Basic concepts: molecular biology, DNA, RNAs, chemical bonds, importance of water, chemical reactions, organic compounds, carbohydrates, lipids, cholesterol, proteins, amino acids, fats, steroids, emulsifiers, etc.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm I | Midterm II | Final Exam
Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm III
Congratulations - you have completed Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm III.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
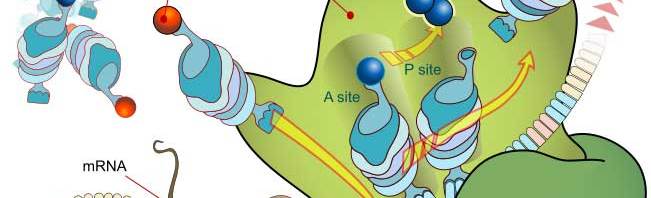
Question 1 |
A | Only the mRNA structure is linear. |
B | Coding of the proteins is done by mRNAs. |
C | The tRNA carries amino acids with high energy bound for making proteins. |
D | Only the tRNA structure is linear. |
Question 2 |
6 C? (ID-B03-04)
A | 7 |
B | 6 |
C | 8 |
D | 14 |
Question 3 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 4 |
A | Nucleus, plasma membrane and hemoglobin. |
B | Plasma membrane and hemoglobin. |
C | Ribosomes, organelles and hemoglobin. |
D | Ribosomes, plasma membrane and hemoglobin. |
E | Nucleus, ribosomes and hemoglobin. |
Question 5 |
A | ATP injection |
B | Heating |
C | Hydrolysis |
D | Protein pumps |
Question 6 |
A | Starch |
B | Glycogen |
C | Cellulose |
D | Carboxylic acids |
Question 7 |
A | Lipids |
B | Carbohydrates |
C | Nucleic Acids |
D | Proteins |
Question 8 |
A | They usually characterized by three double bonded C-O structures. |
B | They often form ring structures. |
C | Most common two; glucose forms 5 membered structures while fructose forms 6 membered structure. |
D | Their molecular formulas are usually multiples of CH2O2. |
Question 9 |
A | They slow down chemical reaction by acting as a buffer. |
B | They speed up chemical reactions without participating in the reaction. |
C | They speed up chemical reactions by participating in the reaction. |
D | They slow down chemical reaction by participating in the reaction. |
Question 10 |
A | 2 |
B | 3 |
C | 4 |
D | 5 |
Question 11 |
A | Movement of an organism in response to a chemical stimulus. |
B | Process in which chemical difference between inside and outside the cell is maintained. |
C | Production of proteins by the bone marrow to keep stable white blood cell count. |
D | A digestive process used by herbivorous to break down the plant cells. |
Question 12 |
A | Cell theory |
B | Molecular theory |
C | Theory of evolution |
D | Genetic theory |
E | Laws of inheritance |
Question 13 |
A | Receptor proteins codes the ionic and polar molecules so that it will be accepted by the phospholipids. |
B | Transport proteins form channels which allow ions and polar molecules to move across. |
C | The difference in pH levels inside and outside the cell facilitates movement of ionic and polar molecules. |
