Geography 535 – Geography World Affairs
Regions covered in Midterm I: Europe, Former USSR and Middle America. The in-class exam also will be in multiple choice format.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm II | Final Exam
Geography 213 (GEOG 213-UCAL) Midterm I
Congratulations - you have completed Geography 213 (GEOG 213-UCAL) Midterm I.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | C-Type |
B | B-Type |
C | A-Type |
D | D-Type |
E | E-Type |
Question 2 |
A | West Germany |
B | United States itself |
C | France |
D | United Kingdom |
E | Japan |
Question 3 |
A | Trinidad and Tobago |
B | Cuba and the Dominican Republic |
C | Cuba and Puerto Rico |
D | Antigua and Barbuda |
E | Haiti and the Dominican Republic |
Question 4 |
A | Germany |
B | Britain |
C | Spain |
D | France |
E | Italy |
Question 5 |
A | Proximity to sea routes and the lands of the New World |
B | Unification in the war against the Mongol invaders |
C | Large urban populations |
D | Modern industries |
E | Organization under the Roman Empire |
Question 6 |
A | Peter the Great |
B | Catherine the Great |
C | Nicholas II |
D | Adolf Hitler |
E | Ivan III |
Question 7 |
A | Southwestern Siberia |
B | Along the Baltic coast |
C | Around far NE region |
D | Southern Russia |
E | Around the SE coast of the Black Sea |
Question 8 |
A | Northern |
B | Western |
C | Northwestern |
D | Eastern |
E | Southeastern |
Question 9 |
A | 1999 |
B | 1993 |
C | 1945 |
D | 1960 |
E | 1950 |
Question 10 |
A | Waterways and ocean shipping routes. |
B | Volatile political and economic climate. |
C | Abundance of natural resources. |
D | Favorable climate for the population growth. |
E | Extremely low population growth. |
Question 11 |
A | Andorra |
B | Luxembourg |
C | San Marino |
D | Vatican |
E | Liechtenstein |
Question 12 |
A | Switzerland |
B | Slovenia |
C | Norway |
D | Hungary |
E | Belgium |
Question 13 |
A | Australia |
B | Canada |
C | Africa |
D | United States |
E | India |
Question 14 |
A | Type C |
B | Type E |
C | Type B |
D | Type D |
E | Type A |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 15 |
A | It is impossible to deduce from the given information. |
B | West |
C | South |
D | North |
E | East |
Question 16 |
A | Cordillera |
B | Rocky |
C | Rundle |
D | Andes |
E | Alpine |
Question 17 |
A | Type B |
B | Type A |
C | Type D |
D | Type C |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 18 |
A | Mainland and Central America |
B | Rimland |
C | Caribbean |
D | Central America and Rimland |
E | Caribbean and Rimland |
Question 19 |
A | Four |
B | Three |
C | Five |
D | Six |
E | Two |
Question 20 |
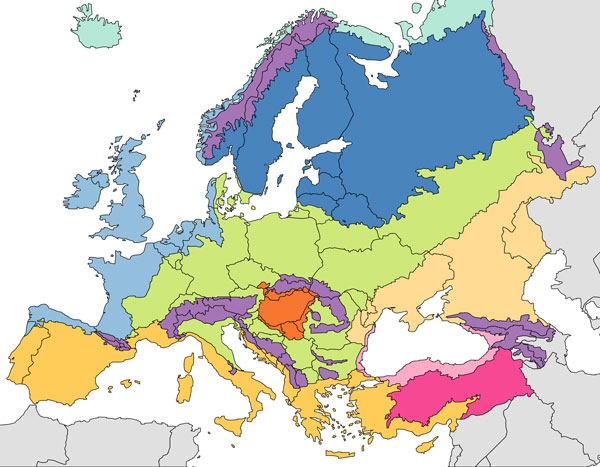
Modified from: http://commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Europe_biogeography_countries.svg
A | Type A |
B | Type B |
C | Type E |
D | Type C |
E | Type D |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 21 |
A | Mountain ranges |
B | Lowland regions |
C | Siberian arctic regions |
D | Eastern highland regions |
E | Arctic regions |
Question 22 |
A | France |
B | Germany |
C | Estonia |
D | Austria |
E | Greece |
Question 23 |
A | ...topographical features. |
B | ...the Brandt Line. |
C | ...the equator. |
D | ...geographical features. |
E | ...political systems. |
Question 24 |
A | Both countries has been a colony of the British Empire at some point of the history. |
B | Both countries composed of similar (if not same) ethnic groups. |
C | Both countries have Germanic language such as English, French and Russian as official languages. |
D | Both countries share a border with Alaska. |
E | Both countries located above the 50-degree North latitude. |
Question 25 |
A | Type D |
B | Type B |
C | Type A |
D | Type C |
E | Type E |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 26 |
A | It is a democratic system very similar to that of the Germany. |
B | It is a Socialist System where the authority is completely controlled by a central government. |
C | It is similar to Canada with a Federal System in place. |
D | It is similar to USA with a State System in place. |
E | It is a Communist System where the authority is completely controlled by a central government. |
Question 27 |
A | Type D |
B | Type E |
C | Type C |
