Notice
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midterm Exam
Geology (GLGY 201-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 201-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | 5 - 7km |
B | 500 - 1000 m |
C | 40 - 50 km |
D | 15 - 20 km |
E | 1000 - 1500 m |
Question 2 |
A | An area that is damaged by a recent earthquake. |
B | An area where geoscientists predicted to have an earthquake in near future. |
C | An area that has been known to have earthquakes in high frequency in the past. |
D | The epicenter of an earthquake. |
E | None of the listed answers are correct. |
Question 3 |
A | The water table must be relatively high in the wetland regions. |
B | The vadose zone must be extremely large (deep) in the wetland regions. |
C | The permeability must be very low in the wetland regions. |
D | The hydraulic head must be very high in the wetland regions. |
Question 4 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | on overriding plate , landwards |
C | seawards , on the extinct arc |
D | landwards , on overriding pate |
Question 5 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | A supercontinent that consisted of today’s South America, Africa, Antarctica, India, and Australia. |
C | The ocean that was once covered the Alberta region, which helped the formation of oil/gas deposits. |
D | A proposed Precambrian supercontinent that existed
around 1 billion years ago. |
E | A continent in the early Paleozoic Era composed of today’s North America and Greenland. |
Question 6 |
A | A meander that has been cut off yet remains filled with water forms an oxbow lake. |
B | Melting of glaciers due to friction between the ground and itself forms oxbow lakes at the base of the glacier. |
C | All meandering rivers always from oxbow lakes. |
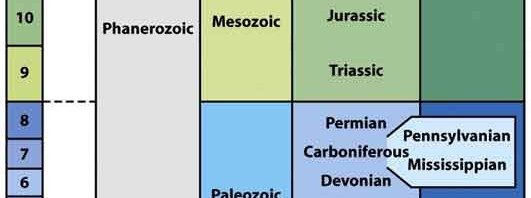
D | Melting of glaciers at the surface (top) due to the heat from sun result in formation of oxbow lakes on top of the glacier itself. |
E | Oxbow lakes are formed as a result of downcutting of the river into soft sediments hence they are unusually deep areas of a river. |
Question 7 |
A | focus |
B | epicenter |
C | slip point |
D | trigger point |
Question 8 |
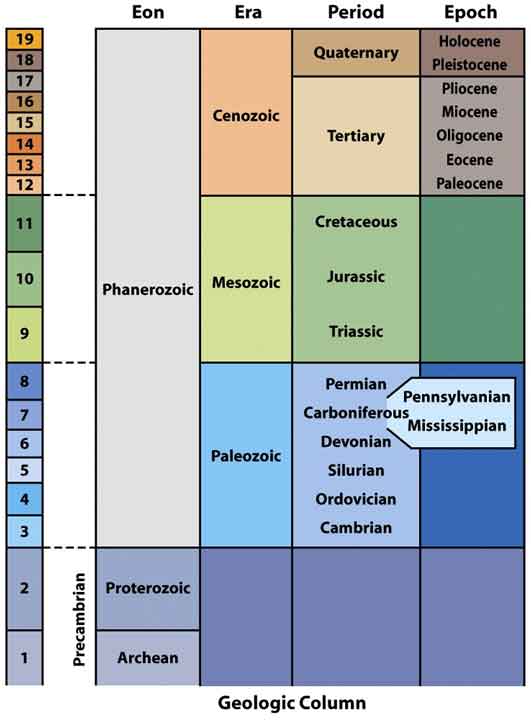
What is 1A on the following diagram? (ID-GLF-24)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.
