Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm I | Midterm III | Final Exam
Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm II
Congratulations - you have completed Biology 205 (BIOL 205-UCAL) Midterm II.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple tries your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
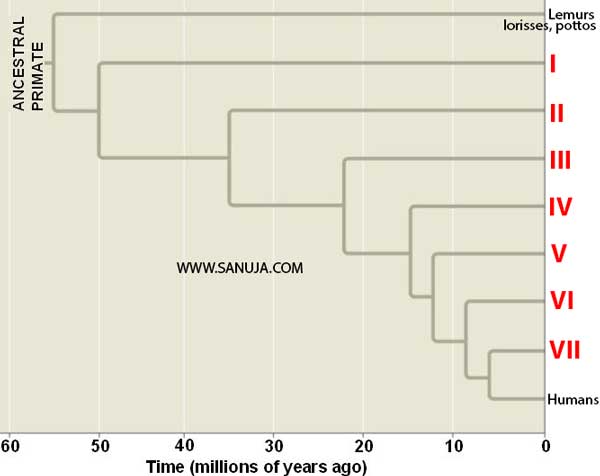
Question 1 |
A | Monkeys |
B | Gorillas |
C | Humans |
D | Gibbons |
E | Tarsiers |
Question 2 |
A | Molluscs |
B | Annelids |
C | Arthropods |
D | Planarians |
E | Cnidarians |
Question 3 |
A | Homo sapiens |
B | Homo ergaster |
C | Homo erectus |
D | Homo neanderthalensis |
E | Homo habilis |
Question 4 |
A | mtDNA |
B | DNA |
C | RNA |
D | rRNA |
Question 5 |
A | ...limited food supply. |
B | ...limited viable offspring. |
C | ...vulnerability to dehydration. |
D | ...large number of predators. |
Question 6 |
A | Adaptive radiation |
B | Temporal isolation |
C | Zygotic barriers |
D | Polyploidy |
E | Sympathetic speciation |
Question 7 |
A | Based on the length ratio of limbs to arms. |
B | Based on the size of the exoskeleton. |
C | Based on the type of tools utilized by the arthropods. |
D | Based on the placement of spinal cord opening on the skulls. |
E | Based on the DNA structure of arthropods. |
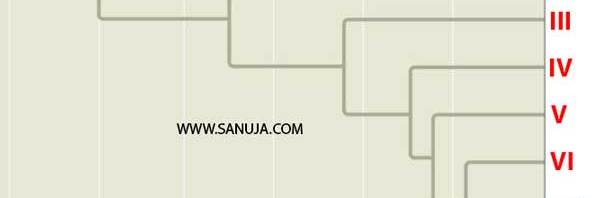
Question 8 |
A | Nucleotides |
B | Amino acids |
C | Glycerol |
D | Fatty acids |
E | Monosaccharides |
Question 9 |
A | Both around the same time |
B | Bipedalism |
C | Large brains |
D | Not enough evidence to support either way. |
Question 10 |
A | ...enteric division of the autonomic nervous system. |
B | ...sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. |
C | ...central nervous system. |
D | ...motor system of the peripheral nervous system. |
E | ...sympathetic division of the motor nervous system. |
Question 11 |
A | Vitamin B1 |
B | Vitamin B12 |
C | Vitamin B6 |
D | Vitamin K |
E | Vitamin A |
Question 12 |
A | Hagfishes lack jaws and lampreys lack endoskeleton. |
B | They both lack endoskeleton. |
C | They both produce slime when threatened and it can be used for manufacturing textiles. |
D | They both lack jaws. |
Question 13 |
A | Structure for the shell in which the honeycomb allantois attached itself to chorion. |
B | Protection of the embryo from the outside environment through temperature regulation. |
C | Production and processing of nutrients for the embryo. |
D | Enables the embryo to obtain oxygen from air and dispose carbon dioxide. |
Question 14 |
A | Meat is more difficult to digest than vegetable matter because of its high protein content. |
B | Omnivores have longer digestive track then carnivores of similar body size because vegetation is more difficult to break digest. |
C | All vertebrates process hard solid foods in the Gizzard before the nutrients are absorbed by the intestine. |
D | Cellulose-digesting microbes are equally abundant both in carnivores and herbivores. |
Question 15 |
A | Nucleic acids |
B | Saccharides |
C | Fat |
D | Protein |
Question 16 |
A | Darwin's finches are unique because they are the only population to have a large variation in beak sizes. |
B | Competition for food can drive evolutionary changes and adaptations. |
C | The response to environmental changes often result in dramatic shift in phenotypes. |
D | Hybrids have better survival rate than the others in a population. |
Question 17 |
A | Resting neurons have a slightly negative charge inside the cell. |
B | Resting neurons have a slightly positive charge inside the cell. |
C | Resting neurons for humans is about +/- 5 mV. |