D | Type A |
E | Type B |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 28 |
A | Spanish, Americans |
B | French, Spanish |
C | Spanish, British |
D | French, British |
E | Spanish, German |
Question 29 |
A | Near St. Petersburg |
B | The Far East close to the international date line |
C | Northern Siberia |
D | Northwestern European Russia (Kola Peninsula) |
E | East closer to the border with China |
Question 30 |
A | Expansion of the Ottoman Empire |
B | World War I |
C | World War II |
D | Fall of the French kingdom |
E | Fall of Roman Empire |
Question 31 |
A | Increased in agricultural production |
B | Britain’s global influence |
C | Increased mechanization |
D | Britain’s technological innovations |
E | Availability of gold and iron ore |
Question 32 |

Modified from: http://commons.wikimedia.org/ wiki/ File:Europe_biogeography_countries.svg
A | Type E |
B | Type C |
C | Type B |
D | Type D |
E | Type A |
B - Dry (Arid) climates
C - Subtropical; Mid-latitude humid; Mediterranean
D - Mid-latitude continental; Subarctic
E - Polar
H - Highland climates
Question 33 |
A | It is a military union between Belgium, Norway and Luxembourg. |
B | It is the term given to describe the first three nations to join the European Union (EU). |
C | It is a economic union between Bulgaria, Norway and Lithuania. |
D | It is an economic union between Belgium, Netherlands and Luxembourg. |
E | It is a military union between Bulgaria, Norway and Lithuania. |
Question 34 |
A | France |
B | Italy |
C | Denmark |
D | Belgium |
E | Germany |
Question 35 |
A | Collapse of the class and caste system after fall of several monarchies. |
B | Economic integration facilitated by greater cooperation between nations. |
C | Rapid increased in inequalities resulting large population growths in poor regions. |
D | Very high social stability of the region. |
E | Agricultural advancement due to industrial revolution. |
Question 36 |
A | About 80% |
B | About 10% |
C | About 50% |
D | About 30% |
E | About 99% |
Question 37 |
A | right after the French revolution. |
B | right after the industrial revolution in Britain. |
C | after the First World War |
D | after the industrial revolution spread across the Western Europe into Eastern Europe. |
E | during the Renaissance |
Question 38 |
A | Mediterranean Sea |
B | North Sea |
C | Black Sea |
D | Baltic Sea |
E | Caspian Sea |
Question 39 |
A | Mexico - United States border region. |
B | Countries that lies along the North Africa and South Africa division. |
C | Kazakhstan - Russia border region. |
D | Canada - United States border region. |
E | Region that has been geographically divided by Caucasus Mountains. |
Question 40 |
A | To rebuild Japan after the World War II |
B | To rebuild Western European economies |
C | To increase the funding for non-military goods during World War II to families at home |
D | To take the United States out of the Great Depression |
E | To increase the funding for manufacturing of weapons during World War I to support troops |
Question 41 |
A | 1850 |
B | 1910 |
C | 1913 |
D | 1867 |
E | 1950 |
Question 42 |
A | Lack of natural resources in continental Europe |
B | Political divisions between major players such as Germany and Russia |
C | Napoleonic Wars |
D | Britain blocked access to waterways |
E | World War I and II |
Question 43 |
A | Slovakia |
B | Serbia |
C | Czech Republic |
D | Belarus |
E | Romania |
Question 44 |
A | The term is only used during the World War I and World War II to describe countries that supported Germany. |
B | The term "Second World" no longer applicable because in modern day, either a country is well developed or not at all. There is no in-between. |
C | The term "Second World" has never been used by North American educators, but it is often a term given to developing nations in other parts of the world. |
D | The term "Second World" has never been officially used by Geographers. |
E | The term "Second World" was used to describe Communist regions. |
Question 45 |
A | The long history of African slave trade. |
B | The tectonic activities that resulted in high frequency of volcanoes. |
C | The unequal distribution of wealth and power among the population. |
D | The horrific conditions of the sugar plantation industry. |
