GLGY 202 – Applications of Geoscience
Disclaimer: While every reasonable effort is made to ensure that the information provided is accurate, no guarantees for the currency or accuracy of information are made. It takes several proof readings and rewrites to bring the quiz to an exceptional level. If you find an error, please contact me as soon as possible. Please indicate the question ID-Number or description because server may randomize the questions and answers.
Geology 202 final exam is typically cumulative with greater emphasis on the last section of the course. It is recommended to use both the Midterm Exam and this Final Exam when preparing for the final exam.
Go to: Midterm Exam
Geology (GLGY 202-UCAL) Final Exam
Congratulations - you have completed Geology (GLGY 202-UCAL) Final Exam.
You scored %%SCORE%% out of %%TOTAL%%. With incorrect multiple attempts your score is %%PERCENTAGE%%
Your performance has been rated as %%RATING%%
Question 1 |
A | Increase in regional pore pressures. |
B | Land subsidence. |
C | Significantly smaller cone of depression. |
D | Lowering of the local water table. |
Question 2 |
A | Nuclear |
B | Hydroelectric |
C | Petroleum or oil |
D | Natural gas |
E | Coal |
Question 3 |
A | Increased in overburden load. |
B | Decrease in pore pressures in the subsurface. |
C | Increased in the groundwater table. |
D | Increased compaction of subsurface sediments. |
E | Rapid melting of permafrost. |
Question 4 |
A | Seismic predictions are all based on imperial evidence. |
B | All determinations are based on random probability statistics. |
C | All models are 100% based on data obtained from past natural seismic activities. |
D | Seismologists are too stupid to understand earthquakes. |
E | Modeling of seismic data can provide more specific time and magnitude intervals for future seismic activities. |
Question 5 |
A | carbon-hydrogen bonds. |
B | kerogen. |
C | transitional metals and carbons. |
D | inorganic compounds. |
E | carbon-oxygen bonds. |
Question 6 |
A | The deposit is too small for exploration and production. |
B | Methane hydrates cannot be used as a fuel source for modern energy needs. |
C | The cost of extraction is too high and cannot be covered due to the current gas market prices. |
D | Political disputes between Norway and Russia is delaying progress towards extraction. |
Question 7 |
A | Can be purified through smelting |
B | Mostly solids at room temperature |
C | Conducts electricity |
D | Malleable |
E | Strong covalent bonds |
Question 8 |
A | It requires specialized micro-bacteria to remove salt. |
B | There is no proven technology. |
C | The process requires large amount of energy. |
D | It takes a lot of time to process just a 1L of water. |
E | It is difficult to build a desalination plant next to the ocean. |
Question 9 |
A | MVT is caused by leeching of existing ore bodies in shallow subsurface and precipitating them elsewhere as a different ore body. |
B | MVT is caused by differential gradient in acidity of ground water. |
C | MVT is caused by magmatic solutions entering lower pressure and lower temperature regions. |
D | MVT is caused by ground water reach in deep into the subsurface which eventually return to surface and precipitate ore minerals. |
Question 10 |
A | Global warming |
B | Floodplains |
C | Volcanoes |
D | Earthquakes |
Question 11 |
A | Provide better eye wear protection equipment. |
B | Decrease the humidity of the mines. |
C | Increase the access to fresh drinking water. |
D | Install better air quality management system. |
E | Reduce acid mine drainage.
