Economics 203 is the Principles Of Macroeconomics class. Depending on the Professor, the exams format may or may not be multiple choice. This quiz only covers materials from Chapters 9, 10, 11, 14, 15 and 16 from 6th Canadian Edition of Principles of Macroeconomics by Mankiw, Kneebone and McKenzie. You may try Midterm I and Final exams for questions from other chapters.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midtrem I | Midtrem II
Economics (ECON 203-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Economics (ECON 203-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple tries your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | A decrease in the price level. |
B | None of the answers are correct. |
C | A decrease in the capital stock. |
D | A decrease in natural resources. |
E | A decrease in the expected price level. |
Question 2 |
A | Individuals who earn high incomes |
B | Landlords who own apartments in cities with rent controls |
C | Individuals who have borrowed money at fixed interest rates. |
D | Individuals who have fixed retirement incomes |
E | Banks that have loaned all excess reserves at a fixed interest rate. |
Question 3 |
A | Nominal exchange rate |
B | Output or real GDP |
C | Real exchange rate |
D | Domestic price level |
Question 4 |
| Country | Currency | Currency per Canadian $ | Canadian Price Index | Currency Price Index |
| Bolivia | Boliviano | 5.00 | 100 | 500 |
| Japan | Yen | 100.00 | 100 | 20,000 |
| Morocco | Dirham | 10.00 | 100 | 2000 |
| Thailand | Baht | 30.00 | 100 | 2500 |
| Australian | Dollar | 2.00 | 100 | 350 |
A | Bolivia |
B | Japan |
C | Japan, Morocco and Thailand |
D | Thailand and Australia |
E | Bolivia and Morocco |
Question 5 |
A | Increase in money supply. |
B | Increase in unemployment. |
C | Contractionary monetary environment. |
D | Increase in public confidence in the economy. |
Question 6 |
A | Government prints more money to generate revenue. |
B | Government restrict the sales of both public and private bonds. |
C | Government increase the reserve ratio for all banks. |
D | Government deregulates the free market. |
E | Government regulates the free market. |
Question 7 |
A | all the people who are currently employed in full time jobs. |
B | all the people that are currently employed. |
C | everyone over the age of 18 in Canada. Hint: In Canada people as young as 14 years old can work. |
D | all the people who are legally allow to work. |
Question 8 |
A | Nominal GDP |
B | Real GDP |
C | Price level |
D | Velocity of money |
Question 9 |
A | It deals with sort run tradeoffs between inflation and unemplymemt. |
B | It deals with long run tradeoffs between inflation and unemplymet. |
C | It deals with sort run tradeoffs between government spending and tax increases. |
D | It deals with long run tradeoffs between government spending and tax increases. |
Question 10 |
A | The aggregate demand curve would move to the left. |
B | The aggregate demand curve would move to the right. |
C | The aggregate demand (AD) curve would not shift, but we would move up along the AD curve. |
D | The aggregate demand (AD) curve would not shift, but we would move down along the AD curve. |
E | The outcome is ambiguous. |
Question 11 |
A | Decrase in government spending and increase in tax rates. |
B | Increase in government spending and increase in tax rate. |
C | Increase in government spending and decrease in tax rate. |
D | Decrease in government spending and decrease in tax rate. |
Question 12 |
A | Workers are most likely to postpone their retirement hence increasing the number of experienced workers. |
B | Workers are least likely to leave the company in the long run hence reducing costs associated with restaffing. |
C | Higher wages will allow the company to be competitive in the open market operations by increasing the profit marking through price adjustments. |
D | Higher the wage, lower will be the cost of obtaining raw materials. |
E | Consumers are most likely to buy goods and use services from companies that offer higher wages. |
Question 13 |
A | Facilitate financial activities of large corporations. |
B | Act as a commercial bank for financial intermediaries. |
C | Manage funds for the federal government. |
D | Issue currency for circulation. |
E | Govern the monitory policies of the country. |
Question 14 |
A | There is no relationship between the nominal interest rate and inflation. |
B | Increasing inflation would lead to decrease in nominal interest rate. |
C | Increasing inflation would lead to increase in nominal interest rate. |
D | Increase in 1% point of inflation would result in increase in 2% point in nominal interest rate. |
E | Increase in 1% point of inflation would result in decrease in 2% point in nominal interest rate. |
Question 15 |
A | Liquidity Effect |
B | Short Run Economics Principle |
C | Principle of Economic Relativity |
D | Crowding Out Effect |
E | Inflation Principle |
F | Okun's Law |
Question 16 |
A | Shift in aggregate demand curve to the right, increased spending and decrease in interest rate. |
B | None of the the answers are correct. |
C | Shift in aggregate demand curve to the right, increased spending and increase in interest rate. |
D | Shift in aggregate demand curve to the left, increased spending and increase in interest rate. |
E | Shift in aggregate demand curve to the left, increased spending and decrease in interest rate. |
Question 17 |
A | credits. |
B | currency. |
C | fiat money. |
D | tender. |
E | bater. |
Question 18 |
Total population = 44 million
Population under 18 = 8 million
Non-residents (visitors) not counted in total population = 4 million
A | 5 million |
B | 36 million |
C | 40 million |
D | Not enough information is provided to answer this question. |
E | 44 million |
Question 19 |
A | global influence. |
B | global input. |
C | global economy. |
D | trade balance. |
E | balanced trade. |
Question 20 |
a) _______ aggregate supply curve
b) _______ aggregate demand curve.
