Economics 203 is the Principles Of Macroeconomics class. Depending on the Professor, the exams format may or may not be multiple choice. This quiz only covers materials from Chapters 7 and 8 from 6th Canadian Edition of Principles of Macroeconomics by Mankiw, Kneebone and McKenzie. You may try Midterm I and Final exams for questions from other chapters.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midtrem I | Final Exam
Economics (ECON 203-UCAL) Midterm Exam II
Congratulations - you have completed Economics (ECON 203-UCAL) Midterm Exam II.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple tries your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Bonds from a Provincial Government in Canada |
B | Bonds from a major established company such as Apple Inc or Google Inc. |
C | Bonds from the Federal Government of India |
D | Bonds from the Federal Government of Canada |
Question 2 |
A | the supply for lonable funds would be lower than the demand for lonable funds. |
B | the equilibrium interest rate would increase. |
C | the equilibrium conditions would not change. |
D | the equilibrium of lonable funds would be lower than that of the supply of lonable funds. |
Question 3 |
A | decrease , raises , raises |
B | decrease , reduces , reduces |
C | increase , raises , reduces |
D | decrease , reduces , raises |
E | increase , raises , raises |
F | increase , reduces , raises |
G | decrease , raises , reduces |
Question 4 |
A | Net exports |
B | Productivity |
C | Interest rates |
D | GDP |
E | Domestic markets |
Question 5 |
A | supply and demand. |
B | face value of the particular bond. |
C | duration of the bond. |
D | number of coupons in the bond certificate. |
E | principle of of the bond. |
Question 6 |
A | Public market policies |
B | Global market policies |
C | Inward-oriented policies |
D | Outward-oriented policies |
Question 7 |
A | 2.5% |
B | 100% |
C | 10% |
D | 5% |
Question 8 |
I. Buying a house with a mortgage to be paid off later.
II. Buying large volume of dry noodles to be sold at a higher price later.
III. Buying stock from Volkswagen AG to be sold at a higher price later.
IV. Buying government bonds to earn interest and face value later.
A | IV only |
B | III only |
C | All of the choices falls under equity finance. |
D | III and IV only |
E | II and III only |
F | I and IV only |
Question 9 |
A | total income in an economy after firms pay for capital goods. |
B | total income in an economy that remains after paying for consumption and government purchases. |
C | differences between government spending and its tax revenue. |
D | total amount of money that is injected into the financial markets. |
E | total amount of money that deposited in the bond market. |
Question 10 |
A | Malthus effect. |
B | catch up effect. |
C | diminishing returns. |
D | constant return to scale. |
E | improvement of productivity. |
Question 11 |
A | Rate of change in nominal GDP per capita. |
B | Rate of change in real GDP per capita. |
C | Rate of change in real GDP |
D | Rate of change in inflation per capita. |
E | Rate of change in nominal GDP. |
F | Rate of change in inflation. |
Question 12 |
GDP = $9.5 trillion
Consumption spending = $4.0 trillion
Taxes = $6.4 trillion
Government transfers = $3.6 trillion
Government purchases = $4.0 trillion
A | $2.8 trillion |
B | $5.5 trillion |
C | $3.6 trillion |
D | $1.5 trillion |
E | $2.7 trillion |
Investments = GDP - Consumption - Govt Spending
I = $9.5 - $4 - $4 = $1.5 trillion
Question 13 |
A | It is the total accumulation of debt for a country since its it has been established. |
B | It is the difference between the amount of money printed by the central bank and the total national resources. |
C | It is the total amount of debt accumulated by a government between elections. For example, every five years. |
D | It is the difference between tax collected and the government spending during a given year or a fixed period. |
E | It is the amount of money and other funds owe by a government to international lenders across the world. |
Question 14 |
A | Large physical capital |
B | Large human capital |
C | Nonrenewable natural resources |
D | Renewable natural resources |
Question 15 |
A | decrease in GDP. |
B | advancement in technology. |
C | decrease in long term economic growth. |
D | decrease in productivity. |
Question 16 |
A | By dividing the entire equation by the quantity of labour, L. |
B | By dividing the entire equation by the quantity of physical capital, K. |
C | By dividing the entire equation by the quantity of natural resources, N. |
D | By dividing the entire equation by the quantity of human capital, H. |
Question 17 |
A | educating the workers. |
B | decreasing the minimum legal age of work hence increasing the available population for work. |
C | increasing the immigration into a country. |
D | increasing (hiring) the number of workers per job. |
E | decrease taxes imposed on individual workers. |