D | Simple diffusion process. |
Question 14 |
I. Covalent bonds are stronger than ionic bonds.
II. Chemical reactions always result in loss of electron(s).
III. Water is slightly polar.
IV. Ionic bonds are bound together with oppositely charged ions.
A | All of the above statements are correct. |
B | I and III |
C | I and II |
D | I , III and IV |
E | II and IV |
F | I , II and III |
Question 15 |
A | To be able to stack together to form tissues. |
B | To be able to communicate to the outside world. |
C | To be able to process food and data. |
D | To allow nutrients and gasses to pass across the cell surface. |
Question 16 |
A | Red blood cells |
B | Platelets |
C | Serum |
D | White blood cells |
Question 17 |
A | polysaccharide |
B | protein |
C | lipid |
D | monsaccharide |
E | disaccharide |
Question 18 |
A | ...always outside cell walls. |
B | ...by heating the reactants. |
C | ...in aqueous environment of cells. |
D | ...only by breaking covalent bonds because living cells cannot break down ionic bonds. |
Question 19 |
A | ...their orientation of the hydrogen atoms. |
B | ...the type of translation. |
C | ...their chemical structures. |
D | ...water solubility level. |
Question 20 |
A | There is a world wide shortage of advanced microscopes. |
B | The techniques used to study microscopic particles in cell biology has not changed since 1665. |
C | Light microscopes are cheaper for a biologist to obtain. |
D | Movement of organic material is magnified in advanced microscopes hence harder to study. |
Question 21 |
A | 2 times more H+ |
B | 100 times less H+ |
C | 10 times less H+ |
D | 10 times more H+ |
E | 100 times more H+ |
[H+] = 10-pH
Question 22 |
A | Centriole |
B | Golgi apparatus |
C | Vesicles |
D | Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
E | Nucleolus |
Question 23 |
A | Fiber junctions |
B | Anchoring junctions |
C | Gap junctions |
D | Tight junctions |
Question 24 |
A | They are the transport vesicles that deliver glycoprotein from ER membrane to Golgi apparatus. |
B | In plants, they store toxins to protect them from predators. |
C | They process materials and produce usable energy for eukaryotic cells. |
D | In humans, they acts as the digestive compartments within cells. |
Question 25 |
A | More triglycerides within the lipoprotein, hence away from the blood. |
B | More cholesterol within the lipoprotein, hence away from the blood. |
C | A very high LDL to HDL ratio. |
D | A very low LDL to HDL ratio. |
Question 26 |
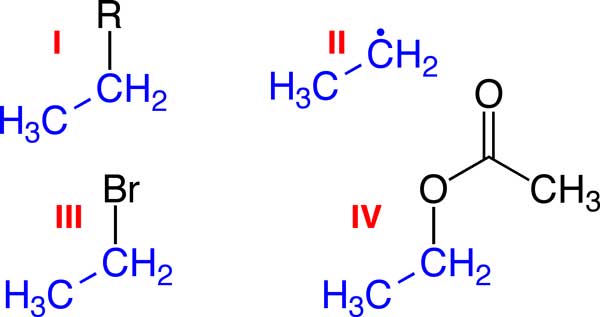
Image mod from: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ethyl_group
A | I, II and IV |
B | I only |
C | II only |
D | IV only |
E | III only |
F | II and IV |
Question 27 |
A | Genetic control of the cell. |
B | Provide structural support for the nucleus. |
C | Manufacture and distribution of molecules. |
D | Provide structural support for the cell wall. |
E | Energy processing. |
Question 28 |
A | Five subatomic particles. |
B | Two subatomic particles. |
C | Three subatomic particles. |
D | Hundreds of subatomic particles. |
Question 29 |
A | DNA as genetic materials |
B | Nucleus |
C | Organelles |
D | Cell walls |
Question 30 |
A | Hydrogen bonding |
B | Acid-base reactions |
C | Chemical precipitation reactions |
D | Vital hormone producing reactions |
Question 31 |
A | ...high cholesterol. |
B | ...obesity. |
C | ...diabetes. |
D | ...thyroid problems. |
Question 32 |
A | Flagella |
B | Peptidoglycan |
C | Chitin |
D | Glucose |
Question 33 |
A | 1.0 to 10 micrometres |
B | 100 to 1000 micrometres |
C | 0.1 to 1.0 micrometres |
D | 10 to 100 micrometres |
Question 34 |
A | Carbon, Oxygen and Nitrogen |
B | Nitrogen and Oxygen |
C | Hydrogen and Oxygen |
D | Hydrogen, Carbon and Oxygen |
E | Hydrogen, Oxygen and Nitrogen |
F | Carbon and Hydrogen |
Question 35 |
A | Carbon-13 |
B | Helium-4 |