E | The annihilation of the Middle American Native population. |
Question 46 |
A | Kazakhstan |
B | Pakistan |
C | India |
D | Singapore |
E | Sri Lanka |
Question 47 |
A | War bodies of seas around Europe |
B | Subtropical to tropical latitude |
C | Large land mass |
D | Gulf Stream |
E | Northwestern winds and low altitude |
Question 48 |
A | 15th century France |
B | 16th century Britain |
C | 14th century Italy |
D | 12th century Russia |
E | 15th century Spain |
Question 49 |
A | Romania |
B | Lithuania |
C | Czech Republic |
D | North Pole |
E | Ukraine |
Question 50 |
A | Alliance of several Roman sub-regions |
B | Slave of Roman Empire |
C | Barbarians |
D | Low class and low caste Romans |
E | Western Europeans |
Question 51 |
A | Balkans |
B | Urals |
C | Caucasus |
D | Pamirs |
E | Carpathians |
Question 52 |
A | Ivan III the Great |
B | Ivan IV the Great |
C | Peter the Great |
D | Catherine the Great |
E | Ivan I the Great |
Question 53 |
A | Northern Europe |
B | Central Europe |
C | Western Europe |
D | Mediterranean Europe |
E | Eastern Europe |
Question 54 |
A | Belgium |
B | Switzerland |
C | Austria |
D | Norway |
E | Czech Republic |
Question 55 |
A | Central Highlands |
B | Western Uplands |
C | The Alpine system |
D | The North European Lowland |
E | Central Uplands |
Question 56 |
A | Political system of the population. |
B | Type of associations to organizations such as NATO. |
C | Cultural and religious aspects of the population. |
D | Specific sociological or economical phenomena. |
E | Geographic location. |
Question 57 |
A | A-Type |
B | E-Type |
C | C-Type |
D | D-Type |
E | None of the listed answers are correct. |
Question 58 |
A | during the early 1900s. |
B | after the Bolshevik Revolution. |
C | during the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. |
D | in the middle of the 1800s. |
E | during the early 1700s with Peter the Great |
Question 59 |
A | Ukrainian |
B | Czech |
C | Polish |
D | Russian |
E | Romanian |
Question 60 |
A | Central Europe |
B | Western Europe |
C | British Isles |
D | Eastern Europe |
E | Northern Europe |
Question 61 |
A | Greece, Denmark and Spain |
B | Spain, Italy and Croatia |
C | Greece, Bulgaria and Spain |
D | France, Spain and Italy |
E | Poland and Germany |
Question 62 |
A | Costa Rica |
B | El Salvador |
C | Guatemala |
D | Jamaica |
E | Cuba |
Question 63 |
A | 3rd millennium B.C. |
B | 1st millennium B.C. |
C | 6th millennium B.C. |
D | 5th millennium B.C. |
E | 4th millennium B.C. |
Question 64 |
A | The specific socio-ethnic background is irrelevant in this approach. |
B | The type of economy can be used to separate one section from another. |
C | North and South America is considered as one section under this approach. |
D | The geographic location is irrelevant in this approach. |
E | Political unity can be used as a method to separate one section from another. |
Question 65 |
A | C-type |
B | E-type |
C | B-type |
D | D-type |
E | A-type |
Question 66 |
A | Spain |
B | Austria |
C | France |
D | Bosnia |
E | Germany |
Question 67 |
A | Shortly after World War II |
B | After the fall of Communism in Eastern Europe |
C | During the 1970s |
D | After World War I during the 1920s |
E | During the Great Depression |
Question 68 |
A | Irish |
B | Ukrainian |
C | Spanish |
D | English |
E | Polish |
Question 69 |
A | Haiti |
B | Cuba |
C | Mexico |
D | Costa Rica |
E | Puerto Rico |
Question 70 |
A | Physical regions |
B | Economic regions |
C | Cultural regions |
D | Religious regions |
E | Political regions |
Question 71 |
A | British Empire was in full control of the Western border. |
B | Russia was fighting wars in several other fronts. |
C | Low population density and relatively flat land mass on the East side. |
D | Ottoman Empire was controlling the other parts of the Russian borders. |
E | All other parts were covered with mountains. |
Question 72 |
A | Gross National Product (GNP) per capita |
B | Ethnic diversity |
C | Distribution of wealth and equality |
D | Energy consumption per capita |
E | Education and literacy levels |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Peter Slezak during Winter 2015.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.
