Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm I | Midtrem II
Geology (GLGY 381-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 381-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
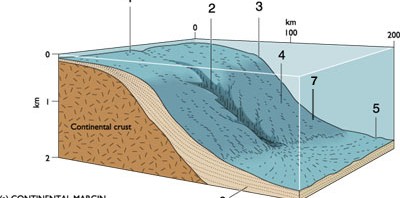
What type of collision occur at the area marked with F? (ID-SSF-39)
A | Rifted Margin Prism |
B | Magmatic Arc |
C | Subduction Complex |
D | Trench |
E | Interarc Basin |
Question 2 |
A | Discharge, subsidence and accommodation are associated with hinterland and subsidence is associated with basin. |
B | Discharge and relief are associated with hinterland and accommodation and slope is associated with basin. |
C | Discharge, relief and subsidence are associated with hinterland and accommodation is associated with basin. |
D | Discharge and relief are associated with hinterland and accommodation and subsidence are associated with basin. |
E | Discharge and subsidence are associated with hinterland and accommodation is associated with basin. |
Question 3 |
A | transgression |
B | forced regression |
C | regression and transgression |
D | regression |
E | regression and forced regression |
Question 4 |
What letter on the following cartoon represent the toplap-downlap sequence? (yes, it is a two different things, so watch out!) (ID-SSF-44)
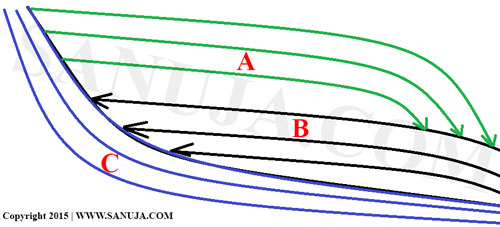
A | A and B |
B | C |
C | B and C |
D | A |
E | A and C |
F | B |
Question 5 |
A | super surge. |
B | super elevation. Hint: READ THE QUESTION CAREFULLY. |
C | torpedo rise. |
D | storm surge. |
Question 6 |
A | counter clockwise direction. (if you take to a bloody British, it will bloody anti-clockwise 🙂 |
B | clockwise direction. |
C | downwards at 90 degrees to the rotational face. |
D | upwards at 90 degrees to the rotational face. |
Question 7 |
A | Rise in relative sea-level and movement of the shoreline seawards. |
B | Fall in relative sea-level and movement of the shoreline landwards. |
C | Fall in relative sea-level and movement of the shoreline seawards. |
D | None of the answers listed here are correct. |
E | Rise in relative sea-level and movement of the shoreline landwards. |
Question 8 |
A | Active spreading ridges would have no impact on either sediment influx or global sea levels because this activity will be balanced through subduction. |
B | Global sea level will be decrease as new oceanic crust is formed due to spreading. |
C | Global sea level will be increase as the new oceanic crust takes up space in basins. |
D | Sediment influx will be significantly increased as continental crust is pushed further upwards resulting greater erosion. |
E | Sediment influx will be significantly decreased as deposited sediments within the accommodation space is used up to produce new oceanic crust. |
Question 9 |
A | Bottomset |
B | Distalset |
C | Foreset |
D | Topset |
Question 10 |
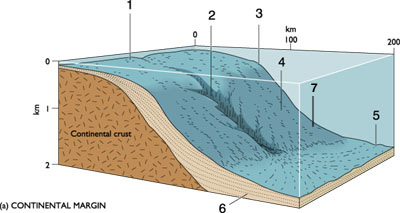
A | 3 |
B | 6 |
C | 4 |
D | 7 |
E | 5 |
Question 11 |

A | 4 |
B | 5 |
C | 3 |
D | 1 |
E | 2 |
Question 12 |
A | continental volcanoes |
B | sea-floor spreading and mid-ocean ridges |
C | subduction and trenches |
D | transform faulting |
E | hot spots |
Question 13 |
A | active margins. |
B | passive margins. |
C | margins with high slope basements. |
D | volcanic regions. |
Question 14 |
A | Rate of chemical weathering |
B | Regression |
C | Transgression |
D | Global tectonics |
E | Forced regression |
Question 15 |
A | False because it can preserve only up to few thousands of years because tidal currents disturb the depositional process. |
B | False because it can only preserve up to about half a million years. |
C | True |
Question 16 |
A | Fan deltas |
B | None of the answers are correct |
C | Tide-dominated deltas |
D | Wave-dominated deltas |
Question 17 |
A | Warm and wet seasons |
B | Lowstand |
C | Highstand |
D | Retrogradation |
Question 18 |
A | It is based on the type of tectonic and basinal setting. |
B | Second-order |
C | First-order |
D | Third-order |
Question 19 |
A | A. Oscillating B. Non-oscillating |
B | A. high B. low |
C | A. low B. high |
D | A. Non-oscillating B. Oscillating |
Question 20 |
A | abyssal plains.. |
B | disconformities. |
C | basins. |
D | paraconformities. |
Question 21 |
A | A sudden increase of deposition in a specific window of geologic time. |
B | A discontinuity in the age of strata due to lack of deposition. |
C | An unexplained nonconformity. |
D | The line between the lateral contact of two sets of widely different strata. |
Question 22 |

