GLGY 202 – Applications of Geoscience
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Final Exam
Geology (GLGY 202-UCAL) Midterm Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 202-UCAL) Midterm Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Area with good subsurface porosity and permeability. |
B | Area with mixture of sand and shale layers with water table cutting across it. |
C | Area with large shale subsurface with water table below the shale layer. |
D | Area with large sand subsurface with water table below the sand layer. |
Question 2 |
A | All of these can be caused by subsidence. |
B | Ground cracks |
C | Flooding |
D | Change in the direction of river flows. |
E | Uplift Hint: Common misconception! |
Question 3 |
A | Radon |
B | Arsenic |
C | Manganese |
D | Fluorine |
E | Iodine |
Question 4 |
A | C type , E type |
B | A type , E type |
C | B type , E type |
D | B type , C type |
E | A type , B type |
Question 5 |
A | Drowning |
B | Radon gas |
C | Natural and man made fires |
D | Drunk driving |
E | Airline crashes |
Question 6 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | Love wave |
C | S-wave |
D | P-wave |
E | Rayleigh wave |
Question 7 |
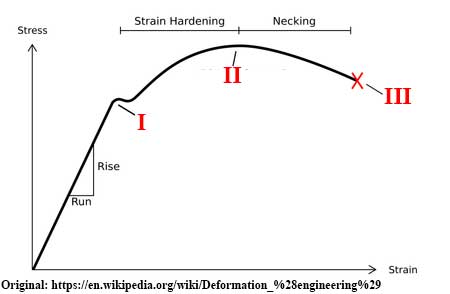
Original: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deformation_%28engineering%29
A | Rupture or fracture strength |
B | Proportional elastic limit or yield strength |
C | Ultimate strength |
D | Rupture point |
Question 8 |
A | It is an event that occurs in all earthquakes where the epicenter is directly on top of the focus. |
B | It occurs when rupture along the fault surface occurs at speeds in excess of the seismic shear wave. |
C | It occurs when two shear waves compliments each other leading to higher frequencies. |
D | It occurs when amplitude attenuates over a very short period of time. |
E | It occurs when the amplitude of shear waves exceeds the velocity of primary wave. |
Question 9 |
A | Earth flows |
B | Debris avalanches |
C | Soil creeps |
D | High angle rockfalls |
E | Mud flows |
Question 10 |

A | B , R and C |
B | B , C and R |
C | B , E and O |
D | A , B and R |
E | A , E and O |
Question 11 |
A | Hydrostatic pressure |
B | Overburden load pressure |
C | Atmospheric pressure |
D | Pore pressure |
E | Static-dynamic pressure |
Question 12 |
A | Areas closer to heat sources such as volcanoes. |
B | Areas with large volume of unconsolidated soils. |
C | Areas with subsurface characterized by alternating strong and weak layers of rocks (eg. schist foliation planes of weakness). |
D | Areas with high seismic activities such as plate boundary regions (eg, Japan). |
E | Areas with large volume of igneous and metamorphic rocks. |
Question 13 |
A | It heavily relies on data obtained through live satellite imagery of tectonic plates. |
B | It was originated as a result of UN conference held in India. |
C | It comes in to service in 2006. |
D | It failed to detect and send out proper warning signals on 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami. |
Question 14 |
A | Temperature and pressure that causes the fracture network. |
B | None of the answers are correct. |
C | Frequency and orientation of fractures. |
D | Depth and overburden pressures that resulted in fractures. |
E | Length and width of fractures. |
Question 15 |
A | Water table must be above the dry zone. |
B | Pore pressure within the dry zone is most likely at zero or close to zero. |
C | Dry zone must be located within a unsaturated zone. |
D | Subsurface geology must be composed of 100% or close to 100% impermeable layers. |
E | Area is not suitable for agricultural development. |
Question 16 |
Driving force = 4.2 x 1010 Nm
Resisting force = 12.6 x 1010 Nm
Shear strength = 2.0 x 106 Nm
A | SF = 6 |
B | SF = 0.33 |
C | SF = 3 |
D | SF = 6 |
E | SF = 2 |
SF = (12.6 x 1010 Nm)/(4.2 x 1010 Nm) =3
Question 17 |
A | A region with highly soluble minerals which could result in landslides and sinkholes. |
B | A zone of contaminant accumulation from a leaching site. |
C | Debris left behind by movement of glaciers. |
D | Exposed surface left behind after a landslide. |
E | Accumulation of rock fragments from a landslide. |
