Basic concepts: cell structure and functions, diffusion, permeability, energy, enzymes, cell division, cell cycle, mitosis, meiosis, caner, chromosomes, DNA and RNA replication / translation / transcription, mutations, genetic diseases, inheritance, molecular genetics, proteins, amino acids, polymers, etc.
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm I | Midterm II | Midterm III
Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
I. Colour of human skin is a character.
II. Green colour of peas as opposed to yellow is a trait.
III. Tall trees as opposed to short trees is a character.
IV. Shape of brain is a character.
A | I, II and III only. |
B | I and III only. |
C | I, II and IV only. |
D | II and III only. |
E | II and IV only. |
F | All four statements are correct. |
Question 2 |
A | About 50% of the total time of the cell cycle. |
B | About 90% of the total time of the cell cycle. |
C | About 35% of the total time of the cell cycle. |
D | About 10% of the total time of the cell cycle. |
Question 3 |
A | 30 |
B | 10 |
C | 6 |
D | 60 |
Question 4 |
A | The reaction require a catalyst such as an enzyme to proceed. |
B | The reaction is an endothermic reaction. |
C | The potential energy of the products is more than that of the reactant. |
D | The potential energy of the products is less than that of the reactant. |
Question 5 |
A | 1:1:1:1 |
B | 9:3:3:1 |
C | 16:0:0:0 |
D | 8:4:2:2 |
E | 1:3:3:2 |
Question 6 |
A | ...a duplication. |
B | ...an inversion. |
C | ...a deletion. |
D | ...a translocation. |
Question 7 |
A | Use of two ATPs to drive a single reaction. |
B | Breaking down of molecules to obtain energy from both ATP and ADP. |
C | Use of two phosphates from ATP to drive a single reaction. |
D | Use of energy released from exergonic reactions to drive endergonic reactions. |
Question 8 |
A | ...homolgous chromosomes. |
B | ...sister chromatids. |
C | ...DNA transcripts. |
D | ...sister chromosomes. |
E | ...chromatin. |
Question 9 |
A | Prophase |
B | Prometaphase |
C | Anaphase |
D | Metaphase |
E | Interphase |
Question 10 |
A | Metaphase |
B | Interphase |
C | Anaphase |
D | Telophase |
E | Prophase |
Question 11 |
A | Nucleotide insertion. |
B | Nucleotide deletion. |
C | Nucleotide substitution. |
D | Rearrangement of codons. |
E | Alteration of the start codon. |
Question 12 |
A | Four |
B | Three |
C | Nine |
D | One |
E | Two |
Question 13 |
A | RNA splicing |
B | Translation |
C | DNA packing/unpacking |
D | Adding a cap and tail to RNA |
E | Transcription |
Question 14 |
A | ...exon. |
B | ...intron. |
C | ...centromere. |
D | ...splicer. |
E | ...loci. |
Question 15 |
A | Darwin did not know that mechanisms that causes genetic variations in plants are similar to that of animals. |
B | Darwin did not know which mechanisms were responsible for the variation he saw. |
