Computer Science 217 – Introduction to Python
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Go to: Midtrem Exam
Computer Science (CPSC 217-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Computer Science (CPSC 217-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%.
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Take a return from the reading function and pass the return to a variable. Then pass the variable to the next function. |
B | In Python 3, you cannot take data from one function and pass it to another. It is not a valid argument. |
C | Take a reading from the first function and pass it to a variable. Then pass the variable to the next function. |
D | After the writing the two functions, make first function equals to the second function. eg. fun1() = fun2() |
Question 2 |
s = 0
while s < 5:
.... s = (s + 1) % 2
.... print (s)
A | 0 1 0 1 0 1 |
B | 1 0 1 0 1 0 |
C | 1 0 1 0 1 0... to infinity |
D | 0 1 0 1 0 1... to infinity |
E | 1 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0... to infinity |
Question 3 |
A | open |
B | sys |
C | file |
D | sttder |
E | math |
Question 4 |
A | True |
B | False |
Windows \r\n
Question 5 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 6 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 7 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 8 |
A | The structure of the data. |
B | The user input processing by the database. |
C | The complexity of the database. |
D | The fail-over rate of a database. |
E | The actual data that being stored. |
Question 9 |
s = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[6,7],[8,9]]
what will be the output if you were to call in len(s) ?
A | 1 |
B | 4 |
C | 2 |
D | 5 |
E | 10 |
Question 10 |
fun1():
.... print ("Done")
A | The function is not defined. |
B | The print statement formatting is wrong. |
C | The indentation pf the function is wrong. |
D | The function failed to return any useful data. |
E | The function lacks any meaningful operations. |
Question 11 |
A | It takes the code from Python 3 and use it to process graphical information using Java. |
B | It injects the codes of Java into a Python 3 program for processing. |
C | It takes the output of the Python 3 program and use it as inputs for Java. |
D | It makes the communication between Python 3 and Java possible by opening input/output sequences on both direction. |
Question 12 |

A | 9 |
B | 3 |
C | [1, 2, 3] |
D | [4, 5, 6] |
E | An error |
Question 13 |
s = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[6,7],[8,9]]
what will be the output if you were to call in s[-2][0] ?
A | 8 |
B | [8,9] |
C | 6 |
D | 2 |
E | Invalid Index Error |
Question 14 |
Python 3 is extensively used in which of the following programs/areas? (Not going to show up on the exam, but just for fun)
A | Online MMO servers |
B | MS Access Database system |
C | Android OS |
D | Windows Server 2012 / Windows 8 Pro |
E | BlackBerry 10 OS |
Question 15 |
data = input("Please enter your name: ").rstrip()
A | To add the carriage return into the input statement. |
B | Take the white space out of the end print statement. |
C | Take the carriage return out of the input statement. |
D | To add the white space formatting at the end of the print statement. |
Question 16 |
data = "A male who lives in Calgary, Alberta, Canada."
A | print([data:25]) |
B | print(data[20: ]) |
C | print(data[25: ]) |
D | print([data:20]) |
E | print(data[ :20]) |
F | print(data[ :25]) |
Question 17 |
A | set of binary codes. |
B | database. |
C | low level programming code. |
D | encrypted text files (128-bit to 256-bit server side). |
Question 18 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 19 |
A | The formal parameters are variables in a function definition and actual parameters are the values passed into a function when it is called in. |
B | The formal parameters are often used by armature programmers while, most companies and professionals opt for actual parameters in a function definition due it's flexibility. Hint: Whhhhahhhat? Nooooo! It is other way around you buffoon! 🙂 |
C | The formal parameters are post defined and actual parameters are pre defined. |
D | The formal parameters are the values passed into a function when it is called in and the actual parameters are variables in a function definition. |
Question 20 |
myList = [ ]
A | append.myList("sanuja") |
B | append.myList(125) |
C | myList.append("125") |
D | myList.append(sanuja) |
Question 21 |
A | Creation of the except block. |
B | Creation of the try block. |
C | Crash of the program. |
D | Quitting the program by quit() function. |
Question 22 |
sanuja = { }
A | sanuja[keyName] = valueName |
B | sanuja["keyName"] = "valueName" |
C | sanuja[keyName] = valueName |
D | sanuja["keyName"] = valueName |
Question 23 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 24 |
A | "\tab text here" |
B | "\space text here" |
C | "\t text here" |
D | "\n text here" |
Question 25 |
data = "Sanuja Senanayake , Calgary , http://sanuja.com , (403) 111-1111"
The elements should seperate; full name, city, web address, phone number. How do you do that?