A | have no effect on , shift |
B | None of the listed answers are correct. |
C | have no effect on , have no effect on |
D | shift , shift |
E | shift , have no effect on |
Question 21 |
| Country | Currency | Currency per Canadian $ | Canadian Price Index | Currency Price Index |
| Bolivia | Boliviano | 5.00 | 100 | 500 |
| Japan | Yen | 100.00 | 100 | 20,000 |
| Morocco | Dirham | 10.00 | 100 | 2000 |
| Thailand | Baht | 30.00 | 100 | 2500 |
| Australian | Dollar | 2.00 | 100 | 350 |
A | Japanese Yen |
B | Japanese Yen, Moroccan Dirham and Australian Dollar |
C | Thai Baht |
D | Moroccan Dirham |
E | Australian Dollar and Japanese Yen |
F | Bolivian Boliviano |
Question 22 |
A | Government producing coins with lower amounts of precious metals during a recession. |
B | Clipping of money by the population that uses it. |
C | Replacement of one currency by a lower valued currency. |
D | Unintentional wear off of coins. |
E | Acquisition of less goods at a higher price level. |
Question 23 |
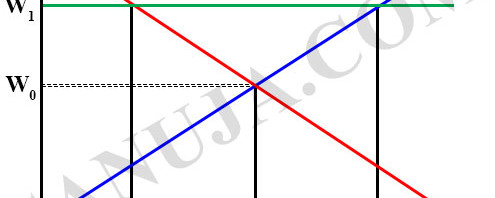
A | W1 , L0 |
B | W0 , L1 |
C | W1 , L2 |
D | W0 , L0 |
E | W1 , L1 |
Question 24 |
A | It is depend on the adult population. |
B | The unemployment rate cannot be determined with the given information. |
C | 15% because labor force must add up to 100%. |
D | 42.5% or half of employment rate. |
Question 25 |
A | prices and quantity demand. |
B | income and consumption. |
C | inflation & unemployment. |
D | interest rates and borrowing. |
E | wage rate and unemployment. |
Question 26 |
A | When the price levels in Canada is lower than rest of the world. |
B | During periods of appreciation in Canadian dollar. |
C | When the purchasing power parity is at the equilibrium. |
D | During an inflation in the Canadian market. |
Question 27 |
A | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would depreciate. |
B | Increase in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would appreciate. |
C | Increase in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would depreciate. |
D | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and no ambiguous change to the Canadian dollar. |
E | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would appreciate. |
Question 28 |
A | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would depreciate. |
B | Increase in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would depreciate. |
C | Increase in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would appreciate. |
D | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and no ambiguous change to the Canadian dollar. |
E | Decrease in nominal exchange rate and the Canadian dollar would appreciate. |
Question 29 |
A | revalued. |
B | appreciated. |
C | depreciated. |
D | devalued. |
Question 30 |
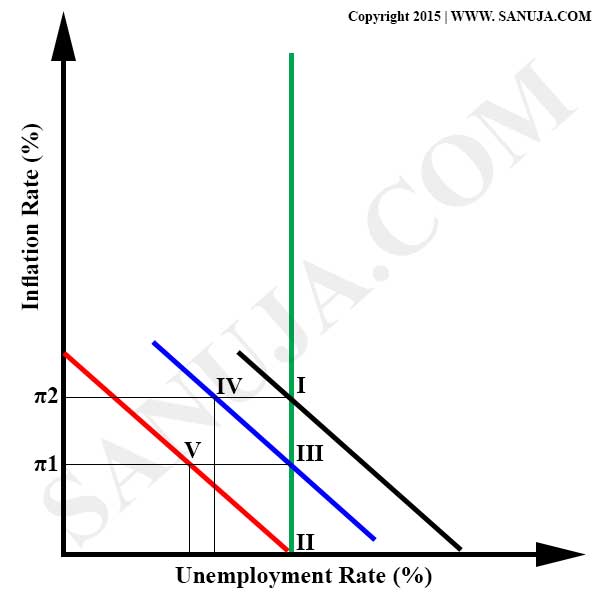
A | Long run Phillip equilibrium. |
B | Natural rate of unemployment at equilibrium. |
C | Short run inflation rate. |
D | Expected inflation under expansionary monitory policy. |
Question 31 |
A | increase by $50 million and money supply decreases by $200 million. |
B | increase by $50 million and money supply decreases by $300 million. |
C | decrease by $50 million and money supply decreases by $800 million. |
D | decrease by $50 million and money supply decreases by $200 million. |
E | increase by $50 million and money supply decreases by $800 million. |
Question 32 |
A | They are inversely related to each other. |
B | They are directly related to each other. |
C | The interest rate changes at a rate of as twice as much as the money demanded. |
D | The money demanded changes at a rate of as twice as much as the interest rate. |
Question 33 |
A | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation increases. |
B | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
C | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation decreases. |
D | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
E | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation decreases. |
F | the unemployment rate is unaffected and the labor force participation increases. |
Question 34 |
A | increase and aggregate demand curve will not shift. |
B | decrease and aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. |
C | decrease and aggregate demand curve will not shift. |
D | increase and aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. |
E | increase and aggregate demand curve will shift to the left. |
Question 35 |

A | Open market operations of selling bonds. |
B | Lower the bank rate. |
C | Lower the reserve ratio. |
D | Increase the money supply. |
Question 36 |
A | $20,000 |
B | $3000 |
C | $10,000 |
D | $5000 |
E | $4500 |
Question 37 |
A | Increase in velocity of money |
B | Increase in inflation rate |
C | Decrease in velocity of money |
D | Decrease in price |
Question 38 |
A | 70 |
B | 30 |
C | 5 |
D | 56 |
Note 50 loonies = $50; suppose it is 50 ten dollar bills, then you must multiply 50 x 10 = $500 to obtain the value for M. M variable is the monitory value of the money itself not how many coins/notes in circulation.