C | Darwin received Mendel's paper but did not understand its significance. |
D | The explanation for genetics had no implications for evolution. |
E | The blending theory of inheritance provides support for evolution. |
Question 16 |
A | Size and type of the chromosome. |
B | Type of ATP compound that assist in the movement. |
C | Shape of the mitotic spindle. |
D | The location of the centrosomes. |
Question 17 |
A | Carbon dioxide |
B | Positivity charged sodium ion. |
C | A small, nonpolar molecule such as butane (C4H10). |
D | Oxygen |
Question 18 |
A | RNA |
B | DNA and Proteins |
C | DNA and RNA |
D | Proteins |
E | DNA |
Question 19 |
A | Chromosomes undergo segregation and independent assortment. |
B | Only few selected chromosomes are responsible for inheritance. |
C | Chromosomes undergo segregation and but do not independent assortment. |
D | Chromosomes themselves do not control the patterns of inheritance. |
Question 20 |
A | Homozygous dominant female |
B | Heterozygous male |
C | Homozygous male |
D | Heterozygous female |
E | Homozygous recessive female |
Question 21 |
A | F2 generation |
B | P2 generation |
C | A1 generation |
D | P1 generation |
E | H1 generation |
F | F1 generation |
Question 22 |
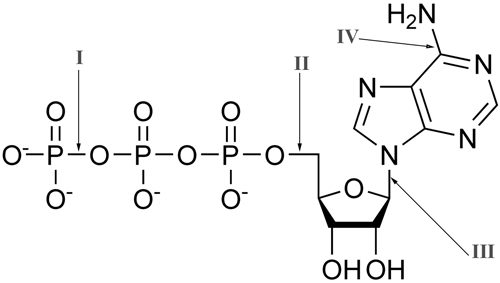
A | II |
B | IV |
C | I |
D | III |
Question 23 |
I. Translocation
II. Renegotiation of the start codon.
III. Codon recognition by pairing tRNA anticodon with mRNA codon.
IV. Peptide bond formation.
A | III (first) --> III --> IV --> I (last) |
B | III (first) --> II --> I--> IV (last) |
C | II (first) --> III --> II--> IV (last) |
D | II (first) --> III --> IV --> I (last) |
Question 24 |
A | Receptor-neduated endocytosis |
B | Pinocytosis |
C | Active diffusion |
D | Phagacytosis |
E | Facilitated diffusion |
Question 25 |
A | Telophase |
B | Prophase |
C | Prometaphase |
D | Metaphase |
E | Anaphase |
Question 26 |
A | T-G-T-G-T-A-G |
B | G-A-T-C-A-C-A |
C | G-T-A-G-A-C-T |
D | T-C-A-G-A-C-G |
E | T-A-G-A-T-C-G |
Question 27 |
A | Codons and anticodons |
B | tRNAs |
C | Ribosomes |
D | Polypeptides |
Question 28 |
A | sexual reproduction , asexual reproduction |
B | genetic mutations , natural gene evolution |
C | natural gene evolution , genetic mutations |
D | asexual reproduction , sexual reproduction |
E | mitosis cell division , meiosis cell division |
Question 29 |
A | ...feedback inhibitor. |
B | ...product inhibitor. |
C | ...reactant inhibitor. |
D | ...noncompetitive inhibitor. |
E | ...competitive inhibitor. |
Question 30 |
A | Excessive use of antibiotics will create drug resistant bacteria also known as superbugs. |
B | Antibiotics not only can be used as a preventive medication, but also can be used to treat existing infections. |
C | Antibiotics work by either killing or inhibiting the growth of undesirable bacteria. |
D | Penicillin antibiotic is derived from a fungi and belongs to β-Lactam antibiotics class. |
Question 31 |
A | Interruption of phospholipid synthesis. |
B | Prevention of translation. |
C | Prevention of the nucleic acid formation. |
D | Prevention of transcription. |
E | Interruption of DNA replication. |
Question 32 |
A | binary fission |
B | replication |
C | mitosis |
D | meiosis |
Question 33 |
A | Polymerization |
B | Hydrolysis |
C | Phosphorylation |
D | Energization |
Question 34 |
A | isotonic |
B | diffusion |
C | hypotonic |
D | hypertonic |
E | non-equilibrium |
Question 35 |
A | They were able to identify nucleotides which provided the proof needed to show that DNA is the genetic material. |
B | They injected different radioactive isotopes label DNA and protein then trace it using phage. |
C | They observed the nucleus under high powered microscopes and discovered that the DNA is much larger than proteins. |
D | They separated the DNA from the rest of the cell structure using centrifuged mixture and discovered DNA is the only living material. |
Question 36 |
A | I. metabolic II. catabolic |
B | I. anabolic II. catabolic |
C | I. metabolic II. anabolic |
D | I. catabolic II. anabolic |
E | I. anabolic II. metabolic |
F | I. catabolic II. metabolic |
Question 37 |
A | It is a laboratory process used in in vitro fertilization. |
B | It is the process in which the speed of the cell division is controlled by several genetic factors. |
C | It is a laboratory process used for production of genetically modified foods. |