A | list = split.data(" , ") |
B | list = split.data(" ") |
C | list = data.split(" , ") |
D | data = data.split(" , ") |
E | list = data.split(" ") |
Question 26 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 27 |
4 in [11,4,73,19,13,24]
A | No |
B | False |
C | 4 |
D | Yes |
E | True |
Question 28 |
A | To avoid limitations of Python 3 coding structure. |
B | There is absolutely no reason to create any global variable regardless of the programming language. |
C | Only to create small scale programs. |
D | To avoid repetition of the same variable in several functions. |
E | To create low memory intensive programs. |
Question 29 |
A | Print() |
B | input() |
C | float() |
D | for i in range(9): |
Question 30 |
Find the smallest number in the unsorted list, remove that number and add it to the end o the sorted list. Repeat this sequence until there are no numbers in the unsorted list.
A | selection sort |
B | bubble sort |
C | quick sort |
D | insertion sort |
Question 31 |
A | selection sort |
B | quick sort |
C | bubble sort |
D | loop sort |
E | insertion sort |
Question 32 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 33 |

A | 1 |
B | 9999 |
C | -1 |
D | 0 |
E | 5 |
Question 34 |

A | 3 |
B | [7, 8, 9] |
C | [4, 5, 6] |
D | 2 |
E | 5 |
Question 35 |
A | def function (i, x, y, z) |
B | pass (i, x, y, z) = function (2, 90, 57, 23) |
C | def function (i=2, x=90, y=57, z=23) |
D | function (i=2, x=90, y=57, z=23) Hint: No, you cannot assign default parameters to a function when it is called in! |
Question 36 |
A | my1988 |
B | my Dictionary |
C | c _b999 |
D | myDic |
E | haha |
Question 37 |
A | A dictionary cannot be updated using a loop (for loop or while loop) because a dictionary contains more than one dimension. Hint: You can use a loop with two conditions to append to a dictionary. |
B | In a relational database, the schema describes the structure of the data in the database |
C | Text files and databases are both viable options for managing large amounts of data |
D | In a string, there is a unique index number associated with each value. Hint: Strings do not have index numbers. |
E | A primary key is a unique value associated with each row in a table |
Question 38 |
A | inf = open ("file_name.txt", "a") |
B | inf = open ("file_name.txt", "r") |
C | inf = open ("file_name.txt", "w") |
D | inf = open ("file_name.txt", "e") |
Question 39 |
A | It will skip over the body of the function and run the rest of the code. |
B | It will either crash or look for an except block once it has at least entered the function once. |
C | It will either crash or look for an except block before it will reach the function. |
D | It will stop working, just before it run to to the incorrect values. |
Question 40 |
A | Replacing data with information AFTER processing the initial condition. |
B | Pulling data out one at a time and comparing the values against information. |
C | Splitting of large scale data schemes into small scale schemes. |
D | Replacing data with information BEFORE processing them. |
E | Organization of data into tables. |
Question 41 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 42 |
s = "Love Canada"
A | all of the answers are incorrect! |
B | 10 |
C | 8 |
D | 11 |
Question 43 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 44 |
A | More than one and less than zero |
B | Cannot be more than the number of keys in a particular dictionary |
C | Unlimited given the condition that resources are unlimited |
D | One |
Question 45 |
s1 = [0, 1, 2, 3]
s2 = [4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
A | Slice the either one of the lists into its elements and place them in a new list called s3. |
B | Writing a "for" loop with an empty list called s3 = [] that will take each value of s1 and combine it with s2 using s3.append() |
C | Writing a "while" loop with an empty list called s3 = [] that will take each value of s1 and combine it with s2 using s3.append() |
D | s3 = s1 + s2 |
Question 46 |
A | Use of English language with UTF-8 and up coding system. |
B | Built in libraries and and functions. |
C | Use of command line infrastructure. |
D | Use of binary based commands. |
Question 47 |
A | tp = [ ] |
B | tp = ( ) |
C | tp = { } |
D | tp = " " |
Question 48 |
A | Insertion |
B | Selection |
C | Bubble |
D | Quick |
Question 49 |
A | x and y values are both exclusive. |
B | x is exclusive and y is inclusive. |
C | x is inclusive and y is exclusive. |
D | x and y values are both inclusive. |
Question 50 |
A | A function must be predefined in order to call it in. |
B | A single function cannot have more than one result. |
C | Functions must always return a result. |
D | A function must take a parameter. |
Question 51 |
A | invalid parameter error(s). |
B | runtime error(s). |
C | Boolean error(s). |
D | syntax error(s). |
E | logic error(s). |
Question 52 |

A | 5 |
B | 6 |
C | 8 |
D | 2 |
E | An error |
Question 53 |
while k > 10:
.... print ("ha")
.... k = k + 2
What's wrong with the code?