A | 1 |
B | 7 |
C | 2 |
D | 4 |
E | 3 |
Question 23 |
A | groups |
B | formations |
C | beds |
D | members |
E | supergroups |
Question 24 |
A | near mid ocean ridges(MOR) |
B | on the basin floor fan. |
C | on the volcanic arc |
D | near paraconformities |
E | near nonconformities |
Question 25 |
A | counter clockwise direction. (if you take to a bloody British, it will bloody anti-clockwise 🙂 |
B | upwards at 90 degrees to the rotational face. |
C | downwards at 90 degrees to the rotational face. |
D | clockwise direction. |
Question 26 |
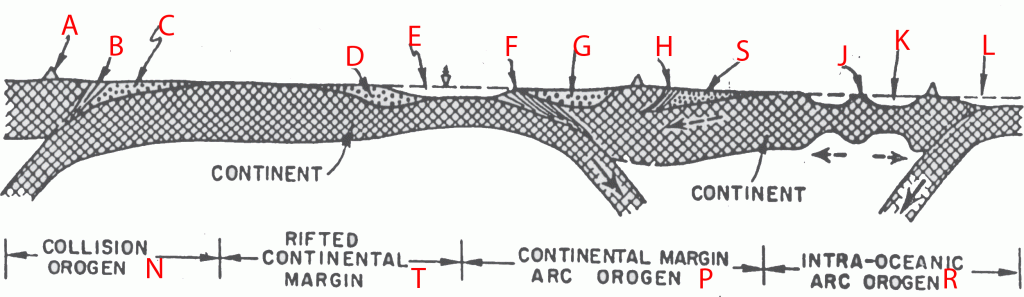
In which area would you expect to find the passive margin (choose from red letters)? (ID-SSF-41)

A | P |
B | R |
C | H |
D | T |
E | N |
Question 27 |
A | more granitic |
B | more basaltic |
C | more denser |
D | more mafic |
Question 28 |
A | toplap |
B | erosional surface |
C | onlap |
D | downlap |
Question 29 |
A | coral reef zone. |
B | active zone. |
C | passive zone. |
D | photic zone. |
Question 30 |
A | highstand |
B | rise in sea level |
C | sudden decrease in regional sed load. |
D | lowstand |
E | sudden increase in regional sed load. |
Question 31 |
A | Coastal plain deposits |
B | Muddy deposits |
C | Clastic deposits |
D | Sandy deposits |
Question 32 |
A | near the shore line |
B | near the mid ocean ridge |
C | inner the inner shelf |
D | near the wave base |
Question 33 |
A | Disconformity |
B | Angular unconformity |
C | Paraconformity |
D | Hiatus |
E | Nonconformity |
Question 34 |
A | Global tectonics |
B | Relative base level |
C | Rate of chemical weathering |
D | Rifting mechanisms |
E | Eustasy |
Question 35 |
A | Increase in relative sea level and increased in sediment input at the same time. |
B | Increase in relative sea level and increase in subsidence the same time. |
C | Decrease in relative sea level and uplift occurring at the same time. |
D | Decrease in relative sea level and increased in sediment input at the same time. |
E | Increase in relative sea level and uplift occurring at the same time. |
Question 36 |
A | Dominant sandy deposits at the base |
B | Coarsening upward |
C | Fining upward |
D | Dominant muddy deposits in distal regions |
Question 37 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 38 |
A | Progradational |
B | Aggradational |
C | Transgressional |
D | Retogradational |
Question 39 |
A | Extremely low subsidence |
B | Sand dominated deposits |
C | Mud and silt dominated deposits |
D | Gravel dominated deposits |
E | Extremely high subsidence |
Question 40 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 41 |
A | A. Rising inflection point (RIP)
B. highstand |
B | A. Lowstand
B. falling inflection point (FIP) |
C | A. Highstand
B. rising inflection point (RIP) |
D | A. Highstand
B. falling inflection point (FIP) |
E | A. Highstand
B. rising inflection point (RIP) |
Question 42 |
A | Progradation |
B | Regression Hint: Close, but this is not the right term! |
C | Increase in accommodation space |
D | Transgression |
E | Rising sea level |
Question 43 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 44 |
A | When analyzing fossils and chemical composition (carbon) to date formations. |
B | When analyzing data collected from a large region. |
C | When dealing with areas that is difficult to access. |
D | When analyzing data collected in a small region. |
Question 45 |
A | Long term variations in global temperatures that is caused by natural cycles of the Sun. |
B | Long term variations in the rate of sea floor spreading and subduction which result in global sea-level changes. |
C | Long term variation in atmospheric conditions which results in global changes in sedimentary processes. |
D | Long term variations in the orbit of the Earth which result in changes in climate. |
E | Long term variations in the volume of glaciers which result in global sea level changes. |
Question 46 |
A | The first term describes the landwards movement of the shoreline and the second term describes the seawards movement of the shoreline. |
B | The first term is used in depositional descriptions and the second term is used in fluvial descriptions. |
C | The first term describes the seawards movement of the shoreline and the second term describes the landwards movement of the shoreline. |
D | They are the same; therefore the question is wrong. |
Question 47 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 48 |
A | the basin. |
B | oceanic shelf. |
C | continental shelf. |
D | continental boundary. |
E | the mid ocean ridge. |
Question 49 |
A | I. fining upwards II. fining upwards III. fining upwards |
B | I. fining upwards II. coarsening upwards III. coarsening upwards |
C | I. fining upwards II. coarsening upwards III. fining upwards |
D | I. fining upwards II. fining upwards III. coarsening upwards |
E | I. coarsening upwards II. fining upwards III. fining upwards |
Question 50 |
A | backbulge |
B | wedgetop |
C | foredeep |
D | suckdeep |
E | forebulge |
Question 51 |
A | Velocity of rivers |
B | Sediment load |
C | Tectonics such as subsidence and uplift |
D | None of the answers are correct. |
E | Climate and weather |
Question 52 |
What type of collision can occur at the area marked with N? (ID-SSF-38)

