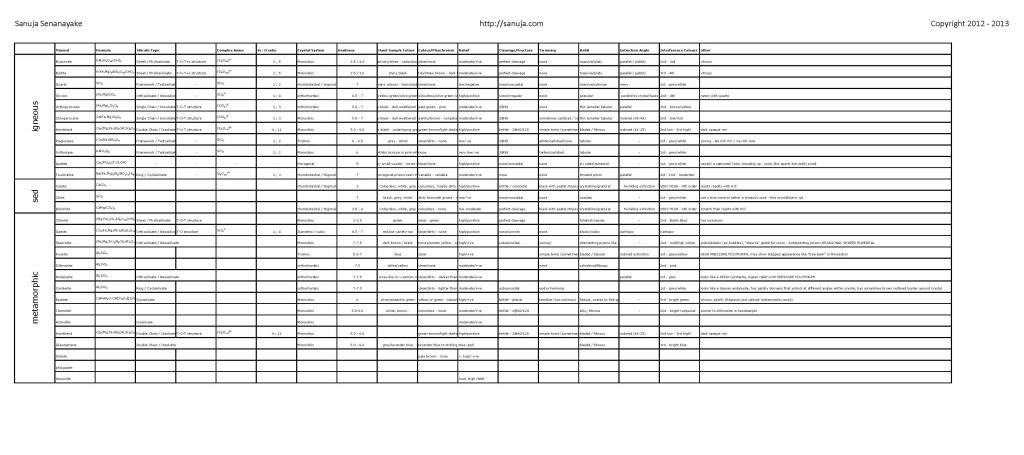
Go to: Midterm Exam
Geology (GLGY 423-UCAL) Final
Some questions have hints and explanations. Click Start to begin.
Start
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 423-UCAL) Final.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Your answers are highlighted below.
Question 1 |
The chemical formula for the Pyroxene iron end-member Orthoferrosilite is Fe2SiO3.
A | False |
B | True |
Question 1 Explanation:
FeSiO3 would be correct.
Question 2 |
What is the chemical formula for Anthophyllite?
A | Ca2Fe5Si8O22(OH)2 |
B | Mg7Si8O22(OH)2 |
C | Ca2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 |
D | Fe7Si8O22(OH)2 |
Question 3 |
__I__ are low-T, slow cooled alkali feldspars and their Optic Axis Plane (OAP) is __II__ to 010.
A | I. Microcline and Sanidine II. parallel |
B | I. Microcline and Sanidine II. perpendicular |
C | I. Sanidine and Orthoclase II. perpendicular |
D | I. Microcline and Orthoclase II. parallel |
E | I. Microcline and Orthoclase II. perpendicular |
Question 4 |
Which of the following analytical methods should you use for determining the crystal structure of a mineral? (choose the best answer)
A | Electron Microprobe |
B | XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence) |
C | SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope) |
D | ICP and AAS |
E | X-ray Diffraction |
Question 4 Explanation:
While none of the above techniques world provide good details on crystal structures, the X-ray Diffraction is the best choice.
Question 5 |
What is the crystal system and the optic sign of the following crystal?

Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
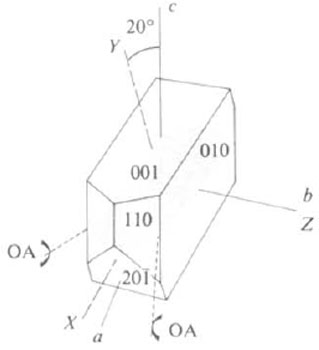
Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
A | Monoclinic / negative |
B | Triclinic / positive |
C | Orthorhombic / negative |
D | Triclinic / negative |
E | Monoclinic / positive |
F | Orthorhombic / positive |
Question 6 |
Which of the following is the best way to identify a mineral?
A | Interference Figure |
B | Properties in hand sample (physical properties) |
C | Refractive Index |
D | Chemical composition analysis. |
E | Birefringence |
Question 7 |
What is the crystal system and the optic sign of the following crystal?

Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
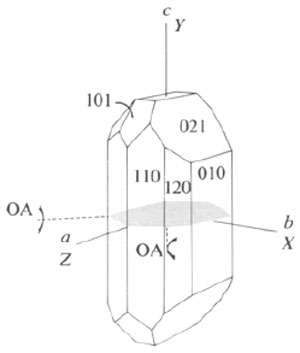
Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
A | Triclinic / positive |
B | Monoclinic / negative |
C | Triclinic / negative |
D | Orthorhombic / negative |
E | Monoclinic / positive |
F | Orthorhombic / positive |
Question 8 |
Given the following information, calculate the 2θ angle.
λ = 0.3419 m
d210 = 3.92564 Å
n = 1
λ = 0.3419 m
d210 = 3.92564 Å
n = 1
A | 22.96 degrees |
B | 4.992 degrees |
C | 11.48 degrees |
D | 6.495 degrees |
E | 2.495 degrees |
Question 8 Explanation:
Don't forget it is asking for 2θ not theta; = 2.495 degrees.

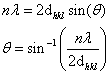
Question 9 |
Minerals with same/similar structure but different compositions is known as...
A | ordered |
B | isomorphs |
C | disordered |
D | polymorphs |
Question 10 |
Which of the following planes lines on the [1 1 1] zone?
A | (112) |
B | (212) |
C | (121) |
D | (122) |
E | (132) |
Question 11 |
Polymorphism is caused by differences in thermodynamic properties at different P-T conditions.
A | True |
B | False |
Question 12 |
What is the best description for the following effect in Calcite crystals?
A | This is a result of internal diffraction of natural light. |
B | This is an optical property that would only occur in Calcite crystals. Hence it is a good property for mineral identification. |
C | This is caused by the difference in velocities between the epsilon and omega rays. |
D | This is caused by the difference in Birefringence. |
E | This is an optical property caused by non-visible UV light interacting with the visible light spectrum. |
Question 13 |
The best property to identify feldspars is the unique twining.
A | False |
B | True |
Question 13 Explanation:
"In metamorphic rocks, and in low temperature diagenetic rocks in which secondary feldspars may grow, feldspars are typically untwinned." - Dr. Sytle Antao
Question 14 |
What is the universally accepted standard thickness of a petrographic thin section?
A | 0.03 nm |
B | 0.30 mm |
C | 0.003 mm |
D | 0.35 mm |
E | 30 000 nm |
Question 14 Explanation:
Remember, 30 000 nm = 0.03 mm
Question 15 |
The "phase-diagrams" are used to describe what type of chemical reactions?
A | Reversible chemical reactions. |
B | Rock forming chemical reactions. Hint: Not the best choice out of the given choices here. |
C | Organic chemical reactions. |
D | Chemical reactions occurred in solid solutions. |
E | Chemical reactions involving solid materials. |
Question 16 |
The length fast direction is at ___ degrees to the length slow direction.
A | 180 |
B | 45 |
C | between 45 - 90 |
D | between 90 - 180 |
E | 90 |
Question 17 |
The chemical formula for the Pyroxene end-member Enstatite is MgSiO3.
A | True |
B | False |
Question 18 |
Which cut will provide a Bxo figure for the following crystal?

Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
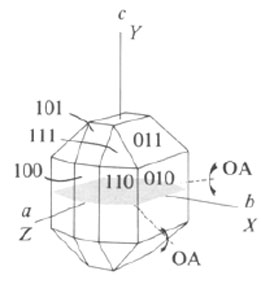
Image credit: Zoltai and Stout (1985) Mineralogy: Problems and solutions
A | 111 |
B | 110 |
C | 101 |
D | 001 |
E | 100 |
Question 19 |
What are the bottom two end-members of Olivine ternary diagram?
A | Forsterite and Ferrosilite |
B | Faylite and Enstatite |
C | Forsterite and Faylite |
D | Forsterite and Enstatite |
E | Ferrosilite and Faylite |
F | Ferrosilite and Enstatite |
Question 20 |
The following interference diagram can be best described as...