A | The variable k is not defined causing a NameError |
B | The program will crash due to inaccurate print statement. |
C | The program will NOT crash, but will also provide no print statements in the terminal. |
D | The usage of a while loop instead of a for loop will create inaccurate results. |
Question 54 |

A | 15 |
B | 54 |
C | 19 |
D | 45 |
E | 0 |
Question 55 |
A | 7C4 |
B | 7DDC |
C | 8DCD |
D | 7DC |
Question 56 |
power = input("Please enter a value: ")
answer = 5**power
print (answer)
A | 10 |
B | 125 |
C | Error, mathematical operation with a string. |
D | 25 |
Question 57 |
myList = [1,2,3,8,4,5,6]
A | append.myList(8) |
B | myList.pop(8) |
C | myList.append(8) |
D | myList = [8] |
Question 58 |
value = 55
result = sqrt(55)
print (result)
A | Call in the math library; import math Request the function from sys; sys.sqrt() |
B | Call in the sys library; import sys Request the function from sys; sys.sqrt() |
C | Call in the sys library; import sys Request the function from math; math.sqrt() |
D | Call in the math library; import math Request the function from math; math.sqrt() |
E | Call in the math library; import math |
Question 59 |
A | A dictionary |
B | A string |
C | A list |
D | A tuple |
Question 60 |
A | A dictionary |
B | A while loop |
C | A iteration loop |
D | A for loop |
Question 61 |
A | Machine code |
B | Binary Code |
C | English |
D | Japanese |
E | Python 3 only |
F | Any version of Python up to and including Python 3 |
Question 62 |
A | multipliers |
B | index numbers |
C | lengths |
D | values |
E | keys |
Question 63 |
A | To print out a meaningful error messages. |
B | To crash the program in an event the output is invalid. |
C | To quite a program in an event the output is invalid. Hint: No, you are confused with INPUT is invalid. This answer reads OUTPUT, hence it is wrong. |
D | To limit errors. |
Question 64 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 65 |
s = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[6,7],[8,9]]
what will be the output if you were to call in s[3][1] ?
A | 4 |
B | An Index Error message |
C | 6 |
D | 7 |
E | 5 |
Question 66 |
a = [ ] is a ...
b = { } is a ...
A | a = [ ] is a dictionary. b = { } is a tuple. |
B | a = [ ] is ais a tuple. b = { } is a dictionary. |
C | a = [ ] is a list. b = { } is a dictionary. |
D | a = [ ] is a dictionary. b = { } is a list. |
Question 67 |
A | myList = [peace, "25", sanuja, "666", BBC, 2012] |
B | myList = {peace, "25", sanuja, "666", BBC, 2012} |
C | myList = [2.5, -9.9, "sanuja", 9615, "BBC", 12] |
D | myList = [peace, "25", sanuja, "666", BBC, 2012] |
E | myList = {2.5, -9.9, "sanuja", 9615, "BBC", 12} |
F | myList = (1,2,3,UofC,5.5,#) |
Question 68 |
A | F8D5 |
B | 10 0010 |
C | D56 |
D | 10 1101 |
Question 69 |
A | All of the answers are wrong. |
B | All the keys and associated values in two independent lists. |
C | A list of any dimension, except 1D containing all the values. |
D | All the keys with no value data in a list. |
E | A list of all the values in the dictionary, cbc. |
Question 70 |
A | for p in dic.keys(): |
B | for k in keys.dic(): |
C | for j in key.dic(): |
D | for i in dic.key(): |
Question 71 |
University of Calgary = Calgary
A | No |
B | Yes |
On the left side "University of Calgary" is NOT a valid variable name because you cannot have white space(in this case space) between variable letters. You MAY fix this by replacing a the variable name with, UniversityOfCalgary
Question 72 |
s = [[0,1],[2,3],[4,5],[6,7],[8,9]]
what will be the output if you were to call in s[3] ?