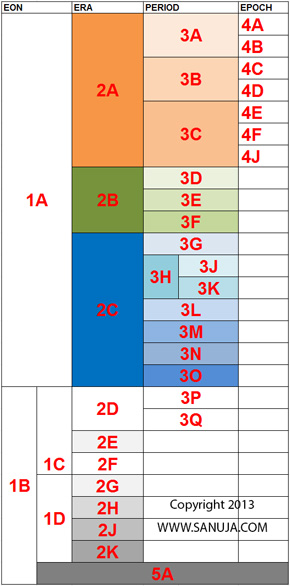
A | Proterozoic |
B | Mesozoic |
C | Pennsylvanian |
D | Phanerozoic |
E | Cenozoic |
Question 9 |
A | Thermosphere |
B | Ionosphere |
C | Stratosphere |
D | Exosphere |
E | Troposphere |
F | Mesosphere |
Question 10 |
A | We cannot directly measure stress, but we can infer stress using strain preserved as deformations in minerals and rocks. |
B | We measure stress based on detection of earthquakes and their magnitudes with respect to location. |
C | We measure stress using changes in pressure and temperature observed within geologic materials over a period. |
D | None of the answers are correct. |
E | We measure stress using specialized equipment that keep track of movement of geologic masses. |
Note: Most than one answer is correct. But on multiple choice exams, you should choose the MOST suitable answer. Consider this question as a good example for your future university exams.
Question 11 |
A | Change in stress fields during metamorphism creating a differential stress which result in lineation of minerals. |
B | Change in pressure and temperature in magma underground which eventually leads to fractional crystallization. |
C | Forces and events leading to a large structural deformation of the Earth's lithosphere resulting mountain building. |
D | Collision of two or more air masses which result in formation of clouds, wind and rain. |
E | Movement of tectonic plates that result in formation of new crust due to upwelling of magma. |
Question 12 |
A | slab pull |
B | suction force |
C | ridge push |
D | trench roll back |
Question 13 |
A | It measures the largest clast/sediment size a stream/river can transport. |
B | It measures the rate of sediment supply to a stream/river system. |
C | It measures the volume of sediments transported by a stream/river system. |
D | It measures the rate at which the transport system deposit its load. |
E | It measure the flow rate of sediments at a fixed given location. |
Question 14 |
A | Weight of the materials used to construct the road surface is effecting the groundwater pressures in the subsurface. |
B | The groundwater must be flowing at a faster rate during wet spring and summer than during winter causing subsurface erosion. |
C | There must be a very large cone of depression directly under the road surface in question causing surface to subside during warm and dry seasons. |
D | Pore pressures that holds the grains apart fluctuates causing subsidence during warm summers and uplift during wet winters and springs. |
Question 15 |
A | Metamorphic rocks due to contact metamorphism. |
B | Igneous rocks due to uplift. |
C | Sedimentary rocks due to regional subduction. |
D | Sedimentary rocks due to regional heating. |
Question 16 |
A | Ridge or hill top |
B | Valley or topographic depression |
C | Reverse fault line |
D | Normal fault line |
Question 17 |
A | Induced stability |
B | Orogeny |
C | Equilibrium |
D | Isostasy |
Question 18 |
A | disintegrate |
B | bent away from the normal |
C | split into several rays |
D | bent towards the normal |
E | be refracted |
Question 19 |
A | increase in density. |
B | decrease in density of the medium. |
C | increase in density of the medium. |
D | increase in travel distance. |
Note: Any changes in density of the medium affect both P and S waves.
Question 20 |
A | Surface seismic waves are the fastest in terms of travel time. |
B | Seismic waves travel faster in high density mediums. |
C | Seismic waves are able to sustain their energy in softer mediums for a longer period of time. |
D | Seismic waves were first discovered by Andrija Mohorovicic. |
E | Seismic waves that enters a faster medium from a slower medium will undergo refraction towards the normal. |
Question 21 |
A | Appalachian orogeny occurred after the Grenville orogeny. |
B | Allegheny Mountains formed before the both of the Appalachian and Grenville orogenies. |
C | Appalachian orogeny occurred at the same time as the Grenville orogeny. |
D | Appalachian orogeny is occurred as a result of four separate continental collisions. Hint: Three separate continental collisions. |
Question 22 |
A | 125 Ma |
B | 100 Ma |
C | 250 Ma |
