Economics 201 is the Principles of Microeconomics class. Depending on the Professor, the exams format may or may not be multiple choice.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Final Exam
Economics (ECON 201-UCAL) Midterm Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Economics (ECON 201-UCAL) Midterm Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | $375 |
B | $35.5 |
C | $53.5 |
D | $710 |
Question 2 |
A | Input: commodities and consumption Output: revenue and resource services |
B | Input: commodities and consumption Output: income and resource services |
C | Input: revenue and resource services Output: commodities and costs |
D | Input: commodities and costs Output: revenue and resource services |
E | Input: income and resource services Output: commodities and consumption |
Question 3 |
| ... | Hours needed for 1 unit | Amount procuded in 24 hours | ||
| Cheese | Jam | Cheese | Jam | |
| Canada | 6 | 2 | 4 | 12 |
| USA | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 |
A | ...neither good and USA has an absolute advantage in Cheese. |
B | ...neither good and USA has an absolute advantage in Jam. |
C | ...Jam and USA has an absolute advantage in Cheese. |
D | ...Cheese and USA has an absolute advantage in Jam. |
E | ....(cannot be answered due to lack of information). |
Question 4 |
A | $1500 |
B | $700 |
C | $350 |
D | $3000 |
Question 5 |
A | human resources |
B | market fluctuations |
C | capital costs |
D | non-renewable resources |
Question 6 |
A | Externality causing the market to shrink during a crisis. |
B | Endogenous variables causing the market demand for beef to drop. |
C | An example of the "invisible hand" in action. |
D | Exogenous variables causing the market demand for beef to drop. |
E | Market failure due to Alberta's monopoly on the beef industry. |
Question 7 |
A | Lower rent with lower quality housing. |
B | Lower rent with higher quality housing. |
C | Higher rent with lower quality housing. |
D | Higher rent with higher quality housing. |
Question 8 |
A | ...increase the usage fees. |
B | ...increase the maintenance budget. |
C | ...decrease the management costs. |
D | ...reduce the quality of pools and facilities. |
Question 9 |
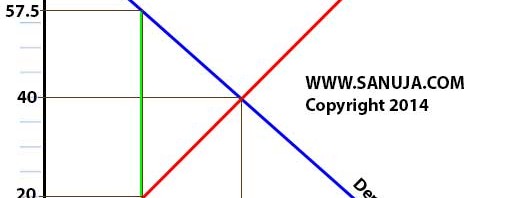
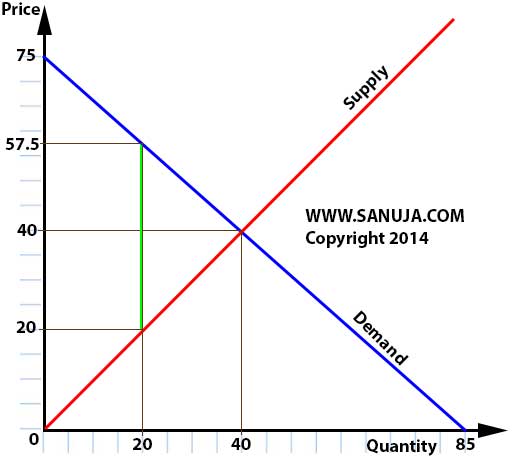
A | It is the area above the Supply curve and under the market price. |
B | It is the area under the Supply curve and above the market price. |
C | It is the area above the Demand curve and under the market price. |
D | It is the area under the Demand curve and above the market price. |
Question 10 |
A | ...shortage of good decrease in demand. |
B | ...shortage of goods and increase in demand. |
C | ...will help the customers. |
D | ...abundance of good and decrease in demand. |
Question 11 |
A | $800 |
B | $1150 |
C | $1600 |
D | $575 |
E | $710 |
Question 12 |
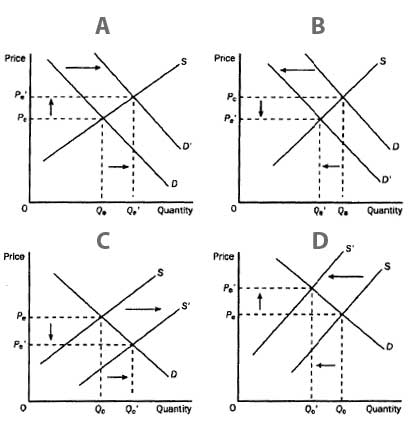
A | C and D |
B | B and C |
C | B |
D | A |
E | A and B |
Question 13 |
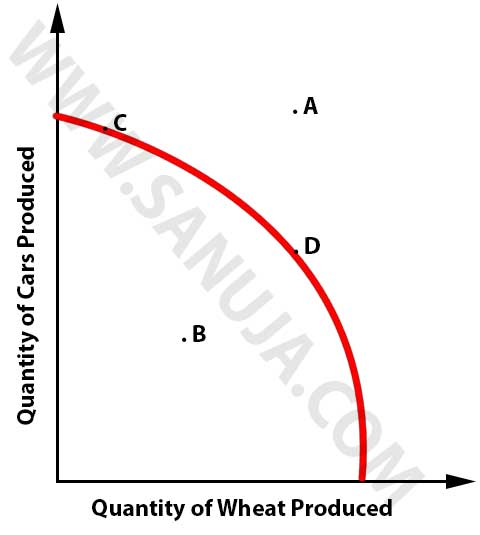
A | It is a mathematical model used for calculating the per unit opportunity cost for a given item. |
B | It is a mathematical model used for determining the inflation rate and its relationship to the unemployment rate. |
C | It is a graphical representation of the maximum output obtain from a given unlimited resource base. |
D | It is a mathematical model used for determining the inflation rate and its relationship to the economic growth. |
E | It is a graphical representation of the relationship between the output of products and the limited resources available to produce the products. |
Question 14 |
A | 0% |
B | 30 - 35% |
C | 15 - 20% |
D | 4 - 6% |
E | 40 - 45% |
Question 15 |
A | the amount of money invested. |
B | the amount of money grained from profits. |