A | 3 |
B | [4,5] |
C | [6,7] |
D | 2 |
Question 73 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 74 |
A | Data |
B | Stack |
C | Text |
D | Heap |
Question 75 |
A | It is used to take commands from several databases for comparison and analysis. |
B | It is a client side programming language used to display server side Python 3 language operations. |
C | It is used to take commands from a database. |
D | It is used to send commands to database. |
Question 76 |
A | print ("It is %.2f" % VARIABLE, "TEXT HERE !") |
B | print ("It is %2f" VARIABLE % , "TEXT HERE !") |
C | print ("It is %.2" % VARIABLE, "TEXT HERE !") |
D | print ("It is 2f" % VARIABLE, "TEXT HERE !") |
E | print ("It is %.2" % VARIABLE, "TEXT HERE !") |
Question 77 |

A | 1 |
B | 0 |
C | 3 |
D | 45 |
E | 9 |
Question 78 |
myName = "Sanuja\nSenanayake"
print (myName)
A | Sanuja\nSenanayake |
B | Sanuja Senanayake |
C | SanujaSenanayake |
D | Senanayake Sanuja |
E | Sanuja Senanayake |
Question 79 |
cost = 55.99
gst_multiplier = 0.07
gst = cost * gst_multiplier
total = cost + gst
print ("The total amount you pay %.2f" % total)
A | No, this program will not work because the GST calculation is wrong for Fall 2012. |
B | Yes, this simple program may work. |
C | No, this program will generate a no print statements because the initial amount is NOT a user input variable. |
D | No, this program will crash due to Syntax Error caused by invalid format specifiers. |
Question 80 |
A | fclosed() |
B | quit() |
C | quit(-1) |
D | closed(-1) |
E | closed() |
Question 81 |
A | del.keys() |
B | delete.test() |
C | del.test() |
D | clear.test() |
E | test.clear() |
Question 82 |
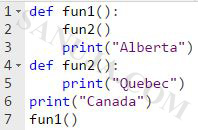
A | Canada Quebec Alberta |
B | An error will be printed because this code is not valid in Python 3. |
C | Canada Alberta Alberta Quebec |
D | Canada Alberta Quebec |
E | Alberta Quebec Canada |
F | Canada Alberta Quebec Alberta |
Question 83 |
A | inf = open ("fileName.txt", r) |
B | inf = open (fileName.txt, "r") |
C | inf = open (fileName.txt, r) |
D | inf = open ("fileName.txt", "r") |
E | inf = open ("fileName.txt", w) |
Question 84 |
A | units |
B | values |
C | commas |
D | keys |
Question 85 |
A | False |
B | True |
Question 86 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 87 |
A | To create Python code with low level programing codes. |
B | To allow flexibility for multiple programming languages to interact with each other. |
C | To lower failure rate of the connection between data and information. |
D | To deal with large amounts of data. |
Question 88 |
A | Yes |
B | No |
Question 89 |
A | True |
B | False |
Question 90 |
A | integer |
B | string |
C | lists |
D | boolean |
E | float |
Question 91 |
A | relatively complex programming language. |
B | low level programming language. |
C | C# based programming language. |
D | high level programming language. |
Question 92 |
A | Data is human readable and text is not human readable. |
B | Data points to information and text point to all global consents and variables. |
C | Text hold program instructions typically in machine code and data point to all global consents and variables. |
D | Data hold program instructions typically in machine code and text point to all global consents and variables. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 |
| 86 | 87 | 88 | 89 | 90 |
| 91 | 92 | End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Ben Stephenson during Fall 2012.
FAQ | Report an Error | Basic Mode-under development
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.