|
Question 12 |
A | subject to rapid oxidation. |
B | undergoing rapid deposition and sedimentation. |
C | undergoing subsidence. |
D | rich in organic matter. |
E | characterized by a large basin. |
Question 13 |
A | coal , bitumen |
B | unconsolidated materials , solid rock materials |
C | heavy metals , precious metals |
D | minerals , aggregates |
E | uranium , aluminum |
Question 14 |
A | Chemical mitigation |
B | Environmental mitigation |
C | Consolidation |
D | Bioremediation |
E | Intervention |
Question 15 |
A | magmatic deposit. |
B | Mississippi Valley-type deposit. |
C | placer deposit. |
D | residual mineral deposit. |
E | secondary-enrichment deposit. |
Question 16 |
A | Confined aquifers only formed in high depths in the subsurface while unconfined aquifers formed closer to the surface. |
B | Confined aquifers are characterized by having an impermeable lithologic layer above the aquifer. |
C | Determination of confined or unconfined condition is based on overall porosity of the aquifer with confined having much lower porosity than the surrounding region. |
D | Confined aquifers are characterized by having an impermeable lithologic layers around the aquifer. |
E | Confined aquifers are characterized by having low permeability and low flow rate in lateral direction. |
Question 17 |
A | Epidote |
B | Orthoclase feldspar |
C | Calcite |
D | Quartz |
E | Plagioclase Feldspar |
Question 18 |
A | Permian |
B | Cretaceous |
C | Triassic |
D | Devonian |
E | Cambrian |
Question 19 |
A | Lack of funding for research |
B | Not having enough data to prove one way another |
C | Poor understanding of the Earth as a system rather than a single entity |
D | Politicization of science itself |
E | Overpopulation due to higher human reproduction |
Question 20 |
A | earth system science. |
B | natural science. |
C | global science. |
D | climate change science. |
E | evolutionary natural science. |
Question 21 |
A | Silt |
B | Gravel |
C | Clay |
D | Sand |
E | Cobble |
Question 22 |
A | well within natural Holocene range of variability with some anomalies. |
B | showing exponential increased in temperatures. |
C | composed of very high variability than what you would expect in Holocene. |
D | much higher than the previous decade. |
Question 23 |
A | are always scary. |
B | have distinctive amplitudes and wavelengths, which can be used to detect them earlier. |
C | are about 10 times faster than a regular waves. |
D | generate high frequency noise. |
E | travel perpendicular to the equator. |
Question 24 |
A | Eustatic change and isostatic uplift |
B | Increased in rainfall and surface runoff |
C | Increased in soil and land erosion in the area |
D | Global warming or climate change |
E | Natural subsidence |
Question 25 |
A | Scraping left behind by glaciers such as glacial migration. |
B | Channels cut in to the soil by erosion. |
C | Type of sand that liquefy during an earthquake. |
D | Sandy deposits found near the mouth of deltas. |
Question 26 |
A | after the French revolution. |
B | as a result of improvements in technological industry. |
C | as a result of the industrial revolution. |
D | due to over population. |
E | as a result of America (USA) becoming a superpower. |
Question 27 |
A | Radium-226 |
B | Thorium-234 |
C | Lead-206 |
D | Lead-214 |
E | Polonium-218 |
Question 28 |
A | Formations dominated by unfractured limestone and clay. |
B | Formations with large volumes of shale with some quartz dominated regions. |
C | Layered interbedded formation of siltstone and shale. |
D | Predominantly sandstone based formations with small volumes of shale. |
Question 29 |
A | Dolomite |
B | Hematite |
C | Chromite |
D | Galena |
E | Bornite |
Question 30 |
A | Petrol (gasoline) |
B | Natural Gas |
C | Diesel |
D | Coal |
Question 31 |
A | Tens of years |
B | 2 weeks |
C | Up to tens of thousands of years |
D | 10 days |
E | Thousands of years |
Question 32 |
A | Railways |
B | Fresh water pipelines |
C | Air pumps |
D | Mineral or metal deposit itself |
E | New roads |
Question 33 |
A | Bodies of water that can sustain a diverse range of aquatic life. |
B | Areas with high enough hydraulic gradients that can support flow of water. |
C | Areas of high hydraulic pressures. |
D | Earth material capable of supplying groundwater at a useful rate from a well. |
E | None of the listed answers are correct. |
Question 34 |
A | Significant decrease in groundwater pollution due to advanced water treatment facilities in urban areas. |
B | The groundwater discharge rate increases with increased in surface water runoff. |
C | The groundwater reservoirs are often being depleted due to reduction in seepage and infiltration. |
D | Increase groundwater recharge due to higher infiltration of water during storm events. |
Question 35 |
A | Asteroids are originates in the near Earth elliptical orbit, while comets originates between Jupiter and Mars. |
B | Asteroids are made up of metals and rocky material, while comets are made up of ice, dust and rocky material. |
C | Comets are larger versions of asteroids that are heavier, |
D | Comets usually burn out in the Earth's atmosphere while asteroids can travel across it to reach the Earth's surface. |
E | Comets contains specific assemblage of minerals that are not found in asteroids. |
Question 36 |
A | The 100 year flood only occurs in every 100 years or so. |
B | Floodplains floods are typical and can be predicted with very good accuracy (within a week). |
C | Rivers with larger lateral movement (meanderings) trend to have wider floodplains. |
D | Oxbow lakes forms outside of floodplains. |
E | There are no historical records of floods near Bow and Elbow rivers in Calgary. |
Question 37 |
A | factor of soil cover. |
B | soil erodibility index. |
C | factor of hillslope/length |
D | short term rain fall runoff. |
E | average annual soil loss. |
Universal soil loss equation is used for long term calculations.