D | 300 Ma |
E | 375 Ma |
Question 23 |
-Deformation
-Faulting
-Folding
-Partial melting
-Foliation
-Metamorphism
-Glaciation
-Erosion
-Sedimentation
A | All of the above can be observed in mountain building processes. |
B | Partial melting and Sedimentation |
C | Partial melting, Sedimentation and Glaciation |
D | Glaciation and Sedimentation |
E | Partial melting |
Question 24 |
A | oxygen |
B | nitrogen |
C | carbon dioxide |
D | water vapor |
E | ammonia |
Question 25 |
A | Normal faults |
B | Reverse faults |
C | Abnormal faults |
D | Strike-slip faults |
E | Thrust faults |
Question 26 |
A | Theory of Rock Cycle |
B | Theory of Plate Tectonics |
C | Principle of Original Horizontality |
D | Principle of Uniformitarianism |
E | Theory of Geologic Evolution |
F | Principle of Superposition |
Question 27 |
A | It occurs when the last member of a given kingdom dies without producing any offspring. |
B | It occurs when the last member of a given genus dies without producing any offspring. |
C | It occurs when the last member of a given family dies without producing any offspring. |
D | It occurs when the last member of a given species dies without producing any offspring. |
E | It occurs when the last member of a given class dies without producing any offspring. |
Question 28 |
A | phylogenetic tree |
B | taxonomy diagram |
C | ancestral diagram |
D | hierarchical diagram |
E | historical tree |
Question 29 |
A | 5% |
B | 31.6% |
C | 5.5% |
D | 0.5% |
Question 30 |
A | A supercontinent that consisted of today’s South America, Africa, Antarctica, India, and Australia. |
B | The creatonic platform that forms the modern day Canada, USA and Mexico. |
C | The ocean that was once covered the Alberta region, which helped the formation of oil/gas deposits. |
D | A continent in the early Paleozoic Era composed of today’s North America and Greenland. |
E | A proposed Precambrian supercontinent that existed
around 1 billion years ago. |
Question 31 |
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.
A | Cambrian |
B | Silurian |
C | Devonian |
D | Paleogene |
E | Cretaceous |
Question 32 |
A | exosphere |
B | mesosphere |
C | thermosphere |
D | ionosphere |
E | stratosphere |
F | troposphere |
Question 33 |
A | Subsidence |
B | Uplift |
C | Smaller lobes |
D | Downcutting |
E | Headward erosion |
Question 34 |
A | Within sedimentary rocks |
B | Withing igneous rocks |
C | Within fluvial deposits |
D | Within metamorphic rocks |
E | Within underwater mudslides |
Question 35 |
A | Siltstone |
B | Conglomerate |
C | Mudstone |
D | Sandstone |
Question 36 |
A | stratosphere |
B | thermosphere |
C | troposphere |
D | exosphere |
E | mesosphere |
Question 37 |
A | I. anticlines II. synclines |
B | I basins II. arcs |
C | I. synclines II. anticlines |
D | I. arcs II. basins |
Question 38 |
A | Asymmetric syncline |
B | Overturned syncline |
C | Asymmetric anticline |
D | Symmetric anticline |
E | Symmetric syncline |
Question 39 |
A | Earth's crust |
B | Radioactive decay within the Earth's core |
C | Earth's mantle |
D | Heat absorbed by surface rocks |
E | Friction heat produced at plate margins |
Question 40 |
What is 3H on the following diagram? (ID-GLF-30)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.

A | Permian |
B | Jurassic |
C | Cretaceous |
D | Pennsylvanian |
E | Devonian |
F | Carboniferous |
Question 41 |
A | Hawaiian Islands |
B | Canadian Rockies |
C | Himalayas |
D | Basin and Range |
Question 42 |
A | Soft substrate with high degree of erosion |
B | Very low stream gradient |
C | High sediment carrying capacity |
D | Narrow flood plains |
Question 43 |
A | Divergent lifting |
B | Convergence lifting |
C | Orographic lifting |
D | Frontal lifting |
E | Convective lifting |
Question 44 |
A | Cooling or heating of air or matter without the addition or subtraction of atoms or molecules. |
B | Cooling or heating of air or matter through geologic uplift. |
C | Cooling or heating of air or matter without increasing or decreasing of pressure. |
D | Cooling or heating of air or matter through compression solidification or decompression melting. |
E | Cooling or heating of air or matter without decreasing or increasing of temperature. |