D | It is the process in which genes are turned "on" and "off" as a response to stimuli. |
Question 38 |
A | Monogenetic inheritance |
B | Pleiotropy |
C | Achondroplasia |
D | Polygenetic inheritance |
E | Promoter |
Question 39 |
A | ... all forms of reproduction. |
B | ...sexual reproduction between different species. |
C | ...asexual reproduction only. |
D | ...sexual reproduction only. |
Question 40 |
A | ...applies only to sex-linked genes. |
B | ...deals with the alleles governing two different traits. |
C | ...explains the behavior of a pair of alleles during meiosis. |
D | applies only to linked genes. |
Question 41 |
A | A site in which a particular gene is located in the chromosome. |
B | The region of a duplicated chromosomes where two sister chromatids are joined. |
C | A region where the end codon is located. |
D | A type of mutation within a chromosome caused by an unmatched allele. |
E | A region where the start codon is located. |
Question 42 |
A | allosteric |
B | inhibitory |
C | active |
D | phosphate |
Question 43 |
A | Naturally occurring genetic mutations. |
B | Genetic mutations caused by external factors. |
C | Increased in genetic diversity. |
D | Inbreeding |
Question 44 |
A | The dog dog did not eat. |
B | The did not eat. |
C | The did dog not eat. |
D | The dod idn ote at. |
E | The dog did dog did not eat. |
Question 45 |
A | Heterosomes |
B | Autosomes |
C | Nucleosomes |
D | Genomes |
E | Alleles |
Question 46 |
A | DNA Pectinase |
B | DNA ligase |
C | DNA Invertase |
D | DNA polymerase |
E | DNA thymine |
Question 47 |
A | Petals |
B | Stigmas |
C | Stamens |
D | Flowers |
E | Pistils |
Question 48 |
A | Only certain forms of domesticated plants and animals bred true. |
B | The inheritance of traits was controlled by blood. |
C | The characteristics of parents were blended in the offspring. |
D | Acquired characteristics were inherited. |
E | All genetic traits bred true. |
Question 49 |
A | temperature only |
B | pH and temperature |
C | pH only |
D | pH, chemical balance and temperature |
E | temperature and chemical balance |
Question 50 |
A | A cross between individuals from the same species. |
B | A cross between individuals that are identical. In other words, no difference between any charter. |
C | A cross between individuals with different P-generations. |
D | A cross between individuals that only differ due to one F-generation. |
E | A cross between individuals that only differ in one character. |
Question 51 |
A | four |
B | one |
C | two |
D | five |
E | three |
Question 52 |
A | The frequencies with which the genes are inherited from the mother and from the father. |
B | The frequencies with which the genes exhibit incomplete dominance over each other. |
C | The frequencies with which the corresponding traits occur together in offspring. |
D | The frequencies of mutations in the genes. |
Question 53 |
A | ...destruction of the nucleus. |
B | ...reduction in RNA replication. |
C | ...destruction of the cell. |
D | ...reduction in protein synthesis. |
Question 54 |
A | Interphase I |
B | Metaphase II |
C | Metaphase I |
D | Prophase II |
E | Prophase I |
Question 55 |
A | The cycle typically leads to the lysis of the host cell. |
B | The viral DNA is inserted into a bacterial chromosome. |
C | The viral genes typically remain inactive once they are inside the host cell. |
D | The virus reproduces outside of the host cell. |
E | The cycle typically ends when the host bacterium divides. |
Question 56 |
A | Missense mutation |
B | Reading frame mutation |
C | Silent mutation |
D | Nonsense mutation |
Question 57 |
A | AA |
B | AA and aa |
C | Aa |
D | AA and Aa |
E | aa |
Question 58 |
A | ...men acquire two copies of the defective gene during fertilization. |
B | ...men need to inherit only one copy of the recessive allele for the condition to be fully expressed. |
C | ...the sex chromosomes are more active in men than in women. |
D | ...the genes associated with the sex-linked conditions are linked to the Y chromosome, which determines maleness. |
Question 59 |
A | Both plants and animals can produce offspring through sexual reproduction. |
B | Early plants sexually reproduced their offspring. |
C | Early humans asexually reproduced their offspring. |
D | Only the organisms in the Kingdom Animalia undergo sexual reproduction. |