Question 18 |
A | A measure of goods and services available for consumers within a given economy. |
B | A measure of net output of domestically produced goods. |
C | The ability of a country to produce goods at the lowest cost. |
D | A measure of goods and services produced for each hour of a worker's time. |
E | A measure of goods and services produced per person in a given country or population. |
Question 19 |
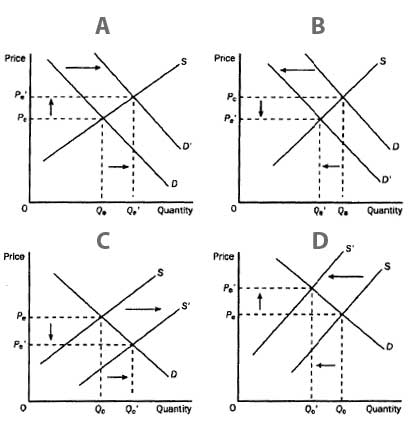
A | Graph D |
B | Graph A |
C | Graph B |
D | Graph C |
Question 20 |
A | Graph B |
B | Graph D |
C | Graph C |
D | None of the graphs depict the correct answer. |
E | Graph A |
Question 21 |
A | A multinational investment in a country where it is operated by the domestic residents. |
B | An investment that is financed with foreign money but operated by domestic residents. |
C | A capital investment made by individuals using personal wealth in a different country that their own. |
D | A capital investment that is owned and operated by a foreign entity. |
E | An investment made by a country using tax revenue in another country to boost federal reserves. |
Question 22 |
A | Payments made for the Members of the Parliament for their official work. |
B | Payments for companies who completed a project for the government. |
C | Payment of Employment Insurance to people who lost their jobs. |
D | Purchase of military equipment for national armed forces. |
E | Government salaries paid to individuals. |
Question 23 |
A | Return to normal |
B | Economies of scale |
C | Diminishing returns |
D | Catch-up effect |
Question 24 |
A | ~ $100 |
B | ~ $300 |
C | ~ $140 |
D | ~ $120 |
Question 25 |
A | Government spending is higher than the tax revenue. |
B | Increased in market for loanable funds. |
C | Higher productivity level. |
D | Increased in government investments. Hint: If the government investments are balanced by the tax intake, it will not lead to a deficit. |
Question 26 |
GDP = $9.5 trillion
Consumption spending = $4.0 trillion
Taxes = $6.4 trillion
Government transfers = $3.6 trillion
Government purchases = $4.0 trillion
A | 0.6 trillion dollars |
B | 5.5 trillion dollars |
C | 1.9 trillion dollars |
D | 0.4 trillion dollars |
E | -1.2 trillion dollars |
Public savings = $6.4 - $3.6 - $4.0 = -$1.2 trillion
Question 27 |
A | Money saved by households after taxes and consumption. |
B | Investments made by private companies for future gains. |
C | Savings made by private financial institutions such as banks. |
D | Savings made by private companies through profits. |
Question 28 |
A | tax collected by the government is greater then that of government spending. |
B | tax collected by the government is equal to that of government spending. |
C | the supply of the available credits are greater than the demand for investments. |
D | tax collected by the government is lower than that of government spending. |
E | the supply of the available credits are lower than the demand for investments. |
Question 29 |
A | 5 years |
B | ~ 11.7 years |
C | 30 years |
D | ~ 4.3 years |
E | 6 years |
F | ~ 2.3 years |
70 / 6 = 11.6660... years
Question 30 |
A | Nominal GDP |
B | Real GDP |
C | Inflation rate |
D | Productivity |
E | Population growth |
Question 31 |
A | Discourage consumers from purchasing products made outside of Canada. |
B | Engage in military wars against countries with high manufacturing output such as China. |
C | Increase the printing of monetary funds (money) using government bonds as collateral to increase investments in manufacturing. |
D | Encourage investments in technology and human capital. |
E | Increase the exploitation of natural resources. |
Question 32 |
A | There would be no change in the amount of lonable funds borrowed. |
B | There would be a reduction in the amount of lonable funds borrowed. |
C | There would be an increase in the amount of lonable funds borrowed. |
D | The change in lonable funds borrowed would be ambiguous. |
Question 33 |
A | ~ $80 |
B | ~ $120 |
C | ~ $100 |
D | ~ $90 |
present value = $110/(1.10)^1 = $100
Question 34 |
A | The end of a Government of Canada GIC bond period, you will collect only the interest of the face value. |
B | Net exports do not include products exported or imported under free trade agreements such as NAFTA. |
C | The primary purpose of a banking system is the distribution of wealth through loans/mortgages. |
D | Publicly traded companies are always more stable than private organizations. |
E | Mutual funds companies buy stocks and bonds to maintain their portfolio. |
Question 35 |
A | The country must be experiencing a higher than normal inflation. |
B | The country must be a developing or poor nation with a low GDP. |
C | The government must be running a deficit budget. |
D | The market of this particular country must be highly regulated. |
E | The manufacturing and services (quantity of output) must be negative. |
Question 36 |
A | $1854 million |
B | $1080 million |