F | Cooling or heating of air or matter without the addition or subtraction of thermal energy. |
Question 45 |
A | P-waves disappeared at the mantle-outer core boundary |
B | S-waves disappeared at the mantle-outer core boundary |
C | L-waves disappeared at the mantle-outer core boundary |
D | R-waves disappeared at the mantle-outer core boundary |
Question 46 |
A | precipitation. |
B | transpiration. |
C | sublimation. |
D | evaporation. |
E | infiltration. |
Question 47 |
A | About 30 to 40 km |
B | About 50 to 70 km |
C | About 0 to 5 km |
D | About 90 to 100 km |
E | About 10 to 15 km |
Question 48 |
A | plinean |
B | strombolian |
C | surtseyan |
D | vulcanian |
E | phreatic |
Question 49 |
A | Interior waves |
B | Love waves |
C | Body waves |
D | Rayleigh waves |
Question 50 |
A | on the continental shelf |
B | in rift valleys |
C | on the abyssal plain |
D | in oceanic trenches |
Question 51 |
A | Carbon, hydrogen and oxygen |
B | Carbon and hydrogen |
C | Carbon and oxygen |
D | Carbon and nitrogen |
E | Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen |
Question 52 |
A | pressures. |
B | strain. |
C | stress. |
D | lineation. Hint: This is true, but this is an observation and not a measurement. |
E | foliations. Hint: This is true, but this is an observation and not a measurement. |
Question 53 |
A | 250 parent isotopes |
B | 125 parent isotopes |
C | 100 parent isotopes |
D | 160 parent isotopes |
E | 40 parent isotopes |
Question 54 |
A | Sm/Nd |
B | K/Ar |
C | Rb/Sr |
D | U/Pb |
Question 55 |
A | lowering of the groundwater table at the regional scale. |
B | increased availability of groundwater in shallow wells. |
C | lowering of the groundwater table at the global scale. |
D | raising of the groundwater table at the regional scale. |
E | raising of the groundwater table at the global scale. |
Question 56 |
A | Joints are usually associated with igneous processes and faults are usually associated with orogenic processes. |
B | Joints are much smaller in scale than faults. |
C | Joints are planar metamorphic fabrics while faults are planer surfaces of physical separations within rocks. |
D | Joints are fractures that have no offsets, while faults are fractures with offsets. |
E | Joints only occur in softer materials such as sediments and faults occur in hard rocks. |
Question 57 |
A | shear |
B | stress |
C | deformation |
D | strain |
Question 58 |
A | Theory of Plate Tectonics |
B | Principle of Original Horizontality |
C | Principle of Uniformitarianism |
D | Theory of Geologic Evolution |
E | Principle of Superposition |
Question 59 |
A | Marginal faults |
B | Inactive faults |
C | Active faults |
D | Crustal faults |
E | Blind faults |
Question 60 |
A | Early Cenozoic |
B | Late Cenozoic |
C | Late Mesozoic |
D | Early Cambrian |
E | Early Proterozoic |
Question 61 |
A | basalt and shale |
B | shale and limestone |
C | shale and gabbro |
D | basalt and gabbro |
Question 62 |
A | The ocean that was once covered the Alberta region, which helped the formation of oil/gas deposits. |
B | A continent in the early Paleozoic Era composed of today’s North America and Greenland. |
C | A proposed Precambrian supercontinent that existed
around 1 billion years ago. |
D | None of the answers are correct. |
E | A supercontinent that consisted of today’s South America, Africa, Antarctica, India, and Australia. |
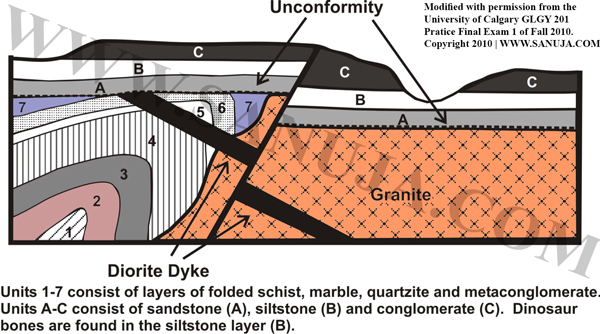
Question 63 |

I. Deposition and folding of units 1 to 7
II. Intrusion of the granite pluton
III. Deposition of units A to C
IV. Formation of the unconformity
V. Faulting
VI. Intrusion of the gabbro dyke
A | I (oldest) , III , VI , IV , II , V (youngest) |
B | V (oldest) , III , VI , IV , II , I (youngest) |
C | VI (oldest) , I , III , V , II , IV (youngest) |
D | VI (oldest) , II , III , IV , I , V (youngest) |
E | V (oldest) , II , VI , IV , III , I (youngest) |
F | I (oldest) , II , VI , IV , III , V (youngest) |
Question 64 |
A | fractional melting |
B | decompression crystallization |
C | partial crystallization |
D | fractional crystallization |
Question 65 |