Question 38 |
A | Papers are highly weighted towards evidence. |
B | Too many contradicting statements in published papers. |
C | Propaganda based science taking over facts bases science. |
D | Research are influenced by ideologies of funding organizations. |
E | Influence of political and social pressures on scientists. |
Question 39 |
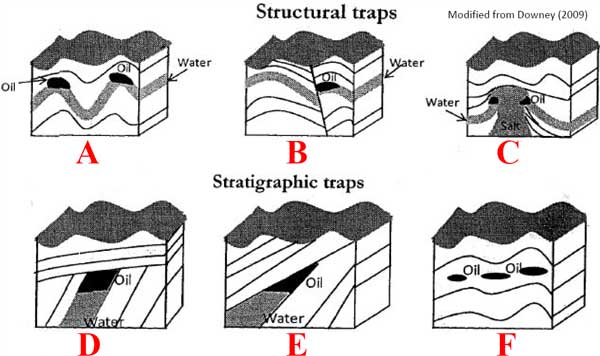
A | Salt dome trap |
B | Unconformity trap |
C | Fault trap |
D | Pinchout trap |
E | Lens trap |
F | Anticline trap |
Question 40 |
A | Shortwave |
B | Ultraviolet Rays |
C | X-Rays |
D | Visible light |
E | Gamma Rays |
Question 41 |
A | Sandstone |
B | Limestone |
C | Clay |
D | Gravel |
E | Sand |
Question 42 |
A | A mineral that is extracted from the upper crust that is used by people. |
B | A mineral that has a very high density. |
C | A mineral that falls under one of the toughest and strongest categories of Moh Scale of Hardness. |
D | A mineral that can be used to for vital processes such in the medical industry. |
E | A mineral that expensive due to rarity. |
Question 43 |
A | It is only caused by human activities such as agriculture. |
B | It is only observed in regions where there are mines. |
C | In occurs only in coastal regions where there is an abundant of salts. |
D | It can be caused by both natural and human processes. |
Question 44 |
A | Sudden lowering of the water table. |
B | Loud noises produced at the fault line. |
C | Shaking of buildings and other infrastructures. |
D | Compressional wave. |
E | Violent shaking of the ground. |
Question 45 |
A | About 50% |
B | About 90% |
C | About 70% |
D | About 1% |
E | About 30% |
Question 46 |
A | at higher depths , at shallower depths |
B | at specific temperature interval , only from specific types of organic matter |
C | under low pressure environments , under high pressure environments |
D | two carbon atoms , three or more carbon atoms |
E | animals , plants |
Question 47 |
A | hydrological water reservoirs. |
B | oceans. |
C | mantle. |
D | upper crust. |
E | lower atmosphere. |
Question 48 |
A | Above the the vadose zone. |
B | Between vadose and saturation zones. |
C | Below the saturation zone and above the vadose zone. |
D | Below the saturation zone. |
E | Above the B soil horizon. |
Question 49 |
A | Gradients less than the slope of the land which they form |
B | Deposits of sand bodies on the channel floor |
C | Nearly straight and shallow channels |
D | Meandering sequences |
E | Sharp and steep channel walls |
Question 50 |
A | Agricultural industry. |
B | Uranium mining industry. |
C | Petroleum refining industry. |
D | Coal industry. |
E | Aluminum mining industry. |
Question 51 |
A | It is dividing the world leading to wars |
B | Not enough scientific data |
C | Not enough research funds |
D | Not enough researchers working in this area |
E | Politicization of science |
Question 52 |
A | C horizon |
B | A horizon |
C | E horizon |
D | B horizon |
Question 53 |
A | Radium |
B | Arsenic |
C | Uranium |
D | Thorium |
E | Gold |
Question 54 |
A | Middle East and North America |
B | Middle East and Europe/Eurasia |
C | Middle East and Latin America |
D | Middle East and Asia/Australia |
E | Middle East and Africa |
