This page is best viewed in desktop mode. If you are using a mobile device, you can switch to desktop site using the switch link at the bottom of the page. Additional tools are available under Geology 491 – Paleobiology and the identification steps chart here. For more in-depth detailed information on how we classify the following fossils, please read, Classification of Fossils.
Category Archives: Earth Science
Also known as Geology, Geosciences, etc. It is a science that deal with Geologic materials and processes which made them. A multidisciplinary field in which also includes Geophysics, Hydrology, Structure and Civil Engineering and many more.
How to use a Brunton Compass
It is essential for a Earth Scientist to be skilled at using the tools of the trade. From day one, students are trained to use the Brunton Compass, a highly popular measuring tool. I am very proud to say it was first designed and developed by a Canadian Geologist, David W. Brunton. If properly used it is a great tool for taking precise geological measurements within few degrees or meters of accuracy.
Introduction to Paleobiology
This is one of the new specializations in Geoscience in which academics study the history of the Earth (or other planets 🙂 ) using fossil records. This is such a large field, it is further broken down into several other specializations such as Paleobotany (plants records), Paleobiochemistry (organic chem) and so on. This diversification has allow scientists from wide range of backgrounds to study the history of Earth. I am going to narrow this article down to Geologists perspective on paleobiology because I am a Geology student myself.
Geologists should study Biology
All scientists are like detectives. Some of us will try to create something for the future or solve problems at hand (For example, Petroleum Geologists) and some of us will try to understand the past in order to improve on how we solve problems. Paleobiology is the later in which we will use the historical records to study the Geological processes in the past and present. Geologists who have some form of education in Biology will most likely find this specialization intriguing. To me this is a good example why I think all three major sciences, Biology, Chemistry and Physics are useful in all flavors of science and engineering.
What do we do?
As mention above, we are interested in historical records preferably well-preserved in the rock and sedimentary record. Most of you heard about dinosaurs from popular media. That is paleobiology! You may argue that it is probably obvious when a Geologist come across a dino bone in the sedimentary record. The is far from the truth because we have to use deductive reasoning in order to arrive at that conclusion. If you talk to anyone who is in the “fossils hunting” field, they will tell you that numerous observations often result in may be one or two identifications of new fossils. Scientifically speaking those Jurassic Park movies are insults to the paleobiology.
One of my professors told me that Geologists love diagrams. Well, he is right and for those who are just getting into this area, flow charts are your friends. Even well experienced Geologists and Paleobiologists use charts to narrow down their observations to a single group, family and ultimately a single type of fossil.
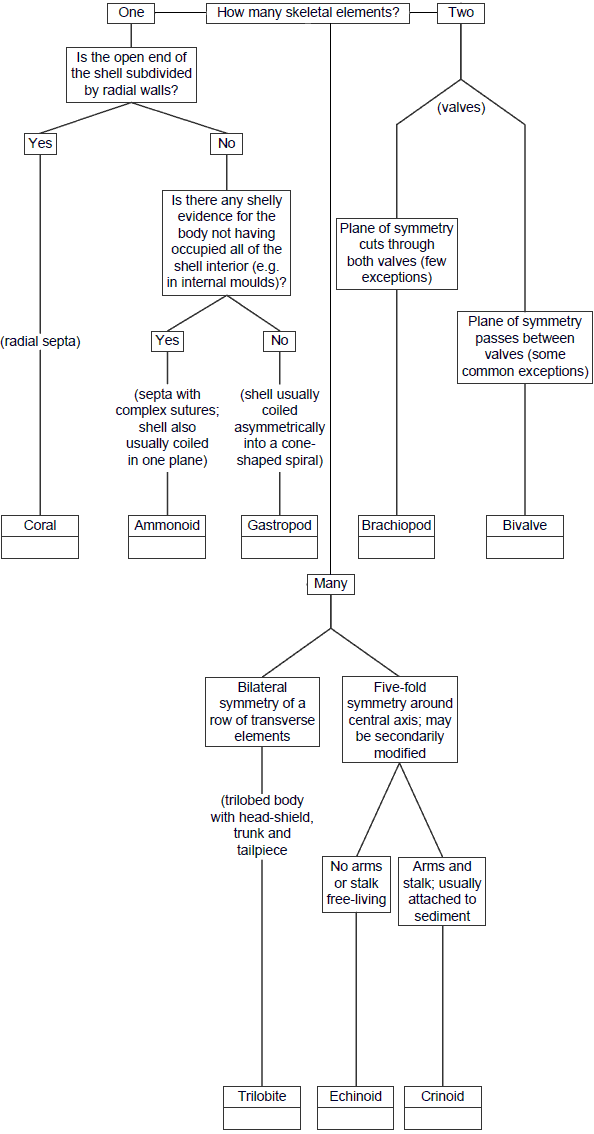
Sometimes it is hard to identify fossils. You could even entirely miss them in the field. It takes a lot of experience and practice in order to find and classify fossils. What makes Geological Paleobiologists unique is that their ability to connect the dots between ancient life and the condition of Earth. The Earth has evolved millions of years and life forms have adopted to varying geological and environmental conditions.
