Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm I | Final Exam
Anthropology 201 (ANTH 201-UCAL) Midterm Exam II
Congratulations - you have completed Anthropology 201 (ANTH 201-UCAL) Midterm Exam II.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Body size and weight |
B | Availability of food |
C | Rate of active metabolism |
D | Amount of physical activities |
E | Type of organism |
Question 2 |
A | Within or close to mountain ranges |
B | Close to the North Pole |
C | Within North America |
D | Close to the Equator |
E | Within Northern Africa |
Question 3 |
A | It occurs when a specific genetic condition is associated with sex chromosomes. |
B | It is a form of mating system where dominant male or females have the greatest access to reproductive rights (partners, foods, etc). |
C | It occurs when sexual partners are chosen by the males which they mate. |
D | It occurs when sexual partners are chosen by the females which they mate. |
Question 4 |
A | It is a theory that state all primates are capable of advanced behaviors, similar to that of humans, with exposure to proper training. |
B | It is a methodology for analyzing interactions between organisms of the same species from psychological point of view. |
C | It is a methodology to analyze mental state of different organisms. |
D | None of the answers posted here are correct. |
E | It states that some organisms have the capacity to be aware of thought, knowledge and perceptions of others. |
Question 5 |
A | Cladistic taxonomy is based on both patterns of descents and patterns of overall similarity. Evolutionary taxonomy is based on genetics. |
B | Cladistic taxonomy is based on patterns of descents. Evolutionary taxonomy is based on genetics. |
C | Cladistic taxonomy is based on both patterns of descents and patterns of overall similarity. Evolutionary taxonomy is based on patterns of descent. |
D | Cladistic taxonomy is based on patterns of descents. Evolutionary taxonomy includes both patterns of descent and patterns of overall similarity. |
E | Cladistic taxonomy is based genetics. Evolutionary taxonomy includes both genetics and patterns of descents. |
Question 6 |
A | Distinct genetic differences between the sexes of different species of animals hence restricting the changes of cross-breeding. |
B | Distinct genetic and morphological condition that will untimely prevent either successful mating or fertilization of embryos in primates. |
C | Distinct difference in size or appearance between the sexes of an animal in addition to difference between the sexual organs themselves. |
D | Distinct genetic differences between the sexes of an animal within the same species. |
Question 7 |
A | Social groups are always highly beneficial to individual primate. |
B | All primates species are territorial. |
C | All primates have home ranges, but only some species are territorial. |
D | All primates are arboreal animals. |
E | All primates species compete vigorously for mating rights. |
Question 8 |
A | Primates who rely heavily on scavenging (feed on dead animal) to obtain food. |
B | None of the primates have large and prominent incisors. |
C | Primates who rely heavily on gum as their primary food source. |
D | Primates who rely heavily on predatory behaviors (hunting) to obtain food. |
E | Primates who are non-arboreal. |
Question 9 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | The rate at which an animal expends energy to maintain life when at rest. |
C | The rate in which an animal expends energy for genetic diversification. |
D | The rate in which an animal expends energy for mating and reproduction. |
E | The rate in which an organism expends energy to survive (moving around, fighting predators, etc) in the wild without any human intervention. |
Question 10 |
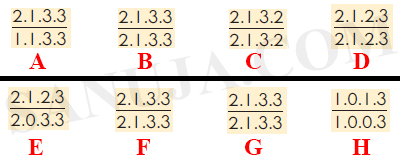
A | Dental formulas A, G , E and H |
B | Dental formulas A, D only |
C | Dental formulas A, E, F and H |
D | Dental formula A only |
E | Dental formulas B , G , E and H |
F | Dental formulas A, C only |
G | Dental formulas A, G only |
Question 11 |
A | Secondary compounds produced and kept in plant tissues to make the plant distasteful or poisonous to herbivores. |
B | A type of growth within the chromosome structure that lead to unfavorable mutations. |
C | Type of molecular evolution occurs through small changes in the molecular or cellular level. |
D | Are mammals that give birth to live young that continue their development in a pouch equipped with mammary glands. |
E | One of the four bases of the DNA molecule. The complementary base of adenine is thymine. |
F | A type of teeth structure that are common to aboreal primates. |
Question 12 |
A | Almost all primates are tree dwellers. |
B | Primates are our closest relatives. |
C | Primates are our direct ancestors. |
D | Primates have limited diversity compared to humans due to limited specializations within the gene pool. |
Question 13 |
A | Groups are composed of several adult males, adult females, and immature animals. |
B | Females maintain separate home ranges or territories and associate mainly with their dependent offspring. |
C | One adult male and one female form a mating relationship and share a territory with their immature offspring. |
D | One male is paired with two or more females. |
E | One female is paired with two or more males. |
Question 14 |
A | Above statement is false because human brain only consumes about 20% of our metabolic energy. |
B | Above statement is false because it is impossible to measure variables stated above due to great diversity among humans. |
C | Above statement is false because human brain is about 5% of our total body weight. |
D | Above statement is true. |
E | Above statement is false because human brain is about 5% of our total body weight and our brain only consumes about 10% of our metabolic energy. |
Question 15 |

A | Dental formula A |
B | Dental formula C |
C | Dental formula E |
D | Dental formula B |
E | Dental formula G |
F | Dental formula F |
G | Dental formula D |
H | Dental formula H |
Question 16 |
A | all produced by the same gene across different populations. |
B | similar in function, but of different basic structure. |
C | different in different animals, but are modifications of the same basic structure. |
D | all recorded in the fossils found across the world. |
Question 17 |
A | Some primates may hide their young offspring in remote isolated areas of their habitat protect them from predators. |
B | Very young females reproduce more successfully than middle-aged and very old females. |
C | Females provide most of the care for the young than their male counterparts. |
D | Female primates are highly adapted for pregnancy and lactation hence require very small amount of additional energy for such reproductive activities. |
E | Female reproductive success exclusively depends on their ability to find a male partner. |
Question 18 |
A | All primates are characterized by very high parental investments compared to all other species. |
B | Most primate offspring have closer relationships with male parent (father) than their female parent (mother) because fathers invest in offspring the most. |
C | Typically primates with mate guarding behavior tend to have the lowest parental investment. |
D | Parental bonding increase as number of sexual partners decreases. |
Question 19 |
A | insectivore |
B | frugivore |
C | gummivore |
D | folivore |
Question 20 |
A | Aotinae |
B | Cebinae |
C | Atelinae |
D | Lemurinae |
E | Callimiconinae |
Question 21 |
A | Reduce population growth hence lowering population pressures. |
B | Used as a reproductive strategy. |
C | Used as a method to remove undesirable phenotype (eg. disable). |
D | Control hierarchy of the pack. |
E | Reduce competition for resources such as food and shelter for the future generation. |
Question 22 |
A | Infants and juveniles |
B | Reproducing adults |
C | Organisms with low active metabolism |
D | Older generation |
E | Arboreal animals |
F | Terrestrial animals |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, TBA during Winter 2013 and textbook ISBN-978-0-393-93271-3. This version has been updated on between September and December 2015.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.