D | Resting neurons have a zero charge inside the cell. |
Question 18 |
A | Fifteen |
B | Ten |
C | Three |
D | Eight |
E | Five |
Question 19 |
A | Fossil record indicating similar characteristics. |
B | Ability to interbreed among individuals. |
C | Common ancestral based decedents. |
D | Common homologous and analogous features. |
E | Ability to interbreed and reproduce viable offspring. |
Question 20 |
A | Breathing by exchanging oxygen atoms from the water. |
B | Pumping water for movement. |
C | Trapping suspended food particles. |
D | Catching or killing the prey. |
E | Crushing and grinding of food particles. |
Question 21 |
A | The modern HIV virus is derived from an ancestor that have the exact same characteristics as the current HIV-1M virus. |
B | The HIV virus originated from primates and transferred to human. |
C | The rate at which the HIV genome evolve is consent at all times. |
D | The HIV genome is composed of fast self replicating DNA that produce a new evolutionary trait at an exponential rate. |
Question 22 |
A | The lack of fossil record to trace the phylogenetic sequence to a common accessory. |
B | The lack of DNA evidence to support most of the lineage events, |
C | The lack of timing for each lineage event. |
D | The rapid evolutionary events are poorly recorded and therefore often not included in phylogenetic trees. |
Question 23 |
A | ...genetically modified character. |
B | ...shared derived character. |
C | ...shared ancestral character. |
D | ...ancestral character. |
E | ...genetically evolved character. |
Question 24 |
A | Homo sapiens |
B | Homo erectus |
C | Homo habilis |
D | Homo neanderthalensis |
E | Homo ergaster |
Question 25 |
A | cell body |
B | axon hillock |
C | myelin sheath and glia |
D | myelin sheath |
E | glia |
Question 26 |
A | Species experienced a punctuated equilibrium. |
B | The species most likely increased in diversity and their hybrid population. |
C | This situation most likely caused by genetic drift. |
D | The population has experienced an allopatric speciation. |
Question 27 |
A | Human |
B | Cockroaches |
C | Crows |
D | Gorilla |
E | Raccoons |
Question 28 |
A | Cerebellum. |
B | Hypothalamus. |
C | Cerebrum. |
D | Medulla oblongata in the Brain Stem. |
E | Pons midbrain in the Brain Stem. |
Question 29 |
A | They are considered to be made up of nonliving materials, but bones are cartilages are generated by living cells. |
B | Skeletal structure of the body is made up of about 90% cartilages. |
C | Exoskeleton doesn't grow at the same rate as the physical growth of an organism. |
D | Primary function of the cartilages is to support mechanical movements of organisms. |
Question 30 |
A | Cecum of a cow is much larger than that of a human. |
B | Humans are generically closer to Chimpanzees than to Gorillas. |
C | Integration of sensory data occurs within the Central Nervous System. |
D | All tissues in a healthy human body have the ability to regenerate. |
E | Food molecules are chemical broken down by specialized enzymes. |
Question 31 |
A | ...mammals do not produce eggs. |
B | ...mammals are also tetrapods. |
C | ...mammals have hair and mammary glands. |
D | ...mammals are part of the primate group. |
E | ...mammals have thick notochords. |
Question 32 |
A | 500 billion |
B | 100 billion |
C | 800 billion |
D | 100 million |
E | 800 million |
Question 33 |
A | Suspension feeders |
B | Fluid feeders |
C | Bulk feeders |
D | Substrate feeders |
Question 34 |
A | Hydrochloric acid |
B | Amino acids |
C | Nucleotides |
D | Glycerol |
E | Monosaccharides |
Question 35 |