C | Carbon-14 |
D | Carbon-12 |
E | Nitrogen-12 |
Question 36 |
A | Radon gas |
B | Natural gas |
C | Sulfur mustard gas |
D | Thorium gas |
Question 37 |
A | 3 |
B | 2 |
C | 4 |
D | 6 |
E | 5 |
Question 38 |
A | RNA has Adenine (Ade) nitrogenous base instead of Cytosine (Cyt). |
B | RNA has Thymine (Thy) nitrogenous base instead of Adenine (Ade). |
C | RNA has Thymine (Thy) nitrogenous base instead of Cytosine (Cyt). |
D | RNA has Cytosine (Cyt) nitrogenous base instead of Adenine (Ade). |
E | RNA has Uracil (Ura) nitrogenous base instead of Thymine (Thy). |
F | RNA has Guanine (Gua) nitrogenous base instead of Cytosine (Cyt). |
Question 39 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 40 |
A | ...Microtubule, Intermediate filament and Microfilament. |
B | ...Centriole, Golgi apparatus and Ribosomes. |
C | ...Plasma membrane, Ribosomes and Lysosome. |
D | ...Ribosomes, Lysosome and Centriole. |
E | ...Lysosome and Centriole. |
Question 41 |
A | Ankrin protein |
B | Aquaporins protein |
C | Band 3 protein |
D | Glycophorin protein |
E | Spectrin protein |
Question 42 |
A | Light Microscope (LM) |
B | Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) |
C | Electron Microscope (EM) |
D | Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) |
Question 43 |
A | Primary structure |
B | Tertiary structure |
C | Quaternary structure |
D | Secondary structure |
Question 44 |
A | Pituitary gland |
B | Salivary gland |
C | Prostate gland |
D | Pineal gland |
E | Thyroid gland |
Question 45 |
A | The chemical properties such as high cohesion and polarity. |
B | Very high reaction rate. |
C | The physical properties such as very low angles between the two H-atoms and the O-atom. |
D | Very high electron transfer rate and high electrical conduction rate. |
Question 46 |
A | Enzyme and proteins synthesis. |
B | Provide structural support. |
C | Locomotion. |
D | DNA and RNA replication. |
E | Protection from the outside environment. |
Question 47 |
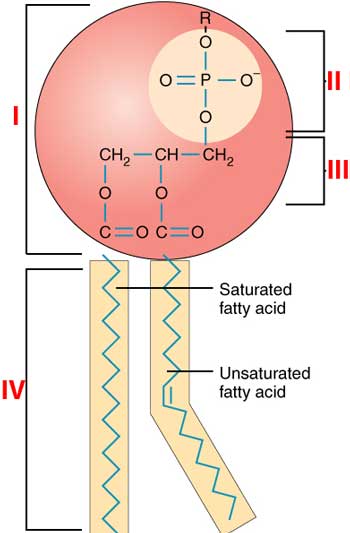
Image mod from: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0301_Phospholipid_Structure.jpg
A | III and IV |
B | III and I |
C | I and III |
D | I and IV |
E | IV and I |
Question 48 |
A | 2 |
B | 5 |
C | 4 |
D | 3 |
E | 6 |
Question 49 |
A | They made the various fiberous proteins of α-helical
coiled-coils that transport materials from one area to another. |
B | They are only found in plant cells because animal cells with movement cannot maintain the structure. |
C | They are composed of globular proteins that are assembled and disassembled in different regions of the cell to form hollow pathways. |
D | They are composed of action and involved in cell movement and maintaining cell structure. |
Question 50 |
A | The base A pairs with base C while base G pairs with base T to form a double helix DNA. |
B | The base A pairs with base T while base C pairs with base G to form a double helix DNA. |
C | The base A pairs with base T while base G pairs with base T to form a double helix RNA. |
D | The base A pairs with base G while base C pairs with base T to form a double helix RNA. |
E | The base A pairs with base G while base C pairs with base T to form a double helix DNA. |
F | The base A pairs with base C while base G pairs with base T to form a double helix RNA. |
Question 51 |
A | 5 electrons. |
B | 13 electrons. |
C | 10 electrons. |
D | 5 electrons. |
E | 8 electrons. |
Question 52 |
A | Maltose |
B | Glucose |
C | Fructose |
D | Cellulose |
Question 53 |
A | Produce molecules and compounds with polarity. Hint: Not always, but sometimes. |
B | Number of electrons within the structure increases. Hint: Not always, but sometimes. |
C | Valance shell electrons react with other atoms to form bonds. |
D | Neutrons and protons from different atoms react with each other. |
Question 54 |
A | Methyl group |
B | Carboxyl group |