A | I. geologic materials that act as a barrier to flow II. geologic materials that act as a barrier to flow |
B | I. subsurface structures that allow free flow of water II. subsurface regions where water accumulates |
C | I. subsurface regions where water accumulates II. subsurface structures that allow free flow of water |
D | I. sediment or rock structures that has very low permeability II. sediment or rock structures that has very high permeability |
E | I. also known as vadose zones II. also known as zones of saturation |
F | I. geologic materials that transmit water II. geologic materials that act as a barrier to flow |
Question 66 |
A | asymmetrical anticline |
B | asymmetrical syncline |
C | symmetrical syncline |
D | symmetrical anticline |
Question 67 |
A | Kerogen forms at the Earth's surface. |
B | Highly permeable rocks make very good petroleum seals/traps. Hint: Seal or trap rock/layers must be non-permeable to prevent hydrocarbons from escaping. |
C | Permeability refers to the fraction of open space within rocks. |
D | Oil window is smaller that that of natural gas window. |
E | Increasing depth often increase in hydrocarbon production. Hint: Yes, when you are within an oil/gas windows. But just because you increase in depth, doesn't mean it will favor formation of oil/gas. |
Question 68 |
A | alluvium fan. |
B | alluvium. |
C | braided plane. |
D | stream terraces. |
E | graded deposits. |
Question 69 |
What is 2A on the following diagram? (ID-GLF-24)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.

A | Pennsylvanian |
B | Cenozoic |
C | Proterozoic |
D | Phanerozoic |
E | Mesozoic |
Question 70 |
A | The temperature below which isotopes are no longer free to move. |
B | The temperature above which crystals are first formed. |
C | The temperature below which magma no longer have the ability to erupt out of the volcano. |
D | The temperature above which the water is neither a gas nor a liquid. |
E | The temperature below which crystals are first formed. |
Question 71 |
A | Between Mesosphere and Troposphere. |
B | Around the 45 km altitude. |
C | Between Mesosphere and Stratosphere. |
D | Between Mesosphere and Thermosphere. |
E | Around the 10 km altitude. |
Question 72 |
Note: Do not worry about the vector arrows. This animation was created for 300/500-level structure classes.
A | Right lateral strike-slip fault |
B | Reverse fault |
C | Normal fault |
D | Left lateral strike-slip fault |
E | Not enough information is provided in the question. |
Question 73 |
A | The term focus is used when the earthquake occur under water/in oceans while the term epicenter is used when it occurs on land. |
B | They are interchangeable terms used geoscientists to describe earthquakes. |
C | The focus is the location where a fault slips during an earthquake while epicenter is the point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus of an earthquake. |
D | The focus is the geographic location of the seismometer and the epicenter is the physical position of the earthquake. |
E | The epicenter is the location where a fault slips during an earthquake while focus is the point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus of an earthquake. |
Question 74 |
A | Bottled gas |
B | Gasoline |
C | Heating oil |
D | Natural gas |
E | Tar |
F | Kerosene |
Question 75 |
What is 3G on the following diagram? (ID-GLF-39)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.

A | Cretaceous |
B | Jurassic |
C | Devonian |
D | Eocene |
E | Permian |
F | Cenozoic |
Question 76 |
What is 3L on the following diagram? (ID-GLF-20)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.

A | Triassic |
B | Ordovician |
C | Jurassic |
D | Pennsylvanian |
E | Devonian |
Question 77 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | A group of fossils native to a specific region. |
C | A set of fossils belongs to the same family of organisms. |
D | A group of fossil species found in a specific sequence of sedimentary rock. |
E | A set of fossils that can be arranged in chronological order. |
Question 78 |
A | Potassium |
B | Chloride |
C | Sodium |
D | Magnesium |
E | Calcium |
Question 79 |
Please pay attention to the circled (green) area of the image.
