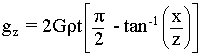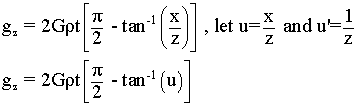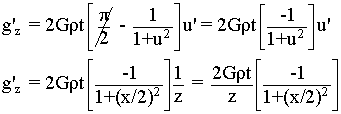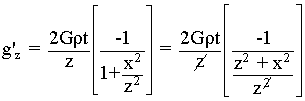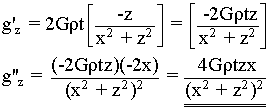Geophysics 559-Geophysical Interpretation
In class midterm will be mostly multiple choice; but there will be also written questions.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Geophysics 559 (GOPH 559) Midterm
Congratulations - you have completed Geophysics 559 (GOPH 559) Midterm.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple tries your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Refraction Law |
B | Fermat's Principle |
C | Principle of Reciprocity |
D | Snell's Law |
Question 2 |
A | 250 - 350 degree Celsius |
B | 50 - 150 degree Celsius |
C | 200 - 350 degree Celsius |
D | 20 - 200 degree Celsius |
E | 0 - 200 degree Celsius |
Question 3 |
A | 4000 m/s |
B | 200 m/s |
C | 6000 m/s |
D | 10 m/s |
E | 1500 m/s |
Question 4 |
A | greater than 10 |
B | greater than 30 |
C | less than 5 |
D | less than 40 |
E | greater than 50 |
Question 5 |
A | It will be a reduced reading by a factor of 2πGρt. |
B | It will be a reduced reading by a factor of 4πGρt. |
C | It will be a increased reading by a factor of 2πGρt. |
D | It will be a increased reading by a factor of 4πGρt. |
Question 6 |
A | Not enough information to answer the question. |
B | low |
C | high |
Question 7 |
A | Direct wave |
B | Refracted arrival |
C | Critically refracted arrival |
D | Guided wave |
E | Transmitted wave |
Question 8 |
A | The head wave travels further than the direct wave, but it has a higher velocity. |
B | The direct wave has a sinusoidal wave form while the head wave does not. |
C | The head wave only travels in the first medium. |
D | The direct wave travels faster than the head wave. |
Question 9 |
A | A body of rock that is capable of containing hydrocarbons due to perfectly impermeable barrier. |
B | A specific area of a specific Formation in which the temperature is between 50 - 150 degree Celsius. |
C | A highly conductive (high effective porosity) stratigraphic or a rock body that is capable of containing hydrocarbon. |
D | A Geologic area that is capable of containing hydrocarbons due to relatively impermeable barrier. |
Question 10 |
A | It depends on the rock type and the formation. |
B | Along any angle between the fractures and natural permeability pathways. |
C | Across or perpendicular to fractures. |
D | Along the plane of the fractures. |
Question 11 |
A | Gravitational and Potential energy |
B | Spring Constant and magnitude of gravity |
C | Gravitational and Magnetic forces |
D | Incident and Refractory rays |
Question 12 |
A | Change in density. |
B | Fractures within the formation. |
C | Change in dip angles. |
D | Change in lithology. |
Question 13 |
A | Gas at the very top of the reservoir followed by oil and water as the depth increases. |
B | A very good reservoir with no significant traps. |
C | A very good reservoir with 100% pure oil and no impurities or other type of fluids. |
D | Oil at the very top of the reservoir followed by gas and water as the depth increases. |
Question 14 |
A | Having a frequency below the Nyquist value. |
B | Increase in seismic frequency. |
C | Decrease in period. |
D | Increasing spatial sampling. |
Question 15 |
A | Deconvolution |
B | Convolution |
C | Normal Moveout |
D | Reciprocity |
Question 16 |
A | ...similarities between seismic events. |
B | ...wavelength (and wavelength only). |
C | ...frequency (and frequency only). |
D | ...time (and time only). |
Question 17 |
A | The location with the lowest elevation and the highest latitude. |
B | The location closest to the equator. |
C | The location with the highest elevation and the lowest latitude. |
D | The location closest to the poles. |
E | The location between the equator and the poles (middle). |
Question 18 |
A | Free Air and Slab effects |
B | Slab and Terrain effects |
C | Latitude and Slab effects |
D | Free Air and Terrain effects |
E | Latitude and Free Air effects |
Question 19 |
A | effect that the distance between a seismic source and a receiver (the offset) has on the arrival time of a reflection. |
B | resolution of layers with extremely small difference in densities. |
C | reduction of seismic resolution as a result of smaller variation in densities of different layers and the depth to the reflection surface. |
D | density contrast between two layers adjacent to each other. |
Question 20 |
A | Shale |
B | Salt |
C | Igneous rocks |
D | Sandstone |
E | Limestone |
Question 21 |
A | 200 degree Celsius |
B | 50 degree Celsius |
C | 150 degree Celsius |
D | 70 degree Celsius |
E | 90 degree Celsius |
Question 22 |
A | Speed or velocity |
B | Vibrations |
C | Density of formations |
D | Depth of reflectors |
Question 23 |
A | A theoretical name given to springs that do not obey its spring constant, k. |
B | A spring that has no length but only diameter. |
C | A theoretical name given to springs that obey its spring constant, k. |
D | A spring that is under maximum tension (maximum stretch). |
E | A theoretical name given to springs that are not being stretch. |
Question 24 |
A | 255.8 hz |
B | 512.2 Hz |
C | 322.9 Hz |
D | 166.7 Hz |
Question 25 |
A | Folds |
B | Foliations |
C | Reefs |
D | Faults |
Question 26 |
A | Porosity |
B | Gravity |
C | Pressure |
D | Buoyancy |
E | Temperature |
Question 27 |
A | Oil |
B | Water |
C | Gas |
D | Cannot be answered with the given information. |
Question 28 |
A | Oil floor |
B | Wet gas preservation limit |
C | Dry gas preservation limit |
D | Oil window |
Question 29 |
A | Gravity survey |
B | Magnetic survey |
C | None of the above |
D | Acoustic impedance |
E | Seismic interference |
Question 30 |
A | 50 years. |
B | 20 years. |
C | 150 years. |
D | 100 years. |
Question 31 |
A | 2D and 3D structural modeling of the area. |
B | Density measurements obtained through seismic data. |
C | Comprehensive understanding of the regional Geology. |
D | Advanced well-logging data obtained through a combination of core samples and seismic data. |
Question 32 |
A | Oil and gas exploration |
B | Hydrological research (drinking water, fresh water) |
C | Identification of basement features |
D | Mineral exploration |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Laurence Lines during Winter 2015.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.
Given the faulted slab equation,