C | Carbonyl group |
D | Phosphate group |
E | Hydroxyl group |
F | Amino group |
Question 55 |
A | 3-carbin sugar, phosphate group and a adenine |
B | 5-carbin sugar, phosphate group and a adenine Hint: While it is true a adenine can be one, it is not a general part! |
C | 5-carbin sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogenous base |
D | 3-carbin sugar, phosphate group and a nitrogenous base |
Question 56 |
A | ...good for human health/digestive system. |
B | ...contain more nutrition than plant based fats. |
C | ...solid at room temperature. |
D | ...unsaturated fats. |
Question 57 |
A | Millions |
B | 100 |
C | 35 |
D | 20 |
E | 50 |
Question 58 |
A | Biological cells have the ability to differentiate Carbon-12 from Carbon-14. |
B | Majority of organic cells lacks nucleus. |
C | Both animal and plant cells contains materials that move around (mobile). |
D | Natural carbon is only produced by plant cells. |
E | Only the animal cells that have materials that move around (mobile). |
Question 59 |
A | Hydrogen bonds are primary structures of proteins. |
B | Some proteins only have α helix structures while others can have only β pleated sheet structures. |
C | Protein structures have four levels of structures. |
D | The α helix and the β pleated sheet structures are tertiary structure. |
Question 60 |
A | Butane |
B | Ethane |
C | Methane |
D | Benzene |
Question 61 |
A | Because CO2 reacts with calcium to produce bicarbonate. |
B | Because CO2 acts as a low pH buffer. |
C | Because CO2 reacts with water to produce carbonic acid. |
D | Because CO2 is an acid. |
Question 62 |
A | The elemental abundance must be less than 0.2% of the human body weight. |
B | The elemental abundance must be less than 0.01% of the human body weight. |
C | The elemental abundance must be less than 0.1% of the human body weight. |
D | The elemental abundance must be less than 1.0% of the human body weight. |
E | The elemental abundance must be less than 0.4% of the human body weight. |
Question 63 |
Note: Moose dung is a traditional Canadian delicacy. Yum yum 🙂
A | Freeze the dung before cooking. |
B | Add salts, ionic compounds, to the moose dung. |
C | Increase the humidity of the cook pot. |
D | Decrease the humidity of the cook pot. |
Question 64 |
A | Fructose is cheaper than glucose. |
B | Fructose is a polymer while glucose is a monomer. |
C | There is more fructose naturally in corn syrup. |
D | Fructose is sweeter than glucose. |
Question 65 |
A | Cellulose |
B | Lipids |
C | Chitin |
D | Glycogen |
E | Starch |
Question 66 |
A | Carry information of amino acid sequence from the genes to make proteins in cells. |
B | Provide energy for the DNA structure by converting energy from cells into ATP and transferring it to the nucleus. |
C | Protect the nucleus from genetic mutations, even though this always does not work. |
D | Develop new genetic codes for evolutionary adaptations. |
Question 67 |
A | Compared to unsaturated fatty acids, they have a very high melting point. |
B | They are often found in olive oil and vegetable oils. |
C | They have the maximum number of hydrogens (alkanes) in the fats and lipid group. |
D | They have kinks caused by double bonding of carbon atoms. |
Question 68 |
A | Phosphate group |
B | Carboxyl group |
C | Amino group |
D | Carbonyl group |
E | Hydroxyl group |
Question 69 |
A | Primary structure: |
B | Quaternary structure |
C | Secondary structure |
D | Tertiary structure |
Question 70 |
A | ...higher the pull of electrons towards its nucleus. |
B | ...higher the radioactivity of the atom. |
C | ...lower the pull of electrons towards its nucleus. |
D | ...lower the radioactivity of the atom. |
E | ...more stable the atom. |
Question 71 |
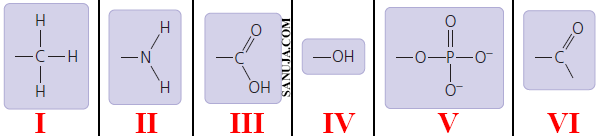
Suggestion: Take your time to answer this question. It can be confusing with 6 types!