C | $1025 million |
D | $1250 million |
E | $1050 million |
GDP_2040 = 1000 (1+0.025)^25 = $1854 million
Question 37 |
A | regulated fixed government rate. |
B | remaining funds according to interest rates. |
C | market price. |
D | face value. |
Question 38 |
A | Gergory Mankiw |
B | Thomas Malthus |
C | David Thompson |
D | Karl Marx |
Question 39 |
A | Increase in price and decrease in interest rate. |
B | Upward shift in the demand curve. |
C | Increase in interest rate. |
D | Decrease in price and increase in interest rate. |
Question 40 |
A | the quantity of output will be increased by six times the original amount. |
B | the state of technology will be increased by at least triple the original amount. |
C | the quantity of output will be increased by more than triple the original amount. |
D | the quantity of physical capital doubles. |
E | the quantity of output will be increased by more than double but less than triple the original amount. |
Question 41 |
A | Erica |
B | Steven |
C | Sanuja |
D | Lauren |
E | Manuja |
Sanuja = 20/5 = 4 wings/hr
Manuja = 30/6 = 5 wings/hr
Steven = 60/20 = 3 wings/hr
Erica = 18/8 = 1.5 wings/hr
Lauren = 55/20 = 2.75 wings/hr
Therefore, Manuja has the highest productivity.
Question 42 |
GDP = $9.5 trillion
Consumption spending = $4.0 trillion
Taxes = $6.4 trillion
Government transfers = $3.6 trillion
Government purchases = $4.0 trillion
A | $6.4 trillion |
B | $2.4 trillion |
C | $3.1 trillion |
D | $3.6 trillion |
E | $2.8 trillion |
Net taxes = $6.4 - $3.6 = $2.8 trillion
Question 43 |
A | Reduce interest rates across all levels of funds. |
B | Increase government spending on small scale projects but at large volumes. |
C | Encourage Canadians to invest outside of the country. |
D | Increase tax on individuals and on industry. |
Question 44 |
A | Investments |
B | Funds collected through interest |
C | Government funds |
D | Central banks |
Question 45 |
A | Decrease in access to higher education among poor populations. |
B | Politicians and policymakers in charge have no or little knowledge and skills in managing the economy. |
C | Emergence of a population with unsuitable educational and skills levels due to improper planing. For example, large enrollment in petroleum industry education when that country has no petroleum natural resources. |
D | Increase in number of people in the workforce while decrease in the quality of education among them. |
E | Emigration of highly educated workers to first world countries. |
Question 46 |
A | A decrease in demand for loanable funds. |
B | A decrease in supply of loanable funds. |
C | An increase in demand for loanable funds and a decrease in supply of loanable funds. |
D | None of the answers are correct. |
E | An increase in demand for loanable funds. |
Question 47 |
A | the quantity of output will be tripled. |
B | the quantity of output will be increased but less than that of human capital increase. |
C | the state of technology will also be tripled. |
D | the quantity of output will be increased more than that of human capital increase. |
E | the quantity of all other variables will be increased but less than that of human capital. |
F | the quantity of all other variables be will increased more than that of human capital. |
Question 48 |
A | Technological knowledge is not a form of physical capital. |
B | Physical capital is the equipment and structures used to produce goods and services. |
C | For maximum productivity, the physical capital should satisfy the demands of the human capital. |
D | Production output of a company cannot be used as physical capital. |
E | Having right tool for the right job, in other word, right physical capital, will drastically increase productivity. |
Question 49 |
A | It is a system fully controlled by the government which keeps the inflation in control. |
B | It is a system in which people who wants to save can supply funds for people who wants to borrow money. |
C | It is a marketplace for companies to exchange their assets. |
D | It is a marketplace for international traders can meet national traders. |
Question 50 |
A | None of the above graphs are correct. |
B | Graph C |
C | Graph D |
D | Graph A |
E | Graph B |
Question 51 |
A | quantity of labour doubles. |
B | quantity of natural resources doubles. |
C | technology for production doubles. |
D | quantity of human capital doubles. |
E | quantity of physical capital doubles. |
Question 52 |
A | Country B with a very low GDP with a rapid economic growth. |
B | Country D with a very low GDP with a slow economic growth. |
C | Country C with a very high GDP with a slow economic growth. |
D | Country E with a very low GDP and a very high emigration of highly educated workers. |
E | Country A with a very high GDP with a rapid economic growth. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Peter Tracey during Fall 2015 and textbook ISBN-978-0-17-653085-3.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.