C | the main City in a country which produces the most goods. |
D | the amount of created resources. |
Question 16 |
A | ...creating more competition hence reducing monopolies. |
B | ...helping the producers by generating more revenuer. |
C | ...hurting the consumers that needed the most help. |
D | ...creating a fair and balanced economies. |
Question 17 |
A | ...deadweight loss. |
B | ...a tax revenue loss. |
C | ...elasticity loss. |
D | ...efficiency loss. |
Question 18 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 19 |
A | It will experience scarcity. |
B | It will result in a market failure. |
C | It will result in larger income gaps between the rich and poor. |
D | It will result in slow rate of inflation growth. |
E | It will experience a rapid growth. |
Question 20 |
| Situation | Capital Goods | Consumer Goods |
| A | 0 | 2000 |
| B | 150 | 1750 |
| C | 300 | 1500 |
| D | 550 | 1050 |
| E | 700 | 500 |
| F | 950 | 0 |
A | 150 capital goods |
B | 550 capital goods |
C | 550 consumer goods |
D | 1050 consumer goods |
Question 21 |
| ... | Hours needed for 1 unit | Amount procuded in 24 hours | ||
| Cheese | Jam | Cheese | Jam | |
| Canada | 6 | 2 | 4 | 12 |
| USA | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 |
A | 4/3 Cheese |
B | 3/4 Cheese |
C | 1/3 Cheese |
D | 4 Cheese |
E | 1/3 Cheese |
Question 22 |
A | The price of Orange and Apples will increase. |
B | The price of Orange and Apples will decrease. |
C | The price of Orange will decrease as the Apples market is experiencing a s scarcity. |
D | The price of Orange will increase as the Apples market is experiencing a scarcity. |
E | The inflation rate will increase due to the shortage of Apples. |
Question 23 |
A | Oranges and bananas |
B | Penicillin antibiotics |
C | Automobiles |
D | University education |
Question 24 |
A | most likely a Capitalist one. |
B | a failure. |
C | expanding. |
D | experiencing scarcity. |
E | most likely a Socialist one. |
Question 25 |
A | 67.5% increase |
B | 6.75% increase |
C | 0.675% increase |
D | 4.5% increase |
Question 26 |
| Situation | Capital Goods | Consumer Goods |
| A | 0 | 2000 |
| B | 150 | 1750 |
| C | 300 | 1500 |
| D | 550 | 1050 |
| E | 700 | 500 |
| F | 950 | 0 |
A | 150 Capital Goods |
B | 300 Capital Goods |
C | 300 Consumer Goods |
D | 1/2 Consumer Goods |
Question 27 |
A | The difference between what the buyer's willingness to pay minus the amount the buyer actually pays. |
B | The amount a buyer would gain before the tax being paid. |
C | The value of everything that a producer earns as a result of selling an item. |
D | The amount a seller is paid by the buyer for a given item minus the seller's cost. |
Question 28 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 29 |

A | B |
B | A and B |
C | A |
D | C |
E | C and D |
Question 30 |

A | C and D |
B | A and B |
C | A |
D | D |
E | B |
Question 31 |
A | The lost time and money from a full time job is the opportunity cost of obtaining an education. |
B | The cost of obtaining an education is always beneficial compared to having a low paying full time job. Hint: This may be true in most cases. But this is not applicable in all situations. For example; Bill Gates, Mark Zuckerberg, etc. |
C | The lost time and money from a full time job is the capital cost of obtaining an education. |
D | The time spent on studying and attending classes is the capital cost of obtaining an education. |
E | The time spent on studying and attending classes is the opportunity cost of obtaining an education. |
Question 32 |
A | $20 |
B | $35.5 |
C | $57.5 |
D | $650 |
E | $750 |
Question 33 |
A | ...increased in spending. |
B | ...technological breakthrough in both goods. |
C | ...decrease in demand for one product over the other. |
