Notice
This is the non-interactive basic mode of GLGY 341 questions database for printing or use in case of SQL database failure on main site. All the questions and answers are identical except the order of questions and answers.Please use the interactive version for more up to date materials.
Geology (GLGY 341-UCAL) Midterm Exam
1. What is the fault separation distance between a stratigraphic section?
A. fault distance
B. stratigraphic separation
C. unit separation
D. unit distance
E. fault separation
2. By referring to the following matrix, if F33 is the only (and one and only) one that underwent change, what type of strain is it?
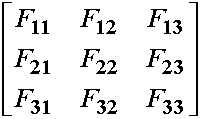
A. Isotropic volume change
B. Symmetric volume change
C. Asymmetric strain
D. Anisotropic volume change
E. Axial strain
3. Relatively, the ductile zone of a fault is ___ the center of the fault.
A. closest to
B. furthest away from
C. 90 degree to
D. at the
4. Generally what type of stresses would you expect in lithosphere?
A. biaxial
B. uniaxial
C. lithostatic
D. deviatoric
E. compressional
F. extensional
5. By referring to the following matrix, if F33 is the only (and one and only) lithostatic stress can be defined when…
A. F11, F22 and F33 have changed at the same rate.
B. F11, F21 and F31 have changed at the same rate.
C. F12, F22 and F32 have changed at the same rate.
D. F13, F23 and F33 have changed at the same rate.
E. F13, F22 and F31 have changed at the same rate.
6. Deformation which will not result in physical change in the structural unit in question has underwent a… (there is more than one possible answer, but choose the MOST suitable one)
A. shear deformation.
B. pure shear deformation.
C. translational deformation.
D. rotational deformation.
7. What type of strains are most common?
A. 3D
B. Depend on the environment, all strains are globally occur at the same rate.
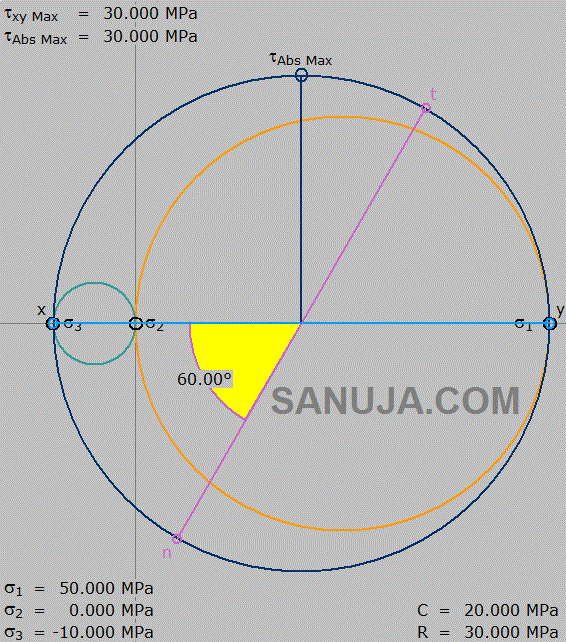
C. 2D
D. 1D
8. What is the fault separation distance between a stratigraphic section?
A. fault distance
B. stratigraphic separation
C. unit distance
D. unit separation
E. fault separation
9. “A discontinuity with wall-parallel displacement dominated by brittle deformation mechanisms.” This is the…
A. dynamic definition of a fault.
B. traditional definition of a fault.
C. specific definition of a fault.
D. general definition of a fault.
E. kinematic definition of a fault.
10. The rocks along a fault line have moved parallel but opposite to each other. What type of strain would you expect to find along the fault line?
A. Pure shear
B. Rotational deformation
C. Translational deformation
D. Super imposed strain
E. Simple shear
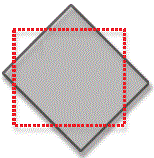
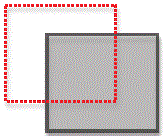
11. What type of transformation is represented by the following diagram? (red dotted line is the original position of the rock mass)
A. Pure shear
B. Translation
C. Rotation
D. Simple shear
E. Sub-simple shear
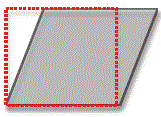
12. What type of transformation is represented by the following diagram? (red dotted line is the original position of the rock mass)