Question 39 |
A | Decrease the minimum wage. |
B | Increase the minimum wage. |
C | Increase funding for post secondary education. |
D | Implement an expansionary fiscal policy. |
Question 40 |
A | A saving account with investments to supply the demands of lonable funds. |
B | Buying a stock from a company. |
C | Buying a bond from a company or the government. |
D | A tax free saving account a high interest and mixed investments. |
E | A chequing account with no interest. |
Question 41 |
A | Supply of goods will decrease as production levels falls. |
B | Wages would not be properly adjusted to the price fluctuations in the market. |
C | Prices would not be adjusted properly to the fluctuations in cost of raw materials. |
D | Wages of workers will increase as profit for companies increase. |
Question 42 |
A | Lonable funds |
B | Doughnuts |
C | Exchange rates |
D | Inflation |
E | Investments |
Question 43 |
A | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
B | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation decreases. |
C | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
D | the unemployment rate is unaffected and the labor force participation increases. |
E | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation decreases. |
F | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation increases. |
Question 44 |
A | the exchange rate falls significantly. |
B | two or more markets are at equilibrium. |
C | the exchange rate increases significantly at the same time the inflation rate falls. |
D | two or more markets are not at equilibrium. |
Question 45 |

A | Inflation Curve |
B | Long Run Demand Curve |
C | Long Run Phillips Curve |
D | Short Run Phillips Curve |
E | Short Run Supply Curve |
F | Employment Curve |
Question 46 |
A | Appreciation of the value of fiat money. |
B | Changes in the inflation rate. |
C | Types of monitory controls by the government. |
D | Depreciation of the value of fiat money. |
Question 47 |
A | 4.00 |
B | 3.00 |
C | 1.00 |
D | 0.75 |
($3.00)/($4.00) = 0.75
Question 48 |
A | employment is hindered or prevented by physical disabilities. |
B | if the person is waiting to start a new job. |
C | if the person has been employed within the last few weeks, but currently have no employment. |
D | if the person is searching for employment, but lacks proper skills or education. |
Question 49 |

A | Expansionary monitory policy involving decrease in money supply. |
B | Expansionary monitory policy involving decrease in banking reserve ratio. |
C | Contractionary monetary policy involving decrease in banking reserve ratio. |
D | Contractionary monetary policy involving buying bonds from the public by Bank of Canada. |
Question 50 |
A | prime rate , standard rate |
B | None of the answers are correct. |
C | overnight rate , prime rate |
D | bank rate , prime rate |
E | standard rate , prime rate |
Question 51 |
A | S = I - G |
B | Y = C + I + G |
C | I = Y - C + G |
D | Y = C + I + G +NX |
E | Y = C + I + G - NX |
Question 52 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | raises , raises , more unemployment |
C | lowers , raises , unemployment |
D | raises , lowers , more unemployment |
E | lowers , lowers , unemployment |
Question 53 |
A | Pigou's Wealth Effect |
B | Sticky-wage Theory |
C | Adverse Supply Shock |
D | Keynes' Effect |
E | Real Exchange Rate Effect |
Question 54 |

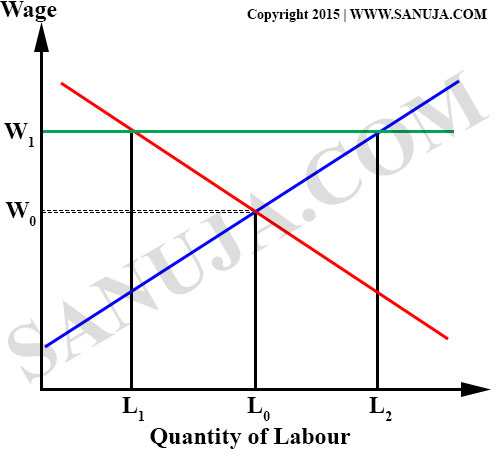
A | W0 , L0 |
B | W1 , L1 |
C | W1 , L2 |
D | W1 , L0 |
E | W0 , L1 |
Question 55 |
A | $30 |
B | None |
C | $940 |
D | $60 |
E | $1160 |
Question 56 |
A | Canadian consumers will buy fewer domestic goods and more foreign goods. |
B | Canadian consumers will buy fewer domestic goods and fewer foreign goods. |
C | Canadian consumers will buy more domestic goods and fewer foreign goods. |
D | Canadian consumers will buy more domestic goods and more foreign goods. |
Question 57 |
A | Cyclical unemployment |
B | Fluidity of natural unemployment |
C | Structural unemployment |
D | Rules imposed by governments |
Question 58 |

A | L1 , L2, zero |
B | L2 , L0, L2 minus L0 |
C | L0 , L1, L0 minus L1 |
D | L2 , L1, L2 minus L1 |
E | L0 , L0, zero |
F | L1 , L1, zero |
Question 59 |
A | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
B | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation increases. |
C | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation is unaffected. |
D | the unemployment rate decreases and the labor force participation decreases. |
E | the unemployment rate increases and the labor force participation decreases. |
F | the unemployment rate is unaffected and the labor force participation increases. |
Question 60 |
A | amount of unemployment that an economy normally experiences. |
B | determined only based on the permanent long-term employment opportunities. |
C | the unemployment rate corrected for inflation, skill levels and other external factors. |
D | rate at which the unemployment fluctuates. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Peter Tracey during Fall 2015 and textbook ISBN-978-0-17-653085-3.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.