D | ...technological breakthrough in one of the two goods. |
E | ...decrease in demand for the two products. |
Question 34 |
| ... | Hours needed for 1 unit | Amount procuded in 24 hours | ||
| Cheese | Jam | Cheese | Jam | |
| Canada | 6 | 2 | 4 | 12 |
| USA | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 |
A | ...Jam and USA has a comparative advantage in Cheese. |
B | ...neither and USA has a comparative advantage in Cheese. |
C | ...neither and USA has a comparative advantage in Jam. |
D | ...Cheese and USA has a comparative advantage in Jam. |
Question 35 |
A | ...no correlation. |
B | ...random correlation. |
C | ...negative correlation. |
D | ...neutral correlation. |
E | ...positive correlation. |
Question 36 |
A | Graph A |
B | Graph B |
C | Graph D |
D | Graph C |
Question 37 |
A | ...distorted. |
B | ...artificial. |
C | ...inelastic. |
D | ...elastic. |
Question 38 |
A | private sector regulations. |
B | government intervention. |
C | market power. |
D | individual property rights. |
E | the invisible hand. |
Question 39 |
A | $1500 |
B | $700 |
C | $800 |
D | $350 |
Question 40 |
A | Market economies. |
B | Free economies. |
C | Mixed economies. |
D | Traditional economies. |
E | Command economies. |
Question 41 |
A | It is a situation in which market on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently. |
B | It is a situation in which wrong products and services in the wrong market results in low demand and eventual failure. |
C | It is a situation in which a product or a service failed to generate enough demand to be successful. |
D | It is a situation in which a firm exits a market due to financial failure. |
Question 42 |
A | Controls put in placed by the free market "invisible hand". |
B | Proper Government regulations on the free market economy. |
C | International trade agreements between Canada and other first world nations, such as NAFTA. |
D | Mark Joseph Carney, the Governor of the Bank of Canada. |
Question 43 |
A | ...market projection. |
B | ...economic projection. |
C | ...normative statement. |
D | ...negative statement. |
E | ...positive statement. |
Question 44 |
| ... | Hours needed for 1 unit | Amount procuded in 24 hours | ||
| Cheese | Jam | Cheese | Jam | |
| Canada | 6 | 2 | 4 | 12 |
| USA | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 |
A | 3 Cheese |
B | 4/3 Cheese |
C | 6 Cheese |
D | 1/3 Cheese |
E | 1 Cheese |
Question 45 |
A | The study of overall production and consumption. |
B | The study of household centered economic systems. |
C | The study of behavior of individual agents and markets. |
D | The study of small industries and companies. |
Question 46 |
A | ....increase the equilibrium quantity. |
B | ...increase the demand for ketchup. |
C | ...decrease the demand for hotdog buns. |
D | ...increase the demand for bananas. |
Question 47 |
A | 1.79 |
B | 2.00 |
C | 1.55 |
D | 2.31 |
E | 0.55 |
Question 48 |
A | ...change in price due to change in quantity demanded. |
B | ...change in price due to change in market demand. |
C | ...change in supply due to change in market prices. |
D | ...change in supply due to change in market competition. |
E | ...change in supply due to producer's ability to fulfill the market demand. |
Question 49 |
A | Increase in the number of substitution products. |
B | Decrease in the number of substitution products. |
C | Increase in consumer income. |
D | Decrease in consumer demand. |
E | Decrease in consumer income. |
Question 50 |
A | The number of items produced. |
B | The all inputs needed to produce an item. |
C | The capital needed to produce an item. |
D | The added costs such as taxes and transportation fees. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Ronald Schlenker during Summer 2014.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.