A. Pure shear
B. Translation
C. Rotation
D. Simple shear
E. Sub-simple shear
13. Triaxial test is used to measure ___ of soil types and rock units.
A. strength
B. history of deformations
C. faulting levels
D. compaction strength
E. porosity
14. A thrust fault is a low angle reverse fault with about 20-30 degree in angle between the fault line and the normal.
A. True
B. False
15. Calculate the lithostatic stress under 10 km of a rock unit composed of olivine which has a density of 3600 kg/m3 (use g = 9.81 m/s2)
A. 35 Gpa
B. 35316 Gpa
C. 0.35 Gpa
D. 98100 Gpa
E. 98.1 Gpa
16. What type of transformation is represented by the following diagram? (red dotted line is the original position of the rock mass)
A. Pure shear
B. Translation
C. Rotation
D. Simple shear
E. Sub-simple shear
17. When dealing with stresses at a point, the maximum stress is in the direction that has the __A__ extension and the maximum strain is in the direction that has the __B__ extension.
A. I. least
II. largest (most)
B. I. largest (most)
II. largest (same)
C. I. largest (most)
II. least
D. I. vertical
II. horizontal
E. I. horizontal
II. vertical
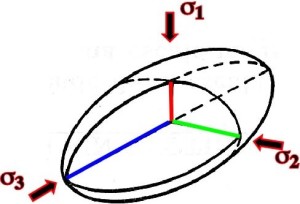
18. In this strain ellipsoid, where is the maximum strain?
A. σ 1
B. σ 2
C. σ 3
D. σ 1 and σ 2
E. σ 2 and 3
19. Upon observations, you determined the sediments have few quartz veins. What type of fracture is this?
A. Mode IV
B. Mode III
C. Mode II
D. Mode I
20. Rocks are weaker in tension because of micro defects.
A. True
B. False, they are weaker due to macro defects
21. Why is the Coulomb failure envelope is not perfect?
A. It under-predicts uniaxial compressive strength at higher confining pressures.
B. It under-predicts strength in tensile regions.
C. Past practical experiments indicates that it will not comply with 90% of the lab tests.
D. It predicts unrealistic strength by over predicting the failure envelope in tensile regions.
22. What is the failure criterion indicated in E?
A. Von Mises
B. Coulomb
C. Griffith
D. Micro
E. Macro
23. What is the failure criterion indicated in A?
A. Von Mises
B. Coulomb
C. Griffith
D. Micro
E. Macro
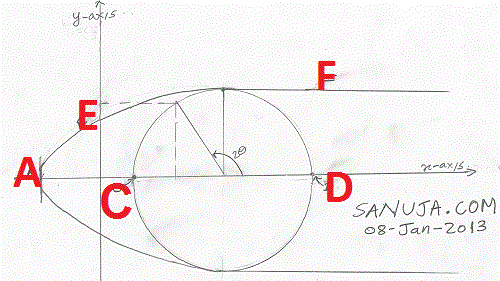
24. According to the following diagram, what do you get if you find the distance between C and D (Note they are pointing to at x-intercepts)?
A. Differential Stress
B. Shear Stress
C. Normal Stress
D. Failure Window
E. Compressional Stress
25. What is the failure criterion indicated in F?
A. Von Mises
B. Coulomb
C. Griffith
D. Micro
E. Macro
26. What is represented on the x-axis?
A. Differential stress
B. Dynamic stress
C. Normal Stress
D. Compressional force
E. Shear stress
27. What is represented on the y-axis?
A. Differential stress
B. Dynamic stress
C. Normal Stress
D. Compressional force
E. Shear stress
28. What is the best indicator of structural deformation history?
A. Undeformed bedding surface
B. Deformed bedding surface
C. Known fossils
D. Mineralogical and chemical composition
29. When using acoustic remote sensing, salts will not appear since salts are great reflectors.
A. True
B. False
30. When will a structure become unstable?
A. 2 θ > 90
B. 2 θ = 90
C. 2 θ < 90
D. 2 θ > 45
E. 2 θ < 45
31. How is stress different from strain?
A. Stress is force per square inch (it can be treated as pressure). Strain is the deformation cause by the applied stress.
B. Stain is force per square inch (it can be treated as pressure). Stress is the deformation cause by the applied strain.
C. Stress is when you pull apart rock units and strain is when rock units are pushed against each other.
D. Strain is a force while stress is a the cause of the force that generate strain.
32. What type of transformation is represented by the following diagram? (red dotted line is the original position of the rock mass)
A. Pure shear
B. Translation
C. Rotation
D. Simple shear
E. Sub-simple shear
33. The most (ultimate) tensile strength a rock can take is indicated by which letter on the following diagram?
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. E
E. F
34. What is strike? (Most likely will be in the oral exam part of the lab).
A. It is the azimuthal bearing to an imaginary line measured from the North.
B. It is the line that will generate at exactly 90-degrees of azimuthal bearing to an imaginary line measured from the North.