A | Chordates, Vertebrates, Jawed vertebrates, Amniotes |
B | Chordates, Vertebrates, Jawed vertebrates |
C | Chordates, Vertebrates |
D | Chordates, Vertebrates, Jawed vertebrates, Tetrapods, Amniotes |
E | Chordates, Vertebrates, Jawed vertebrates, Tetrapods |
Question 36 |
A | Embryo |
B | Amnion |
C | Yolk |
D | Chorion |
E | Allantois |
Question 37 |
A | Orangutans and Gibbons |
B | Gibbons and Orangutans |
C | Gorillas and Chimpanzees |
D | Orangutans and Gorillas |
E | Tarsiers and Gibbons |
Question 38 |
A | Bipedal vertebrates |
B | Animalia |
C | Cordatas |
D | Tetrapods |
Question 39 |
Image Credit: Campbell Biology Concepts & Connections by Reece, Taylor, Simon, Dickey and Soctt
A | Part A |
B | Part C |
C | Part B |
D | Part D |
Question 40 |
A | ...in gametic isolation state. |
B | ...experiencing a reduced hybrid fertility. |
C | ...experiencing a reduced hybrid viability. |
D | ...experiencing a hybrid breakdown. |
E | ...in temporal isolation state. |
Question 41 |
A | 10 mV |
B | 100 mV |
C | -70 mV |
D | +50 mV |
E | -30 mV |
Question 42 |
A | It includes a common ancestor and all its decedents. |
B | It includes the new classification categories such as sub-phylums and sub-domains. |
C | It includes only the evidence from DNA and other genetic materials. |
D | It includes only the evidence from fossils record. |
Question 43 |
I. Cranial nerves
II. Spinal nerves
III. Brain
IV. Spinal cord
A | II and IV |
B | III and IV |
C | I, II and III |
D | I and II |
E | None of the listed items. |
F | All of the listed items. |
Question 44 |
A | ...sting rays with gas exchange lungs. |
B | ...vertebrates with complex lungs. |
C | ...fishes with necks and four limbs. |
D | ...fishes that dragged themselves from one pool of water to another. |
Question 45 |
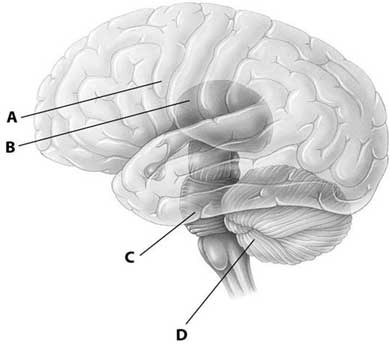
A | Sensory receptor takes in the information and passed to the integration section of the Central Nervous System through Peripheral Nervous System. Once the information is processed, it is passed to organs through Peripheral Nervous System. |
B | Sensory receptor takes in the information and passed to the integration section of the Peripheral Nervous System through Central Nervous System. Once the information is processed, it is passed to organs through Peripheral Nervous System. |
C | Sensory receptor takes in the information and passed to the integration section of the Peripheral Nervous System through Central Nervous System. Once the information is processed, it is passed to organs through Central Nervous System. |
D | Sensory receptor takes in the information and passed to the integration section of the Central Nervous System directly. Once the information is processed, it is passed to organs through Peripheral Nervous System. |
E | Sensory receptor takes in the information and passed to the integration section of Central Nervous System directly. Once the information is processed, it is passed to organs through Central Nervous System. |
Question 46 |
A | I. New World monkeys II. Old World monkeys III. Tarsiers IV. Chimpanzees |
B | I. New World monkeys II. Old World monkeys III. Gibbons IV. Chimpanzees |
C | I. Old World monkeys II. New World monkeys III. Gibbons IV. Orangutans |
D | I. Tarsiers II. New World monkeys III. Gibbons IV. Orangutans |
E | I. Tarsiers II. New World monkeys III. Old World monkeys IV. Gibbons |
Question 47 |
A | While it is possible to live a healthy life without minerals, all humans must requires vitamins. |
B | They are compounds usually acquired from food sources. Vitamins are organic compounds while minerals are inorganic compounds. |