Question 18 |
A | Cesium bearing rocks |
B | Calcium bearing rocks |
C | Gold bearing rocks |
D | Iron and metal oxides bearing rocks |
E | Uranium bearing rocks |
Question 19 |
A | Low temperatures and pressures |
B | High temperatures and pressures |
C | High slope angle or relief |
D | Boulder size sediments |
E | Water runoff |
Question 20 |
A | Interruption of longshore drift result in increased erosion
|
B | Increased in sea level |
C | Subsidence |
D | Increased in tidal current frequency |
Question 21 |
A | The minimum stress required to increase the pressure within the rock above 1000 N. |
B | The ability for a rock to hold a certain weight of materials. |
C | How far above a standard failure envelope, a rock can withstand without failure. |
D | The ability for a rock to withstand shear forces. |
E | The maximum stress a rock can experience before failure. |
Question 22 |
A | Increased in sediment stability in the upstream. |
B | Upstream deposition of sediments while significant downstream erosion. |
C | Increased in river avulsion both upstream and downstream. |
D | Increased in biodiversity in the upstream environments due to higher availability of water. |
Question 23 |
A | Liquefaction caused by earthquakes and other naturally occurring vibrations. |
B | Intrusion of igneous magmas across metamorphic rocks in the subsurface. |
C | Subsurface natural drainage systems. |
D | Chemical weathering of subsurface limestone. |
E | Increased in overburden pressure due to urbanization and building developments. |
Question 24 |
A | high intensity tsunami , low intensity tsunami |
B | coastal tsunami , distal tsunami |
C | Japanese tsunami , Chinese tsunami |
D | low intensity tsunami , high intensity tsunami |
E | local tsunami , distant tsunami |
Question 25 |
A | Rayleigh waves |
B | None of the above answers are correct. |
C | Tsunami |
D | Love waves |
E | S waves |
Question 26 |
A | A branch of science that involved in study of Earth's tectonic plates movement. |
B | None of the listed answers are correct. |
C | The process in which the magnetic reversal occurs. |
D | A type of movement observed in ocean currents during a tsunami. |
E | A situation where odd or uncommon minerals are found within rocks. |
Question 27 |
A | Detailed evaluation of several selected sites. |
B | Finding methods to minimize environmental damage. |
C | Creation of a plan for land-use for the project. |
D | Identification of important environmental issues. |
Question 28 |
A | vibrations per period. |
B | wavelets per minute. |
C | length of signal wavelets. |
D | distance between the peak and trough of a wavelet. |
E | cycles per second. |
Question 29 |
A | Iodine |
B | Manganese |
C | Radon |
D | Fluorine |
E | Arsenic |
Question 30 |
A | Alluvium |
B | Younger silt and mud |
C | Older igneous rocks |
D | Older sedimentary rocks |
E | Older compacted silt and mud |
Question 31 |
A | leaching zone. |
B | low pressure zone. |
C | accumulation zone. |
D | void zone. |
E | vadose zone. |
Question 32 |
A | Cinder cone volcanoes |
B | Composite volcanoes |
C | Dome volcanoes |
D | Shield volcanoes |
E | All of the listed types of volcanoes can have such characteristics. |
Question 33 |
A | B |
B | B and C |
C | O , A and E |
D | C |
E | A and C |
Question 34 |
A | Holding water from a flood indefinitely. |
B | Increasing the volume of water in rivers. |
C | Increasing the penetration of water in the subsurface. |
D | Reducing the storm drainage discharge rate. |
E | Increasing the discharge rate of rivers. |
Question 35 |
A | Body waves |
B | S waves |
C | Rayleigh waves |
D | P waves |
E | Love waves |
Question 36 |
A | Composite volcanoes |
B | Shield volcanoes |
C | Cinder cone volcanoes |
D | Dome volcanoes |
Question 37 |
A | high pressure , negative |
B | saturated , negative |
C | saturated , positive |
D | high pressure , positive |
E | unsaturated , positive |
F | unsaturated , negative |
Question 38 |
A | Strain is force per unit area while stress is the force that result in deformation. |
B | Stress is force per unit area while strain is the deformation resulted from stress. |