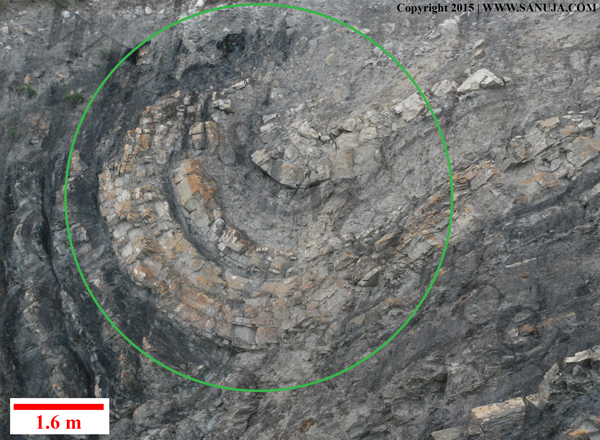

A | deformation that resulted in faulting. |
B | deformation caused by extensional tectonics. |
C | deformation that resulted in folding. |
D | structural feature originated primarily due to an igneous event. |
Question 80 |
A | P-wave |
B | Shock wave |
C | Surface wave |
D | S-wave |
E | Body wave |
Question 81 |
A | It occurs when ground shake due to P-wave vibrates sediments hard enough resulting solids behaving like liquids. |
B | It occurs when sediments from deep underground which are formed under high pressure were exhumed in a short period of time. |
C | It occurs due to nuclear radiation caused by decomposition of radioactive elements within sediments and minerals. |
D | It occurs as the heat from magma melts the wall rock (country rock) resulting melting of the surrounding. |
E | It occur when the pore water pressure increased enough to push sediment grains apart from each other. |
Question 82 |
A | 3.92 Ga |
B | 3.87 Ga |
C | 3.55 Ga |
D | 4.54 Ga |
E | 4.03 Ga |
Question 83 |
A | They are usually stationary and has been that for since the beginning of the Earth. |
B | They are defined by the magnetic forces of the Earth. |
C | They usually coincide with plate boundaries. |
D | They runs parallel to the equator of the Earth. |
E | They only occur in ductile regions. |
Question 84 |
A | Weekly |
B | Monthly |
C | Yearly |
D | Daily |
Question 85 |
A | 100 times less |
B | 10 times more |
C | 100 times more |
D | 10 times less |
E | 1 times less |
F | 1 times more |
Question 86 |
A | The fossilization process in which plant material becomes transformed into rock by the precipitation of silica from groundwater. |
B | The process by which atoms dissolved in a solution come together and form minerals. |
C | Formation of new minerals when preexisting minerals change into new minerals as a result of an increase in pressure and temperature. |
D | The clumping together of clay suspended in river water into bunches that are large enough to settle out. |
E | The process by which a magma becomes progressively more silicic as it cools, because early formed crystals settle out. |
Question 87 |
A | Magma migration |
B | Volcanic eruptions |
C | Sudden changes in mineral structures |
D | Human interference such as construction and nuclear detonations |
E | Crustal fault slips |
Question 88 |
A | Flow rate of the water (velocity) and the volume of water. |
B | Sediment load of the river/stream. |
C | Resistance of its walls to erosion slumping. |
D | Its elevation from the sea level. |
Question 89 |
Precambrian is divided into two Eons as shown on the following diagram as 1C and 1D. What are they? (ID-GLF-62)
Note: DO NOT scroll down to the Geologic Time scale on this page. Answer this question without using any AIDS.