Question 55 |
A | Methane |
B | Propane |
C | Butane |
D | Chlorine vapor/gas |
E | Ethane |
Question 56 |
A | It has a higher energy content per cubic feet than conventional methane. |
B | It has a less impact on the environment than conventional methane. |
C | It is highly abundant in large volumes throughout the world. |
D | It is a much more stable version of the conventional gas hence better safety for those who produce it and use it. |
E | It is found in shallow deposits that are much more economical to drill. |
Question 57 |
A | significant differences between two lithologies. |
B | differences between lithologies when move across an area with change in longitude. |
C | slopes of hills or mountains. |
D | significant differences between two mineral grains next to each other. |
E | difference in elevations between the highest and lowest points of landform. |
Question 58 |
A | Coal |
B | Wind |
C | Hydroelectric |
D | Nuclear |
E | Natural Gas |
Question 59 |
A | Velocity of the tsunami wave is higher if the depth of ocean which the wave originate is higher. |
B | Tsunamis only have devastating effect on Japan and other Asian countries, hence the Japanese term "tsunami". |
C | Frequency of tsunamis has significantly increased due to global warming or climate change. |
D | North American should not worry about tsunamis because it is impossible for occur anywhere near us. |
E | Tsunamis can only originate at plate boundaries. |
Question 60 |
A | A deposit of precious metals. |
B | A concentration of ore grade mineral with at least 3% of precious metals. |
C | A concentration of ore grade minerals that can be economically mined. |
D | A shallow deposits of ore grade minerals within the Earth's crust. |
Question 61 |
A | Increased use of non-renewable products used in the manufacturing of ORVs. |
B | Polluting the drinking water supply. |
C | Noise pollution due to large ORV enthusiasts gatherings. |
D | Mechanical weathering, compaction and erosion of soil. |
E | Chemical pollution through gasoline based ORVs in environmentally sensitive areas. |
Question 62 |
A | The most pressing issue with mercury is that it is a metal but it act as a liquid. |
B | Ice produced by your refrigerator is a mineral by definition. |
C | Typically ore minerals dissolve under oxidizing environments. |
D | Reducing environments are associated with placer deposits. |
E | Staining of beds due to weathering is associated with higher concentration of quartz in the subsurface. |
2. Stating is associated metallic and ore minerals.
Question 63 |
A | Upper most layer of the lithosphere. |
B | Upper most part of the atmosphere that includes only the exosphere. |
C | Lower most part of the atmosphere that includes only the troposphere and stratosphere. |
D | Frozen water part of the Earth system. |
E | Combination of atmosphere and lithosphere (as a one system). |
Question 64 |
A | High urbanization |
B | High permeability |
C | Low vegetation |
D | High porosity |
E | High topographic relief |
Note: You could argue for high porosity. But from physics and fluid dynamic point of view, having high porosity with low permeability would not help the migration of water from the surface to the subsurface.