C | Stress can be directly calculated using alignment of mineral grains and position of fractures. |
D | Stress can be directly calculated using deformation of rocks. |
E | Strain only occurs in solid mediums while stress occurs in both solids, liquids and gases. |
Question 39 |
A | SF is greater than 100. |
B | SF is equal to 1. |
C | SF is greater than 1. |
D | SF is equal 100. |
E | SF is equal to 0. |
Question 40 |
A | Increase in internal friction angle. |
B | Decrease in soil shear strength |
C | Decrease in grain friction. |
D | Decrease in effective stress |
E | Increase in pore pressure |
Question 41 |
A | Seasonal floods that resulting overprinting of existing low elevation regions of floodplains. |
B | Erosion of the floodplain due to increased in flow velocity close to the outside of the bend. |
C | Sediment deposition due to increased in the flow velocity close to the outside of the bend. |
D | Sediment deposition due to decreased in the flow velocity close to the outside of the bend. |
E | Erosion of the floodplain due to increased in flow velocity on both sides of the bend. |
Question 42 |
A | molds , shape |
B | peds , shape |
C | molds , mineral assemblage |
D | peds , mineral assemblage |
E | subsoils , mineral assemblage |
Question 43 |
A | Strong independent activist who advocated for cheap building materials for India. |
B | There are no other cheaper alternative to asbestos in India or elsewhere. |
C | McGill University study proved that asbestos is safe for consumers. |
D | Pressure from the Indian Government to keep the Canadian mine open. |
E | Political corruption within the Canadian Provincial and Federal Governments. |
Question 44 |
A | If the sample has no porosity due to tight compaction. |
B | If the pore space is completely filled with fluid(s). |
C | If the sample shows no evidence of flow or fluid migration. |
D | If the sample has no pore space due to tight compaction. |
E | If the pore space is completely saturated with gas(s). |
Question 45 |
A | Difference in arrival times between the P wave and S wave at the monitoring center. |
B | Distance between the first geophone and the epicenter of an earthquake. |
C | Time duration intervals between each arrival of seismic wavelets to the monitoring center. |
D | Time duration between major earthquakes near an active zone. |
E | It describes our lack of understanding of seismic events due to complexity of plate tectonics and fault propagation mechanisms. |
Question 46 |
A | Plastics |
B | Metals |
C | Wood |
D | Paper |
E | Glass |
Question 47 |
A | natural seepage of fluids from the subsurface. |
B | human extraction of fluids from the subsurface. |
C | tectonic activities near the San Andreas Fault. |
D | human activities such as building large structures hence increasing the pressure in subsurface and increasing subsidence. |
Question 48 |
A | They have the ability to decrease in volume with change water content. |
B | They are mostly made up of silicate minerals such as quartz and pyroxenes. |
C | They have the ability to either increase or decrease in volume with change water content. |
D | They have larger soil particles than other types of soils. |
E | They have the ability to increase in volume with change water content. |
Question 49 |
A | ammonia |
B | methane |
C | nitrogen |
D | carbon dioxide |
E | water |
Question 50 |

Original: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deformation_%28engineering%29
A | Rupture point |
B | Proportional elastic limit or yield strength |
C | Ultimate strength |
D | Rupture or fracture strength |
Question 51 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | Highly concentrated organic matter such as decomposing or decomposed leaves. |
C | Extensive organic root networks. |
D | Unweathered or unaltered materials. |
E | Iron-bearing components. |
Question 52 |
A | large flood plain. |
B | small flood plain. |
C | wider river channel. |
D | low gradient. |
E | high rate of discharge. |
Question 53 |
A | Pressure is the primary cause of all earthquakes. |
B | Earthquake zones are always accompanied by volcanic activities. |
C | At first stage of earthquake development, the elastic strain increases in rocks. |