A | Cenozoic and Mesozoic |
B | Phanerozoic and Proterozoic |
C | Proterozoic and Archean |
D | Paleozoic and Phanerozoic |
E | Paleozoic and Mesozoic |
Question 90 |
A | Gradual decrease in grain size from corasest to finest as moving from the mouth to the distal edge. |
B | Muddy deposits closer to the mouth and sandy deposits distally at the edge. |
C | High clastic sediment deposits on the edge of the fan. |
D | Very thick sandy deposits distally on the edge of the fan. |
Question 91 |
A | About 30 km |
B | About 10 km |
C | About 100 km |
D | About 1 km |
E | About 5 km |
Question 92 |
A | Factor of 1 |
B | Factor of 10,000 |
C | Factor of 20,000 |
D | Factor of 2 |
E | Factor of 3 |
Question 93 |
A | Deposits of rock fragments and sediments left behind after a glacier has migrated through a region. |
B | Accumulation of microscopic shells and file flakes of clay at the ocean floor. |
C | Sudden decrease in energy of a river system result in accumulation of the bedloard. |
D | Erosion of high standing sedimentary structures and subsequent deposition of the materials downstream. |
E | Deposition of organic matter on terrestrial sediments due to decay of plants and organisms. |
Question 94 |
A | Brittle deformation |
B | At extensional settings |
C | Low pressure and high temperature |
D | High pressure and low temperature |
E | Ductile deformation |
Question 95 |
A | It measures the change in capacity of sediment load over a distance. |
B | It measures the rate at which the transport system deposit its load over a distance. |
C | It measures the elevation change over the distance of flow. |
D | It measures the largest clast/sediment size a stream/river can transport. |
E | It measures the speed at which the river flows. |
Question 96 |
A | Process of magma generation and solidification. |
B | Process of biological and geological evolution of life and Earth. |
C | Study of the origins of rocks and minerals. |
D | Study of the origin of Earth and its evolution. |
E | Process of mountain building. |
Question 97 |
A | Skeletons |
B | Burrows |
C | Shell fragments |
D | Petrified wood |
E | Amber embedded fossils |
Question 98 |
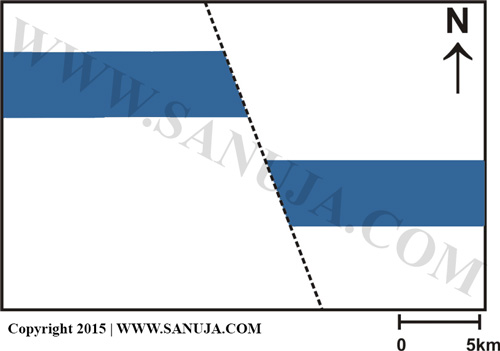
A | Normal fault |
B | Thrust fault |
C | Left-lateral strike slip fault |
D | Right-lateral strike slip fault |
E | Reverse fault |
Question 99 |
A | inclusions are younger than the rock which contains them. |
B | inclusions only occur in magma chambers. |
C | younger rocks are always will be on top of the older rocks. |
D | inclusions never appear on the surface of rocks. |
E | inclusions are always older than the rock which contains them. |
Question 100 |
A | It is a line on a map used to separate different air pressures. |
B | It is a bar where ice cold drinks are served only for cool geoscientists. |
C | It is an imaginary line that separates the four major layers of atmosphere. |
D | It is a representation of pressure - temperature boundaries which specific minerals may form out of a magma. |
E | It is a graphical representation of change in temperature with depth in the lithosphere. |
Question 101 |
A | Higher the friction between a glacier and the ground, faster the migration of the glacier. |
B | Higher the mountains in collisional or convergent orogen, the deeper the crustal root. |
C | Higher the depth of a river, larger the volume of sediment deposition and accumulation on the river bed. |
D | Plate tectonic movement is mostly driven by the energy obtained through the rotation of the Earth. Hint: This is what some scientists thought long time ago. This has been proven to be incorrect. |
E | Dykes are formed primarily due to preexisting weak planes of the country rock. |
Question 102 |
A | Material moves back and forth parallel to the wave direction. |
B | They are P-waves that intersects the land surface. |
C | Causes ground to ripple up and down like water waves in a lake. |
D | Slower than S-waves but faster than Love waves. |
E | They are S-waves that intersects the land surface. |
Question 103 |
A | Wadati-Benioff discontinuity |
B | Mohorovic discontinuity |
C | Mercalli discontinuity |
D | Wegener discontinuity |
Question 104 |
A | Strike-slip environments |
B | Collisional orogenesis environments |
C | Mid-oceanic ridge environments |
D | Extensional rifting environments |
Question 105 |
A | Extraction of groundwater in large volumes in a small period of time. |
B | Extraction of groundwater in large volumes in a long period of time. |
C | Higher rate of leaking groundwater into rivers and lakes due to higher formation pressures. |
D | Injection/addition of water into the ground due to heavy rainfall. |
Ref: Dr. Alexander Dutchak Fall 2015 lecture notes.
