Holocene (recent) |
Question 24 |

A | microsphere |
B | basal ring |
C | cortical shell |
D | medullar shell |
Question 25 |
A | byspines |
B | cortical spines |
C | central spines |
D | polar spines |
Question 26 |
A | They started to dissolve well above the CCD of the water column. |
B | They have animal-type metabolism. |
C | They are typically benthic form of organisms. |
D | They started to dissolve well below the CCD of the water column. |
E | They are closely related to Radiolarians. |
Question 27 |
A | Epitheca |
B | Epiproferia |
C | Epicingulum |
D | Hypotheca |
Question 28 |
A | co-axial |
B | radial |
C | no symmetry; primitive. |
D | bilateral |
Question 29 |
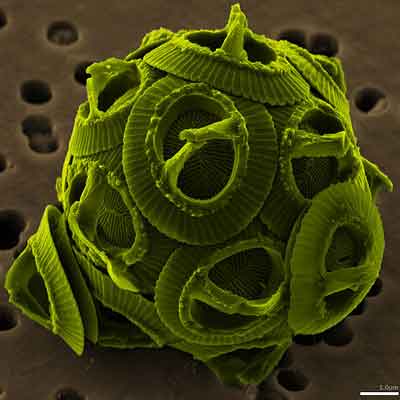
A | Diatom |
B | Spumellaria |
C | Coccolithophorids |
D | Forminifera |
Question 30 |
A | 20 - 200 microns. |
B | 1000 - 5000 microns. |
C | 50 - 900 microns. |
D | 300 - 900 microns. |
Question 31 |
A | Spines (larger) |
B | Basal ring |
C | Apical ring |
D | Bars |
Question 32 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 33 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 34 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 35 |
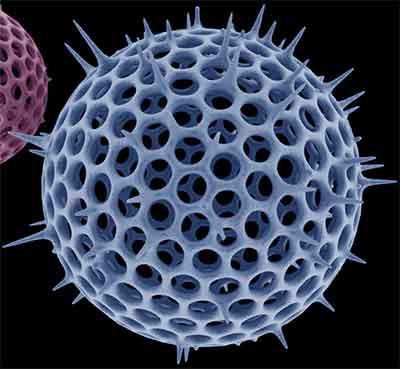
A | Coccolithophorids |
B | Forminifera |
C | Nassellaria |
D | Spumellaria |
Question 36 |
A | Charles Robert Darwin |
B | Joseph Dalton Hooker |
C | Dr. Marius (Dan) Georgescu |
D | Ernst Haeckel |
Question 37 |
A | Spines |
B | Basal ring |
C | Apical ring |
D | Bars |
Question 38 |
A | inorganic reefs |
B | chalks and calcareous oozes |
C | oil shales |
D | clay |
Question 39 |
A | Ordovician |
B | Ediacaran |
C | Late Triassic |
D | Holocene |
Question 40 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 41 |
A | False; it is four bars. |
B | True |
C | False; it is six bars. |
Question 42 |
A | chalks and calcareous oozes |
B | in organic shale |
C | organic reefs and clastic rocks |
D | coccolithoids |
Question 43 |
A | At young stage, active. At adult stage passive. |
B | Active |
C | At young stage, passive. At adult stage active. |
D | Passive; like people high on weed. |
Question 44 |
A | False |
B | True |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | End |
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Marius (Dan) Georgescu during Fall 2013.
FAQ | Report an Error
Hierarchy of Life
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Click here for specific biological taxonomical divisions.
Geologic Time Scale
Mobile Users: Best view in landscape mode when mobile version is active.
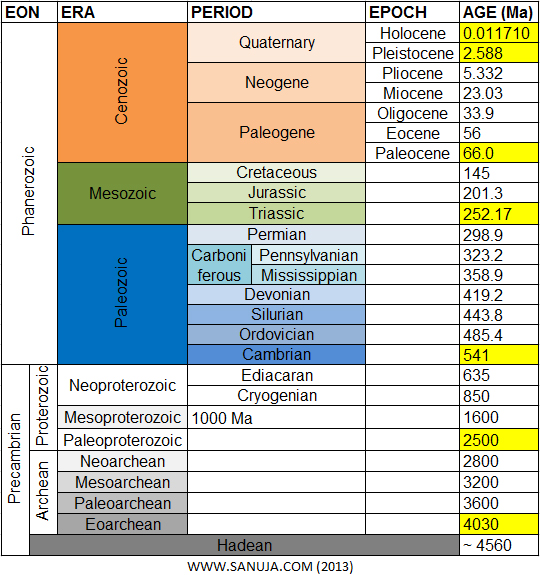
| EON | ERA | PERIOD | EPOCH | AGE (Ma) | ||
-zoic |
Cenozoic (Cz) |
Quaternary (Q) | Holocene | 0.011710 | ||
| Pleistocene (Ps) | 2.588 | |||||
| Neogene (N) | Pliocene (PO) | 5.332 | ||||
| Miocene (MI) | 23.03 | |||||
| Paleogene (PE) | Oligocene(OG) | 33.9 | ||||
| Eocene (EO) | 56 | |||||
| Paleocene (Pε) | 66.0 | |||||
| Mesozoic (MZ) |
Cretaceous (K) | 145 | ||||
| Jurassic (J) | 201.3 | |||||
| Triassic (Tr) | 252.17 | |||||
| Paleozoic (Pz) |
Permian (P) | 298.9 | ||||
| Carboni- -ferous (C) |
Pennsylvanian (|P) | 323.2 | ||||
| Mississippian (M) | 358.9 | |||||
| Devonian (D) | 419.2 | |||||
| Silurian (S) | 443.8 | |||||
| Ordovician (O) | 485.4 | |||||
| Cambrian (∈) | 541 | |||||
| Pre∈ | Pro- -terozoic (Ρ) |
Neo (Z) | 635 | |||
| 850 | ||||||
| Meso (Y) | 1000 Ma | 1600 | ||||
| Paleo (X) | 2500 | |||||
| Archean (A) | 2800 | |||||
| 3200 | ||||||
| 3600 | ||||||
| 4030 | ||||||
| Hadean (ρA) | ~ 4560 | |||||
* Symbols are based on reference USGS reference table.
Image version of the above table for those who are still using stone age computers like Fred Flintstone.