D | Earthquakes are caused as a result of significant movement of tectonic plates. |
E | Earthquakes and other tectonic activities are the major driving forces for global warming. |
Question 54 |
A | Common Load test. |
B | Unconfined Comprehensive Strength test. |
C | Unified Conditional Strength test. |
D | Uniform Comprehensive Force test. |
E | Extensional Strength test. |
Question 55 |
A | lava flow |
B | hyaloclastic flow |
C | pyroclastic flow |
D | mud flow |
E | magma flow |
Question 56 |
A | Natural streams are better at controlling flash floods than channelized streams. |
B | Typically natural streams have much higher flow velocities than channelized streams. |
C | Both natural streams and channelized streams tends to produce meanders. |
D | Natural streams have different sediment depositional sequences (different deposits) than channelized streams. |
E | None of the answers listed here are correct. |
Question 57 |
A | If the fault has moved at least 10 cm during the last 5 years. |
B | If the fault has produced significant earthquakes during the last few years. |
C | If a fault has moved at last 10 cm during the last 10 years. |
D | The definition is depend on the geological regulations in a given region. |
E | The the fault has produced some seismic activities during the last 5 years. |
Question 58 |
A | Strike-slip faulting |
B | Reverse faulting |
C | Spreading of Mid Ocean Ridges |
D | Normal faulting |
Question 59 |
A | broad , steeply |
B | broad , gently |
C | narrow , gently |
D | narrow , steeply |
Question 60 |
A | Some earthquake zones produce radon gas as a byproduct of fiction between rocks. |
B | Expansion of rocks and fractures with influx of water in the region just before an earthquake allow radon gas to migrate. |
C | Build up of pressure causes the radon gas to move from the fault surface to other regions. |
D | Change in density of gases in the subsurface due to multiple forces acting in the fault region result in radon flowing to low density zones. |
E | Energy released just before the earthquakes result in expedite decay of uranium. |
Question 61 |
A | is the pressure exerted by liquids such as lakes and rivers on the subsurface. |
B | is the pressure that is a controlled by the contact surface area between grains within sediments. |
C | typically result in negative pore pressure in deeper parts of subsurface. |
D | typically higher in subduction zones. |
E | typically increases with depth. |
Question 62 |
A | Specific assemblage of minerals and rock fragments. |
B | Solid earth materials that can be removed without blasting. |
C | A material that can support growth of plants through allowing roots to penetrate. |
D | Earth materials that has been altered by biological processes. |
E | Earth materials that has been altered by physical processes. |
Question 63 |
A | ductile. |
B | elastic. |
C | plastic. |
D | brittle. |
Question 64 |

Original: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deformation_%28engineering%29
A | Proportional elastic limit or yield strength |
B | Rupture point |
C | Ultimate strength |
D | Rupture or fracture strength |
Question 65 |
A | They are mostly governed by global climatic changes not local weather events. |
B | They exclusively occur in meandering river floodplains. |
C | There has been no record of flash floods in arid regions such as Las Vegas, Nevada. |
D | They are becoming more uncommon occurrence due to global warming. |
E | They are typically associated with upper parts of the drainage basin. |
Question 66 |
A | Reducing the possibility of subsurface springs within the hazardous zones hence reducing the water accumulation in the region. |
B | Increasing the pore pressure within the subsurface hence increasing the friction between potential failure planes and the subsurface. |
C | Reducing the water flow within the subsurface hence decreasing the pore pressure within subsurface that could encourage landslides. |
D | Completely diverting all possible water drainage into the hazardous zones. Hint: It is impossible to completely divert all sources. |
Question 67 |
"No horizon development; many are recent alluvium; synthetic soils are included; are often young soils."