E | Multicultural organisms only reproduce through sexual reproduction and are not capable of asexual reproduction. |
Question 60 |
A | A lead-based compound used in medical substances usually added to host's blood stream that boost immune system. |
B | A genetically modified version of the the virus used to suppress the host organism's immune system. |
C | A synthetic virus used for infecting the host organism in order to prevent more dangerous strain of the virus from infecting the host. |
D | A derivative of a pathogen used to simulate a host organism's immune system. |
Question 61 |
A | Elongation of the growing RNA molecule. |
B | Initiation of a new RNA molecule. |
C | Termination of the RNA molecule. |
D | Initiation of a new polypeptide chain. |
Question 62 |
A | ...codominance. |
B | ...penetrance. |
C | ...expressivity. |
D | ...multiple alleles. |
E | ...pleiotropy. |
Question 63 |
A | nucleic acid bond repair |
B | DNA ligase repair |
C | thymine insertion repair |
D | DNA polymer repair |
E | nucleotide excision repair |
Question 64 |
A | A protein which can attached to RNA to produce complementary DNA strand. |
B | A transcription enzyme within the RNA structure that allow it to obtain information from the nucleus. |
C | A transcription enzyme within the RNA structure that allow it to pass information to proteins. |
D | A protein which encourages DNA replication by stimulating the DNA. |
E | A specific binding site for sigma factor in DNA which the RNA can bind. |
Question 65 |
A | The creation of a strand of DNA from an RNA molecule. |
B | Assimilation of external DNA into a cell. |
C | The type of semiconservative replication shown by DNA. |
D | The infection of cells by a phage DNA molecule. |
E | The creation of a strand of RNA from a DNA molecule. |
Question 66 |
A | ...hypertonic. |
B | ...hydrotonic. |
C | ...isotonic. |
D | ...static. |
E | ...hypotonic. |
Question 67 |
A | Three |
B | Two |
C | Seven |
D | Eight |
E | Four |
Question 68 |
A | Amino acids |
B | DNA |
C | Polymers |
D | Nucleotides |
E | Nucleic acids |
Question 69 |
A | At equilibrium, transport of particles ceased and there is no net change in concentration. |
B | The diffusion does not allow chemical equilibrium because particles will still be moved across through active transport. |
C | At equilibrium, transport still occurs but there is no net change in concentration. |
D | Even at equilibrium, there is a net diffusion direction but this is balanced by other sources of input into the cell. |
Question 70 |
A | Outside sticking out of the ribosome. |
B | Deep inside the tRNA structure. |
C | At the amino acid attachment site of tRNA. |
D | Outside but exposed within the ribosome. |
Question 71 |
A | ...loci. |
B | ...tetrads. |
C | ...chiasmas. |
D | ...recombs. |
Question 72 |
A | 3 |
B | 2 |
C | 4 |
D | 5 |
Question 73 |
A | Sugar-phosphate backbone |
B | Complementary RNA strand |
C | Amino acid and protein sequences |
D | Nucleotides and polynucleotides framework |
Question 74 |
A | Lethal |
B | Dominant |
C | Recessive |
D | Codominant |
E | Sex-linked |
Question 75 |
A | It creates a hypotonic condition in which the cells lose water. |
B | It creates a hypertonic condition in which the cells lose water. |
C | It leads to lysed condition which eventually caused the bursting of the cell membrane. |
D | It leads to isotonic situation where cells could not obtain nutrients from outside and could not remove waste to outside. |
Question 76 |
A | Muted |
B | Haploid |
C | Diploid |
D | Monosomy |
E | Trisomy |
Question 77 |
A | Anaphase |
B | Prometaphase |
C | Metaphase |
D | Prophase |
E | Telophase |
Question 78 |
A | All dd |
B | 1/2 DD, 1/2 Dd |
C | 1/2 Dd, 1/2 dd |
D | All DD |
E | All Dd |
Question 79 |
A | ...released of energy. |
B | ...decrease in collisions among atoms. |
C | ...increased in in energy. |
D | ...decreased in in energy. |
Question 80 |
A | Cross between a F1 hybrid and a heterozygous organism. |
B | Cross between a F1 hybrid and an organism that is homozygous recessive for that trait. |
C | Cross between a F1 hybrid and the homozygous dominant parent. |
D | Cross between two parental organisms. |
E | Cross between two F1 hybrids. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Lohmeier-Vogel during Fall 2014. Additional study material: Ch. 5, 8, 9, 10 Campbell Biology ISBN-10: 1-269-98476-4.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.