C | They are organic substances which human do not produce its' own. Mostly acquired from food sources. |
D | There are thirty essential vitamins requirements for humans according to Health Canada guidelines. |
E | They are chemicals produced by the monosccharies and absorbed through amino acids. |
Question 48 |
A | Blood clotting |
B | Amino acid metabolism |
C | Visual pigments and epithelial tissues |
D | Synthesis of fat |
E | Collagen synthesis |
Question 49 |
A | I. Eukaryota II. Primates |
B | I. Eukaryota II. Chordata |
C | I. Chordata II. Primates |
D | I. Primates II. Homininae |
E | I. Archaea II. Primates |
Question 50 |
A | They are omnivores that feeds on both seaweeds and fishes. |
B | They are fluid feeders. |
C | They are substrate feeders. |
D | They are suspension feeders. |
E | They are herbivores and the primary diet is eat seaweed. |
Question 51 |
A | Adaptation to terrestrial environments. |
B | Protect the eggs from predators. |
C | As a counteraction to balance the pressure and temperature conditions of the zygote. |
D | Reduce the zygote breakdown. |
Question 52 |
A | outgroup |
B | drifted organisms |
C | ingroup |
D | derived organisms |
Question 53 |
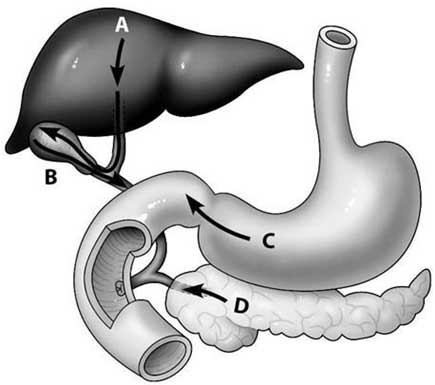
Image Credit: Campbell Biology Concepts & Connections by Reece, Taylor, Simon, Dickey and Soctt
A | Arrow D |
B | Arrow C |
C | Arrow A |
D | Arrow B |
Question 54 |
A | New Zealand |
B | Russia and Canada |
C | South Asia |
D | Antarctic region. |
E | China |
Question 55 |
A | Swim bladders evolved from lungs. |
B | Lugs evolved from swim bladders. |
C | They have no evolutionary connection because they are analogous features. |
D | Both developed at the same time under same environmental conditions. |
Question 56 |
A | Protection of embryo from any external forces; chemical and physical. |
B | Gas exchange for breathing. |
C | Controlling temperature, pressure and chemical compounds for the embryo. |
D | Diffusion of nutrients from mother's blood to embryo's blood. |
E | Storing and processing nutrients. |
Question 57 |
A | Monkeys |
B | Gibbons |
C | Bonobos |
D | Orangutans |
E | Chimpanzees |
Question 58 |
A | ...attack prey. |
B | ...swim against the currents. |
C | ...funnel in water for suspension feeding. |
D | ...move on the seabed and for sediment filtering. |
Question 59 |
A | Biotremes |
B | Euterians |
C | Monotremes |
D | Marsupials |
Question 60 |
A | Organisms with lungs instead of a skin-bases gas exchanges. |
B | Organisms with endohermic metabolism. |
C | Organisms with ectothermic metabolism. |
D | Organisms that can store high volume of water within their bodies. |
E | Organisms that have the ability to fly therefore allowing them to migrate to locations with more food/water. |
Question 61 |
A | To communicate with each other. |
B | To blend into the surrounding environment. |
C | To warn the predators. |
D | For altruism and mimicry where one individual or more benefited by changing appearance, |
Question 62 |
A | There is no relationship between them because feathers are just skin protectors. |
B | The flight and feathers evolved at the same time. |
C | The feathers evolved first as an insulation mechanism and later the flight was evolved. |
D | It is difficult to prove the connection between feathers and flight due to lack of scientific evidence. |
E | The flight evolved first then feathers evolved to insulate high flying birds from old air masses. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. K. Ruckstuhl during Fall 2014.
FAQ | Report an Error
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.