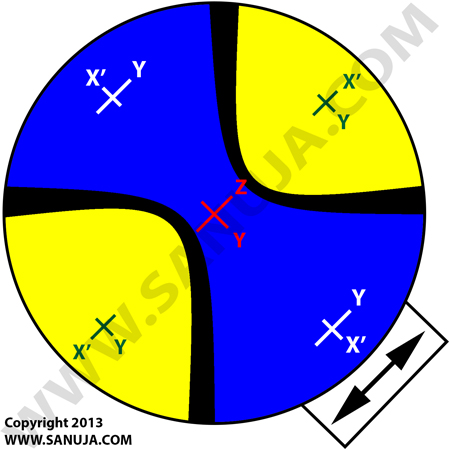
A | a biaxial Bxa negative. |
B | a biaxial Bxa positive. |
C | a biaxial optic axis. |
D | an uniaxial optic axis. |
E | an uniaxial Bxa negative. |
Question 21 |
Uniaxial minerals can have inclined extinction.
A | True |
B | False |
Question 21 Explanation:
straight and symmetrical only
Question 22 |
In X-ray Diffraction Pattern Analysis, the high intensity regions will be recorded as...
A | lower (low amplitude) peaks. |
B | narrower (thinner) peaks. |
C | higher (high amplitude) peaks. |
D | thicker (fatter) peaks. |
Question 23 |
Garnets are isotropic minerals.
A | True |
B | False |
Question 23 Explanation:
Not always buddy!
Question 24 |
Alkali feldspars may have several different types of exsolutions. Which of the following type of exsolution can only be observed under X-ray techniques?
A | Antiperthite |
B | Macroperthite |
C | Perthite |
D | Microperthite |
E | Cryptoperthite |
Question 25 |
The T-O-T offsets structures in clinopyroxenes are situated in such...
A | all facing the same direction. |
B | randomly arranged T-O-Ts alternates every two chains. |
C | longer a - axis compared to the a-axis length of the orthopyroxenes. |
D | alternating between positive and negative faces. |
Question 26 |
In plagioclase solid solution composition diagram, the Albite melting occur at ____ Anorthite melting point.
A | low temperatures compared to |
B | high temperatures compared to |
C | same temperature as |
Question 27 |
Does (123) plain lines in the [210] zone?
A | Yes |
B | No |
Question 27 Explanation:
No because (1X2) + (2X1) + (3X0) is not equal to zero.
Question 28 |
Which of the following is the most dense mineral in terms of it's chemical structure?
A | Carbonates |
B | Kyanite |
C | Epidote |
D | Sillimanite |
E | Andalusite |
Question 29 |
Electromagnetic radiation is always....
A | constructive |
B | destructive |
C | confined and non-scattering |
D | constructive and destructive |
Question 30 |
__I__ temperature reactions will result in __II__.
A | I. high II. low symmetry. |
B | I. low II. high symmetry. |
C | I. high II. ordered minerals. |
D | I. low II. disordered minerals. |
E | I. high II. high symmetry. |
Question 31 |
The analytical methods, ICP and AAS will destroy the tested sample and often the same sample cannot be used for further analysis.
A | False |
B | True |
Question 32 |
Which of the following is the most dense mineral group in terms of it's chemical structure?
A | Amphiboles |
B | Olivines |
C | Pyroxenes |
Question 33 |
What is the Miller index for 10a: 3b: 5c?
A | (1/10 1/3 1/5) |
B | (3 10 6) |
C | (10 3 5) |
D | (1 5 3) |
E | (5 3 10) |
Question 34 |
High temperature and/or dry conditions favors the growth of __I__ crystals over __II__ crystals.
A | I. orthopyroxenes II. clinopyroxenes |
B | I. olivine II. pyroxenes |
C | I. pyroxenes II. olivine |
D | I. hydrous II. anhydrous |
E | I. clinopyroxenes II. orthopyroxenes |
Question 35 |
Given the following information, calculate the wavelength in nm.
Birefringence: 0.024
Thickness of the slide: 0.03 mm
Birefringence: 0.024
Thickness of the slide: 0.03 mm
A | 2.14 -3 nm |
B | 560 nm |
C | 5.60 10-4 nm |
D | 720 nm |
E | 7.20 x 10-4 nm |
F | 650 nm |
Question 35 Explanation:
Question 36 |
Abundance of water in a olivine forming environment will result in formation of serpentine and talc.
A | False |
B | True |
Once you are finished, click the button below. Any items you have not completed will be marked incorrect.
Get Results
There are 36 questions to complete.
← |
List |
→ |
Return
Shaded items are complete.
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | End |
Return
You have completed
questions
question
Your score is
Correct
Wrong
Partial-Credit
You have not finished your quiz. If you leave this page, your progress will be lost.
Correct Answer
You Selected
Not Attempted
Final Score on Quiz
Attempted Questions Correct
Attempted Questions Wrong
Questions Not Attempted
Total Questions on Quiz
Question Details
Results
Date
Score
Hint
Time allowed
minutes
seconds
Time used
Answer Choice(s) Selected
Question Text
All done
Need more practice!
Keep trying!
Not bad!
Good work!
Perfect!
You may download this exam as a PDF file here.
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Sytle Antao during Fall 2013.
FAQ | Report an Error.
Point group animation test run
Lab final cheat sheet