Question 106 |
A | Mantle is ductile |
B | Lack of water |
C | Lower temperatures |
D | Increase in pressure |
E | Increase in frictional forces |
Question 107 |
A | Vesicles and voids within matrix |
B | Inter granular porosity |
C | Dissolution |
D | Reef framework |
Question 108 |
A | surface erosion. |
B | fracture network. |
C | drainage erosion. |
D | dendritic network. |
E | headward erosion. |
Question 109 |
A | hot spots |
B | subduction zones |
C | transform zones |
D | mid-ocean ridges |
Question 110 |
A | Mesopause |
B | Orogeny |
C | Isostasy |
D | Induced equilibrium |
E | Accretion |
Question 111 |
A | Compression pressure along the contact boundary between two moving sections. |
B | Non-uniform boundary conditions between two moving sections. |
C | Ductile nature of the two moving sections. |
D | Mineral alignment along the contact points between two moving sections. |
E | Friction between two moving sections. |
Question 112 |
A | Aquifers with very high porosity, but very low permeability. |
B | Unconfined aquifers with very high permeability. |
C | Aquifers with very low porosity and permeability. |
D | Confined aquifers with very high permeability. |
Question 113 |
A | Folds |
B | Fractures |
C | Upside down beds (oldest on top) |
D | Faults |
Question 114 |
A | Protista |
B | Animalia |
C | Fungi |
D | Bacteria |
E | Plantae |
Question 115 |
A | decomposition temperature. |
B | ideal temperature. |
C | oil window. |
D | critical temperature. |
E | ideal window. |
F | critical window. |
Question 116 |
A | most likely maintain the original mineral composition |
B | change its orientation |
C | change its location |
D | change its shape by shortening |
E | retains the primary igneous structures. |
Question 117 |
A | headward erosion by one stream causes the stream to intersect another stream. |
B | reversing of the flow direction due to change in the direction of slope due to tectonic of other events. |
C | water levels are not high enough to maintain the flow resulting in change in stream direction. |
D | water levels and flow rates are too high for a river bed to maintain its shape result in collapse of valleys or canyons. |
Question 118 |
A | Seismic-moment magnitude scale |
B | Richter scale |
C | Wadati-Benioff scale |
D | Mercalli scale |
Question 119 |
A | climate , weather |
B | temperature . heat |
C | weather seasons , plate tectonics |
D | precipitation . rain |
E | high pressure systems , low pressure systems |
Question 120 |
A | carbon dioxide |
B | water |
C | ammonia |
D | methane |
E | nitrogen |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 |
| 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 |
| 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 |
| 101 | 102 | 103 | 104 | 105 |
| 106 | 107 | 108 | 109 | 110 |
| 111 | 112 | 113 | 114 | 115 |
| 116 | 117 | 118 | 119 | 120 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Gerald Osborn during Fall 2010 and textbook ISBN-978-0-393-93750-3. This version has been updated on between September and December 2015 using excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Glenn Dolphin, Alex Dutchak and Dr. Brandon Karchewski during Fall 2015.
FAQ | Report an Error
Concepts and Additional Questions for Fall 2010 Final
Important!
↑ Some of these are already in the exam type questions in the quiz(above) ↑
Answers to these will NOT be posted. These are based on 2010 lecture notes!
-Know the definitions and features of Composite Volcanos (CV) and Shield volcanos (SV).
-Types of crystallization processes
-Geologic zones; subduction, mid ocean, etc and their features
-Difference between nonconformity and disconformity.
-Difference between stress and strain.
-Differences between tensile stress, compressional stress and shear stress
-Understanding geologic events based on relative deposition.
-Earthquakes and their nature of intensity.
-Types of waves; S-,P-,L- and R- waves.
-Earth’s components and their variation in composition.
-Be able to interpret features on a given map or cross-section.
-Mohorovic discontinuity and it’s importance to geologic studies.
-Know, asymmetrical syncline/anticline, symmetrical syncline/anticline.
-General history of geology as a study subject.
-Concept; slab pull, ridge push and hypothesis on why these occur.
-You should memorize this time scale. Yes, this will most likely appear on the final, but also very useful for the future of your geologic carrier. Most geologists and geophysicsts remember the Geologic Time Scale with respect to important events took place in the history.