C. It is the azimuthal bearing relative to true north of a horizontal line on an inclined planar surface.
D. It is the azimuthal bearing relative to true north of a vertical line on an inclined planar surface.
E. It is the azimuthal bearing to an imaginary line measured from the true North.
35. What is the difference between magnitude and net of a force? (general physics-structure)
A. Magnitude a measure of force regardless of the direction(net force depends on the direction).
B. Net force a measure of force regardless of the direction(magnitude depends on the direction).
C. Magnitude a measure of force in international standards (net force is often use to simplify force distribution).
D. Net force a measure of force in international standards (Magnitude is often use to simplify force distribution).
36. Given the following, calculate the deviatoric stress;
σ1 = 250 MPa
σ2 = σ3= 100 MPa
A. 150 MPa
B. 75 MPa
C. 350 MPa
D. 175 MPa
37. Given C = 100 MPa and D = 150 MPa (note they are pointing to at x-intercepts), calculate mean stress?
A. 150 MPa
B. 250 MPa
C. 25 MPa
D. 125 MPa
38. What type of geological event the following diagram represents?
A. Strike-slip fault
B. Thrust fault
C. Normal fault
D. Erosion
E. Earthquake
39. Planes orinated __A__ to the principle stress directions experiance __B__
A. I. perpendicular
II. normal stress and zero shear stress
B. I. parallel
II. normal stress and zero shear stress
C. I. parallel
II. shar stress and zero normal stress
D. I. perpendicular
II. shar stress and zero normal stress
40. Unfortunately as a Geologist, you were asked to determine which mathematical model should be entered into the modeling software(used for plotting the field data). Knowing that you are in an area with extreme tensile pressure, which model do you choose?
A. Coulomb model
B. Griffith model
C. Von Mises model
D. Envelope model
41. In this computer model, the differential stress is indicated by….
A. large blue circle.
B. orange circle.
C. the 60-degree angle.
D. the green line between x and y.
42. In this computer model, the most left hand circle (blueish-green) between σ3 and σ2 is drawn based on what envelope/principle?
A. Coulomb
B. Von Mises
C. Confining
D. Griffith
43. In this computer model, the most right hand circle (orange) between σ2 and σ1 is drawn based on what envelope/principle? (choose the best)
A. Coulomb
B. Von Mises
C. Confining
D. Griffith
44. The pulling apart a material parallel (aka same plane) to a fracture is known as a… (also the easiest type to observe in field)
A. Mode I
B. Mode II
C. Mode III
D. Mode IV
45. Under high pressure, a quartz vein has dissolved resulting collapse of a fracture. What type of fracture is described here?
A. Mode I
B. Mode II
C. Mode III
D. Mode IV
46. Where on a stereonet a pole to plain will plot?
A. 90 degrees away from the dip.
B. 180 degrees on either direction.
C. 180 degrees towards the dip.
D. 45 degrees away from the dip.
======= END ========
Answers (highlight/copy the text to see the answers!): 1-B, 2-D, 3-B, 4-E, 5-A, 6-C, 7-A, 8-B, 9-D, 10-E, 11-A, 12-C, 13-A, 14-A, 15-C, 16-D, 17-A, 18-C, 19-D, 20-A, 21-D, 22-B, 23-C, 24-A, 25-A, 26-C, 27-E, 28-C, 29-B, 30-C, 31-A, 32-B, 33-A, 34-C, 35-A, 36-B, 37-D, 38-C, 39-A, 40-B, 41-D, 42-D, 43-C, 44-A, 45-D, 46-A,…
Explanations: 2: aka uniaxial strain, 15: Given, stress = = (3600 kg/m3)(9.81 m/s2 )(10,000 m), 19: While it could be a combination of any of the fracture modes, the simplest explanation is Mode I. The simplest one is the explanation for most geologic problems, 29: Salts will often appear clearly not because they are great reflectors, but because they are poor reflectors surrounded by great reflective materials, 36: (σ1 – σ3)/2 = 75 MPa, 37: C and D are σ1 and σ3 respectively; therefore (σ1 – σ3)/2 = 125 MPa, 43: While more than one answer is possible (Coulomb and Von Mises), they all can be explained by confining principle.