A | Continent-Ocean Collision |
B | Ocean-Ocean Collision |
C | Passive Margin Collision |
D | Active Margin Collision |
E | Continent-Continent Collision |
Question 53 |
A | Flase |
B | True |
Question 54 |

A | 3 |
B | 2 |
C | 1 |
D | 5 |
E | 4 |
Question 55 |
A | They only occurred in the per-Cambrian and no longer observed in modern day environments. |
B | They drive the forces needed for delta formation. |
C | They carry sediments on top of sea waters for a long distances out into the ocean before settling to the bottom. |
D | They often result in turbidites deposition. |
E | They are typically associated with low density sediment loads. |
Question 56 |
A | Sediments will be mostly filled in the continental shelf with very little to no sed deposition on the basin. |
B | Sediments will be mostly filled in the basin bypassing the deposition process on the continental shelf. |
C | Accommodation space will be moved towards the shoreline. |
D | Accommodation space always will be deceased significantly. |
Question 57 |
The Magmatic Arc is represented by... (choose from red letters) (ID-SSF-42)

A | B |
B | A |
C | C |
D | D |
E | E |
Question 58 |
A | paraconformity |
B | a hiatus. |
C | a conformity. |
D | angular unconformity. |
E | disconformity |
Question 59 |
A | backbuldge |
B | forebulge |
C | basin |
D | channel |
E | foreland |
F | foredeep |
G | wedgetop |
Question 60 |
A | At first terrigenous clastic supply will rapidly increase the carbonate productivity, but in the long run it will create chemical barriers reducing carbonate productivity. |
B | Increased terrigenous clastic supply reduces carbonate productivity. |
C | At first it will rapidly decrease the carbonate productivity, but in the long run it will increase the carbonate productivity as terrigenous clastic supply will introduce essential chemical components to the system. |
D | There is no effect because the carbonate productivity is independent of terrigenous clastic supply. |
Question 61 |
If you were to indicate the boundary between the Indian-Asian crust, where would it be (choose from red letters)? (ID-SSF-40)

A | D |
B | F |
C | L |
D | A |
E | B |
Question 62 |
A | No |
B | Yes |
Question 63 |
A | The pressure on both sides of the continental or oceanic boundaries must be at equilibrium. |
B | The forces within the crust should exceed the forced applied on the crust by the load resulting flexure. |
C | I have no clue what the hell you are talking about. I hate applied principles of geology. Hint: Since you have pick this one, I suggest that you click and open the renaming choices just to read what it was.....? |
D | The force of the load due to gravity must be large enough to overcome the forces within the crust resulting flexure. |
Question 64 |
A | retogradation |
B | progradation |
C | aggradation |
D | transgredation |
Question 65 |
A | analytical |
B | theoretical |
C | practical |
D | temporal |
E | spatial |
Question 66 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 67 |
A | A. decreases B. decreases |
B | A. increases B. increases |
C | A. decreases B. increases |
D | A. increases B. decreases |
Question 68 |
A | foredeep |
B | backbulge |
C | forebulge |
D | wedgetop |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Melissa Giovanni during Fall 2012.
FAQ | Report an Error