A | IV , VI , II , III , V and I |
B | I , III , IV , V , II and VI |
C | IV , VI , III , II , V and I |
D | VI , IV , III , II , V and I |
E | VI , IV , II , V , III and I |
F | IV , I , VI , V , II and III |
Question 72 |
A | Protons |
B | Electrons |
C | Neutrons |
D | Protons and Neutrons |
E | Protons and Electrons |
Question 73 |
A | Heat is the amount of energy associated with movement of atoms while temperature is the intensity of heat (average speed of atoms). |
B | Heat is produced through instantaneous reactions such as boiling water. Temperature is the quantitative measurement of heat. |
C | Temperature is the amount of energy associated with movement of atoms while heat is the intensity of heat (average speed of atoms). |
D | Temperature is a long term quantitative measurement of energy while heat is a short term measurement of energy. |
Question 74 |
A | Molecules composed of two or more different elements while compounds composed of two or more atoms. |
B | Compounds composed of two or more different elements while molecules composed of two or more atoms. |
C | Molecules are always ionic while compounds could be either ionic or covalent. |
D | All organic matter is compounds while molecules are inorganic. |
E | Molecules easily react with organic matter therefore they often involved in chemical reactions. Compounds are stable entities and are often inert. |
Question 75 |
A | Tight junctions |
B | Messenger junctions |
C | Membrane junctions |
D | Gap junctions |
E | Anchoring junctions |
Question 76 |
A | The very high electronegative nature of the molecule. |
B | The hydrogen bonds. |
C | The high atomic mass. |
D | Low radioactivity and polarity. |
Question 77 |
A | 1/50th of a typical prokaryotic celll. |
B | 1/10th of a typical prokaryotic celll. |
C | 1/30th of a typical prokaryotic celll. |
D | 1/25th of a typical prokaryotic celll. |
E | 1/100th of a typical prokaryotic celll. |
Question 78 |
A | I. lysosomes II. nucleoli |
B | I. ribosomes II. nucleoli |
C | I. chromosomes II. chromatin |
D | I. ribosomes II. lysosomes |
E | I. chromosomes II. ribosomes |
Question 79 |
A | The milk acted as the solute which breaks down the chemical compounds in the cocoa powder. |
B | The temperature of the mixture should have increased as the mixing progresses. |
C | Milk is the solvent while cocoa powder is the solute. |
D | The mixing of the two most likely have broken down the molecular bounds of water and that resulted in reaction with cocoa powder. |
Question 80 |
A | I. ionic bonds II. nucleic bonds |
B | I. covalent bonds II. nucleic bonds |
C | I. ionic bonds II. peptide bonds |
D | I. covalent bonds II. peptide bonds |
Question 81 |
A | A substance that resists changes in pH by accepting or donating hydrogen irons. |
B | A substance that prevent changes in pH by accepting or donating hydrogen irons. |
C | A substance that prevent genetic mutations. |
D | A substance that resists genetic mutations. |
E | A substance that increase the pH level of a high pH solution while decrease the pH level of a low pH solution. |
Question 82 |
A | Decrease production in glycoprotein. |
B | Increase in rough endoplasmic reticulum. |
C | Increase production in glycoprotein. |
D | Increase in smooth endoplasmic reticulum. |
Question 83 |
A | Energy storage and release. |
B | Forms cell membranes. |
C | Synthesis of Amino acids, DNA and RNA. |
D | Signaling molecules for sex hormones. |
Question 84 |
A | I. transcription II. translation |
B | I. transcription II. replication |
C | I. translation II. transcription |
D | I. translation II. replication |
E | I. replication II. transcription |
F | I. replication II. translation |
Question 85 |
A | 15, iron |
B | 22 , iron |
C | 25 , nitrogen |
D | 15 , sodium |
E | 22 , sodium |
F | 15 , nitrogen |
Question 86 |
A | Theory of inheritance |
B | Endosymbiont theory |
C | Genetic theory |
D | Cell theory |
Question 87 |
A | β−1-->4 |
B | α−1-->4 |
C | α−1-->1 |
D | β−1-->1 |
Question 88 |
A | Facilitate active transport and diffusion. |
B | Attaching to host surfaces. |
C | Locomotion. |
D | Isolation from the outside; like a cell wall. |
Question 89 |
A | They do not form polymers. |
B | They are nonploar and therefore hydrophilic. |
C | They are the largest biological molecules. |
D | They can form many different shapes with random orientations. |
Question 90 |
A | 50% |
B | 75% |
C | 100% |
D | 65% |
E | 99% |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 |
| 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Lohmeier-Vogel during Fall 2014.
FAQ | Report an Error
You may download this exam as a PDF file here
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.