Typically a Geologist who is an expert of Paleobiology specialization not only record the information of fossils, but also the sediments, rocks and the formation of the location. We identify important events based on appearance or disappearance of certain fossils and geological materials. This information then analyzed together to hypothesize the history of Earth. The data collected used in various areas from academia, environmental science to oil and gas industry.
So, kids… You may hate the class because there are so many items to be memorized. But it is not simply memorizing because one day you will use the knowledge in the field for great work. No matter what, the ability work with real physical samples comes with experience.
References
1. Geological Field Techniques; Coe, A; Argles, T; Rothery, D; Spicer R.; ISBN-978-1-4443-3061-8
Importance of Hydrology
Recently the sciences behind resource management also have come under the microscope as a result of exponential population growth. In my opinion, other than the sun, the most impotent resource we depend on is water. Hydrology is a branch of Geoscience (Earth Science/Environmental Science) concerning fluid dynamics specifically related to water.
It is a cycle
Like many things in science, in hydrology we can observe different processes and understand the relationships between them. With years and years of experience and wisdom, geo scientists have been able to create a blueprint for processes of water known as the hydrocycle (or water cycle).
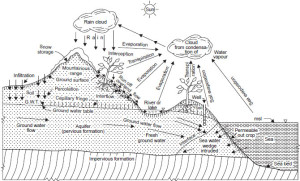
Yes, this is an endless cycle. But, not all the fresh water can be sorted on the continental shelves. While the Earth is covered with a vast volume of water, most of it is not suitable for consumption. The energy required to remove salt from sea water for human consumption have outweighed the benefits. Even if the technology advance to reduce the cost of cleaning sea water, it is not a natural form of drinking water. In other words, the dependency on technology to provide us with the most basic needs is a not a far sighted strategy to combat resources scarcity. Now we know why hydrology is very important. Through the extensive study of principles of hydrology, we can build better system for water management.
We use it for…
The agricultural industry specially in South Asia heavily relied on complex system of water management and irrigation. Some techniques of hydrology can be dated back to as far as 2500 years. The dam building is a evolution of both Engineering and Geological achievements and failures. In the past we have made the mistake of underestimating the power of gravity driven flowing water. It has lead to catastrophes like Italian Val di Stava dam collapse. We learned from our mistakes and today we can build large dams to control massive volume of water such as the Three Gorges Dam in China.
Another application of hydrology (or rather hydro-geology) is the applications of underground water and brine management. Salt deposits for example provide economically valuable hydrocarbon reservoir. Salt structures are also a good option for storing radioactive waste. Salt behave like a fluid even though it is a solid. It can also also sustain considerable amount of shear and compressional forces without breaking apart. However it is weaken by fluids such as water and brine. This is where Hydro-geologists and Engineers have to work together to find a solution to the problem.
We can also utilize the knowledge on hydrology for other resources such as oil and gas. In fact due to the economic impotence of the petroleum industry, millions of dollars have been allocated to research in hydrology. The irony is while petroleum industry may have a significant negative impact on the environment, the industry have helped develop new techniques for fresh water management.
There are many other applications of hydro-geology. If you are interested in this kind of work, ask your professor for more information. Anyway, regardless of the new technologies we still use the simple fundamental principles which helped us understand the hydrological cycle.
References
1. Applied Hydrogeology (4th Edition) By C. W. Fetter
Exploration and exploitation of natural resources
According to UN and numerous other research agencies about 80% of world’s energy demand is satisfied by converting fossil fuels in to usable energy. It involves the process of planning, exploration, exploitation and management of natural resources. These processes inherently have their own set of risks and benefits. By identifying and managing the issues will boost our energy and resource hungry civilization to the next level.
Continue reading Exploration and exploitation of natural resources