Question 65 |
A | Increased in subsurface permeability. |
B | Increased in rainfall. |
C | Increased in surface water evaporation rate. |
D | Increased in sediment compaction rate. |
E | Increased in subsurface porosity. |
Question 66 |
A | None of the answers are correct. |
B | Abundance of subsurface water. |
C | Slow burial and lithification of sediments. |
D | Anoxic subsurface conditions. |
E | Lower pressures in subsurface than normal. |
Question 67 |
A | A type of sedimentary layers that often produce very high grade bitumen in Alberta. |
B | A proposed epoch that begins when human activities started to have a significant global impact on Earth's geology and ecosystems. |
C | A type of activity or activities that would impact the global environment. |
D | An atmospheric condition where the natural chemical composition significantly impact the well-being of organisms. |
E | None of the answers listed here are correct. |
Question 68 |
A | They can be used to model hydrocarbon reservoirs elsewhere. |
B | They can be used for determining the exact location of the true North. |
C | Geologists are looking for new sources of fresh water for the growing human population. |
D | They can provide detailed information on paleo-environments. |
E | They are used to locate large deposits of hydrocarbons in the Canadian Arctic. |
Question 69 |
A | increase potential energy. |
B | release atomic and subatomic particles. |
C | generate light energy. |
D | None of the answers are correct. |
E | slowing down the chemical reaction. |
Question 70 |
A | It measure the capacity to change energy balance. |
B | It measures radiation of the sun and planets. |
C | It measure the energy within the visible light spectrum. |
D | It is a measurement of radioactivity of ore minerals such as uraninite. |
E | It measures the intensity of any wave in the entire light spectrum. |
Question 71 |
A | Mexico |
B | India |
C | Tanzania |
D | Sri Lanka |
E | Canada |
Question 72 |
CO2(aq) + H2O --> H2CO3 --> HCO3− + H+ --> ________ + 2H+.
A | CO32− |
B | H2O |
C | H3O+ |
D | H2O2 |
Question 73 |
A | Volcanic eruptions. |
B | Plate tectonics. |
C | Extraterrestrial impact on Earth. |
D | Positioning of a large asteroid near Earth. |
Question 74 |
A | Liquefaction |
B | Building collapse |
C | Fires |
D | All of the listed can be caused by an earthquake. |
E | Landslides |
Question 75 |
A | Resource Section |
B | Hydrocarbon Sector |
C | Oil Window |
D | Optimal Range |
Question 76 |
A | About 50% |
B | About 90% |
C | About 1% |
D | About 10% |
E | About 70% |
Question 77 |
A | Electronic and computerized earthquake monitoring systems. |
B | Monitoring animal behaviors. |
C | Vibration sensors in very deep sub surface. |
D | Areal electromagnetic surveys. |
E | Clusters of seismic stations near fault zones. |
Question 78 |
A | 90% to100% of world's rivers. |
B | 1/5 of world's rivers. |
C | 2/5 of world's rivers. |
D | 2/3 of world's rivers. |
E | 1/2 of world's rivers. |
Question 79 |
A | Chrome |
B | Titanium |
C | Iron |
D | Nickel |
Question 80 |
A | Radiation energy. |
B | Kinetic energy of the atoms. |
C | Steam produced by heated fluids such as water. |
D | Friction between sub-atomic particles. |
← |
List |
→ |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 |
| 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
| 31 | 32 | 33 | 34 | 35 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 | 44 | 45 |
| 46 | 47 | 48 | 49 | 50 |
| 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | 55 |
| 56 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 60 |
| 61 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 65 |
| 66 | 67 | 68 | 69 | 70 |
| 71 | 72 | 73 | 74 | 75 |
| 76 | 77 | 78 | 79 | 80 |
| End |
Credits: Based on the excellent class notes provided by, Dr. Gerald Osborn and Dr. Glenn Dolphin during Winter 2016 and textbook ISBN-978-0-393-93750-3.
FAQ | Report an Error
If you get a question wrong, you can still click on the other answers. You have multiple opportunities to select the correct answer. This will open up hints and explanations (if available), which will provide additional information.