A | Entisols |
B | Aridisols |
C | Vertisols |
D | Ulfisols |
E | Histosols |
Question 68 |
A | Cinder cone volcanoes |
B | Shield volcanoes |
C | None of the listed answers are correct. |
D | Composite volcanoes |
E | Dome volcanoes |
Question 69 |
A | Majority of the shaking of large tall buildings at a significant distance to epicenter is caused by high frequency seismic waves. |
B | P wave travel at a much slower velocity than the S saves. |
C | Seismic frequency attenuation effect is large with the loner distance from the epicenter. |
D | Magnitude of an earthquake at the focus is directly measured by seismic monitoring centers. |
E | Seismic amplitude arrival times become shorter (faster) as you move away from the epicenter. |
Question 70 |
A | ductility increases. |
B | possibility of faulting decreases. |
C | density increases. |
D | brittleness increases. |
E | None of the answers are correct. |
Question 71 |
A | Magma has a higher viscosity and low flow rate than lava. |
B | Lava is produced when the molten solution has at least 40% of water or hydrous minerals. |
C | Molten rock and minerals in subsurface is known as magma while it is on the surface known as lava. |
D | Magma is produced at plate boundaries without volcanic activity while lava is produced at volcanic zones. |
E | Magma solidify at much higher temperatures than lava. |
Question 72 |
A | There is no economic reasons for soil chronosequence, but it is used in research by scientists. |
B | It can be used to determine the porosity and permeability of older layers, which can be used to interpret groundwater drainage patterns. |
C | It can be used to generate groundwater table. |
D | It can be used to evaluate geologic stability and conditions in the past and predict future conditions. |
E | It can be used to determine the current fertility of soils. |
Question 73 |
A | Physical breakdown of subsurface rocks. |
B | Shrinking of salt deposits due to high overburden pressure. |
C | Physical breakdown of compacted sediments. |
D | Chemical weathering of soluble rocks. |
E | Reduction of pressure caused by extraction of fluids from pores. |
Question 74 |
A | Natural environmental problems such as floods |
B | Wealth and power. |
C | Sudden unexpected failures in environmental mitigation programs. |
D | Natural animal activities such as bears in populated neighborhoods. |
E | Political donations. |
Question 75 |
A | 1 in 10 |
B | 1 in 60 |
C | 1 in 5 |
D | 1 in 30 |
E | 1 in 100 |
Question 76 |
A | Magnitude 6 |
B | Magnitude 7 |
C | Magnitude 4 |
D | Magnitude 3 |
E | Magnitude 5 |
Question 77 |
A | Only occurred during the last 10,000 years. |
B | Generate only P type seismic waves. |
C | Sudden vertical movement of ocean waters caused by an underwater seismic event. |
D | Occurs when two earthquakes occurs under water at the same (or close to each other) time. |
E | A natural hazard that is only found in the Asian regions such as Japan and Indonesia. |
Question 78 |
A | lack of understanding of subsurface salt deposits by the mining company. |
B | drainage of the Lake Peigneur into the Jefferson Island through naturally existing fractures. |
C | increased overburden pressures directly on top of the salt mines. |
D | reduced drainage of subsurface fluids such as water and oil. |
E | poor planing of drilling by the oil company. |
Question 79 |
A | Foreshock |
B | Hypocenter |
C | Focus |
D | Scarp |
E | Epicenter |
Question 80 |
A | It could be quartz. |
B | It could be calcite. |
C | Physical appearance of the rock sample is not that of calcite. |
D | This class is so hip and crazy. |
E | The environment which the movie scene took place cannot be producing calcite. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Gerald Osborn and Dr. Glenn Dolphin during Winter 2016 and textbook ISBN-978-0-393-93750-3.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.
